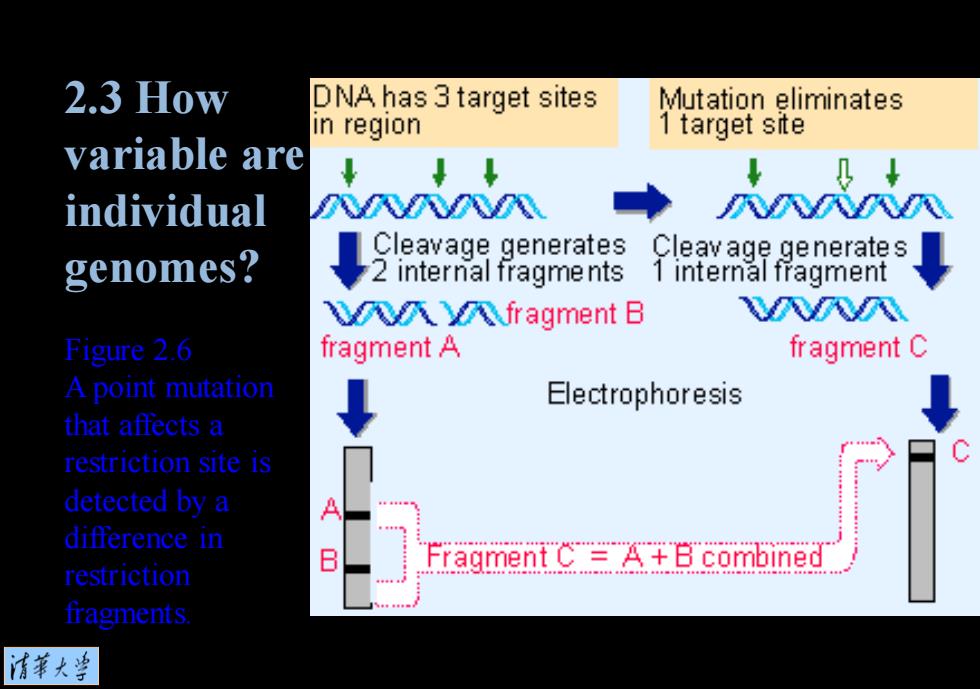
2.3 How DNA has 3 target sites Mutation eliminates in region 1 target site variable are ↓↓ 及+ individual N不F 风风风 Cleavage generates genomes? ↓a8母nems Cleav age generates 1 internal fragment 风r风fragment B 风风风 Figure 2.6 fragment A fragment C A point mutation Electrophoresis that affects a restriction site is detected by a difference in Fragment CA+Bcombined restriction fragments. 清菜大当
Figure 2.6 A point mutation that affects a restriction site is detected by a difference in restriction fragments. 2.3 How variable are individual genomes?

