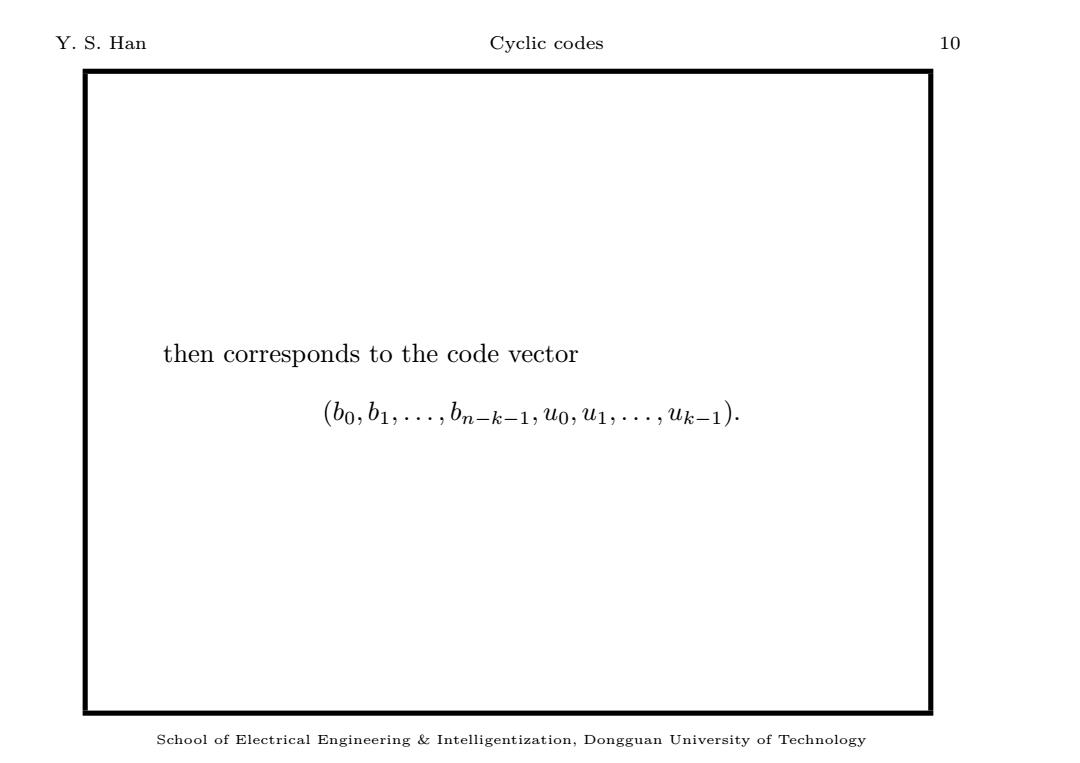
Y.S.Han Cyclic codes 10 then corresponds to the code vector (b0,b1,,bn-k-1,u0,u1,·,-1). School of Electrical Engineering Intelligentization,Dongguan University of Technology
Y. S. Han Cyclic codes 10 then corresponds to the code vector (b0, b1, . . . , bn−k−1, u0, u1, . . . , uk−1). School of Electrical Engineering & Intelligentization, Dongguan University of Technology
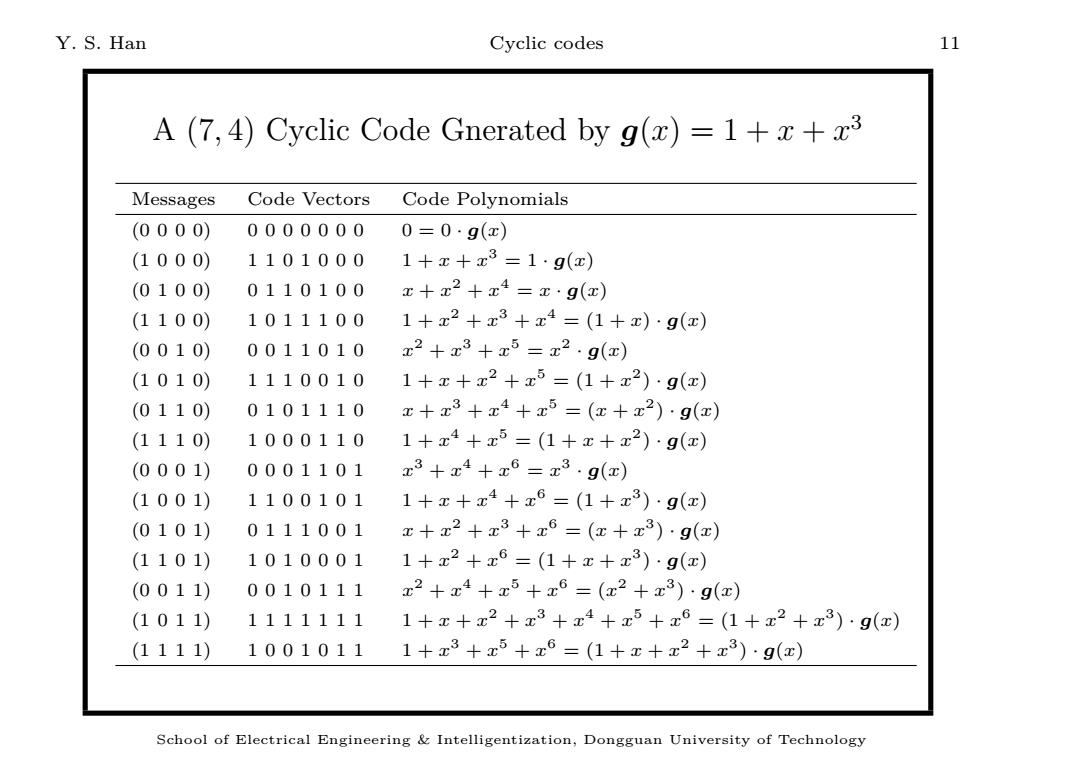
Y.S.Han Cyclic codes 11 A(7,4)Cyclic Code Gnerated by g(x)=1++x3 Messages Code Vectors Code Polynomials (0000) 00000000=0·g(x) (1000) 11010001+x+x3=1·g(x) (0100) 0110100x+x2+x4=x·g(x) (1100) 1011100 1+x2+x3+x4=(1+x)9(e) (0010) 0011010 x2+x3+x5=x2·g(x) (1010) 1110010 1+x+x2+x5=(1+x2)·9(x) (0110) 0101110 x+x3+x4+x5=(z+x2)·g(x) (1110) 1000110 1+x4+x5=(1+x+x2)·g(x) (0001) 0001101 x3+x4+x6=x3g(x) (1001) 11001011+x+x4+x6=(1+x3)·9(x) (0101) 0111001x+x2+x3+x6=(x+x3)·9(x) (1101) 10100011+x2+x6=(1+x+x3)·9(x) (0011) 0010111 x2+x4+x5+x6=(x2+x3)·g(x) (1011) 11111111+x+x2+x3+x4+x5+x6=(1+x2+x3)·g(x) (1111) 10010111+x3+x5+x6=(1+x+x2+x3)·g(x) School of Electrical Engineering Intelligentization,Dongguan University of Technology
Y. S. Han Cyclic codes 11 A (7, 4) Cyclic Code Gnerated by g(x) = 1 + x + x 3 Messages Code Vectors Code Polynomials (0 0 0 0) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 = 0 · g(x) (1 0 0 0) 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 + x + x 3 = 1 · g(x) (0 1 0 0) 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 x + x 2 + x 4 = x · g(x) (1 1 0 0) 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 + x 2 + x 3 + x 4 = (1 + x) · g(x) (0 0 1 0) 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 x 2 + x 3 + x 5 = x 2 · g(x) (1 0 1 0) 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 + x + x 2 + x 5 = (1 + x 2 ) · g(x) (0 1 1 0) 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 x + x 3 + x 4 + x 5 = (x + x 2 ) · g(x) (1 1 1 0) 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 + x 4 + x 5 = (1 + x + x 2 ) · g(x) (0 0 0 1) 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 x 3 + x 4 + x 6 = x 3 · g(x) (1 0 0 1) 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 + x + x 4 + x 6 = (1 + x 3 ) · g(x) (0 1 0 1) 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 x + x 2 + x 3 + x 6 = (x + x 3 ) · g(x) (1 1 0 1) 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 + x 2 + x 6 = (1 + x + x 3 ) · g(x) (0 0 1 1) 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 x 2 + x 4 + x 5 + x 6 = (x 2 + x 3 ) · g(x) (1 0 1 1) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + x 4 + x 5 + x 6 = (1 + x 2 + x 3 ) · g(x) (1 1 1 1) 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 + x 3 + x 5 + x 6 = (1 + x + x 2 + x 3 ) · g(x) School of Electrical Engineering & Intelligentization, Dongguan University of Technology