2.3 How Parents are heterozygous, is homozygous for C variable are F1 individual F2 inherit 台8r88m8eP色a肉吉A genomes? Allele A Figure 2.7 Restriction site Allele B polymorphisms are inherited according Allele C to Mendelian rules Allele D Four alleles for a restriction marker are found in all possible pairwise combinations,and segregate independently at each 情菜大当 generation.Photograph kindly provided by Ray White
Four alleles for a restriction marker are found in all possible pairwise combinations, and segregate independently at each generation. Photograph kindly provided by Ray White. 2.3 How variable are individual genomes? Figure 2.7 Restriction site polymorphisms are inherited according to Mendelian rules
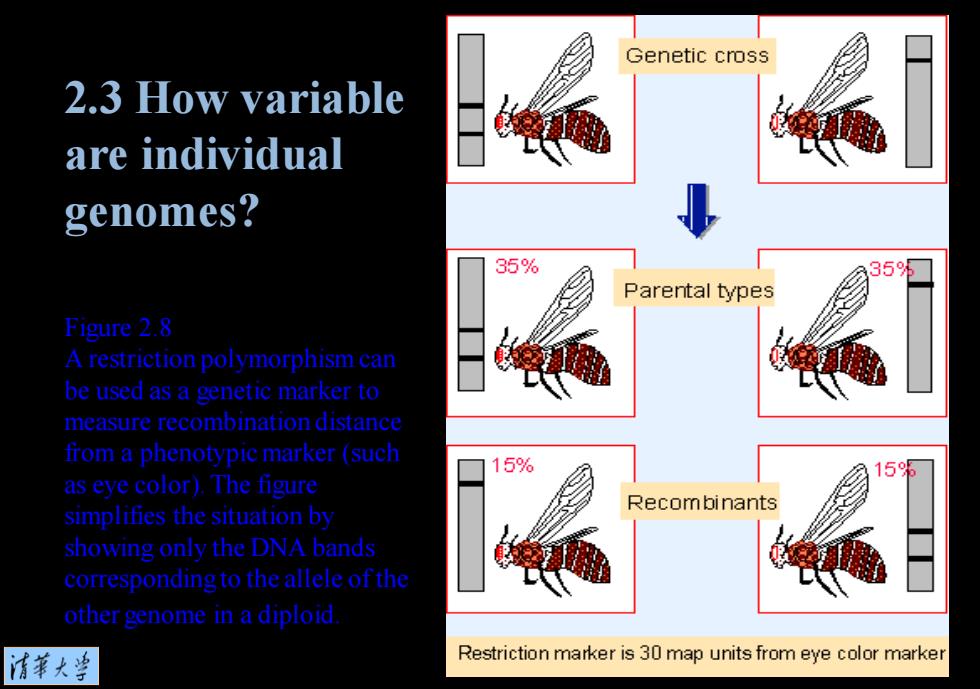
Genetic cross 2.3 How variable are individual genomes? 35% 35 Parental types Figure 2.8 A restriction polymorphism can be used as a genetic marker to measure recombination distance from a phenotypic marker (such 15% 153 as eye color).The figure Recom binants simplities the situation by showing only the DNA bands corresponding to the allele of the other genome in a diploid 清菜大当 Restriction marker is 30 map units from eye color marker
Figure 2.8 A restriction polymorphism can be used as a genetic marker to measure recombination distance from a phenotypic marker (such as eye color). The figure simplifies the situation by showing only the DNA bands corresponding to the allele of the other genome in a diploid. 2.3 How variable are individual genomes?

2.3H0w variable are individual Screen DNA pattems of Screen DNA patterns of patients wth disease nomal people as control genomes? Figure 2.9 If a restriction Band is same in patient and nomal marker is associated Unlinked polymorphism varies with a phenotypic in all samples characteristic.the Band is common to patients restriction site must be located near the Band is com mon to nommal people gene responsible for the phenotype The mutation changing the band that is common in normal people into the 清菜大当 band that is common in patients is very closely linked to the disease gene
Figure 2.9 If a restriction marker is associated with a phenotypic characteristic, the restriction site must be located near the gene responsible for the phenotype. 2.3 How variable are individual genomes? The mutation changing the band that is common in normal people into the band that is common in patients is very closely linked to the disease gene

2.3 How variable are individual Screen DNA pattems of Screen DNA patterns of patients wth disease nomal people as control genomes? Figure 2.9 If a restriction Band is same in patient and nomal marker is associated Unlinked polymorphism varies with a phenotypic in all samples characteristic.the Band is common to patients restriction site must be located near the Band is com mon to nomal people gene responsible for the phenotype The mutation changing the band that is common in normal people into the 清菜大兰 band that is common in patients is very closely linked to the disease gene
Figure 2.9 If a restriction marker is associated with a phenotypic characteristic, the restriction site must be located near the gene responsible for the phenotype. 2.3 How variable are individual genomes? The mutation changing the band that is common in normal people into the band that is common in patients is very closely linked to the disease gene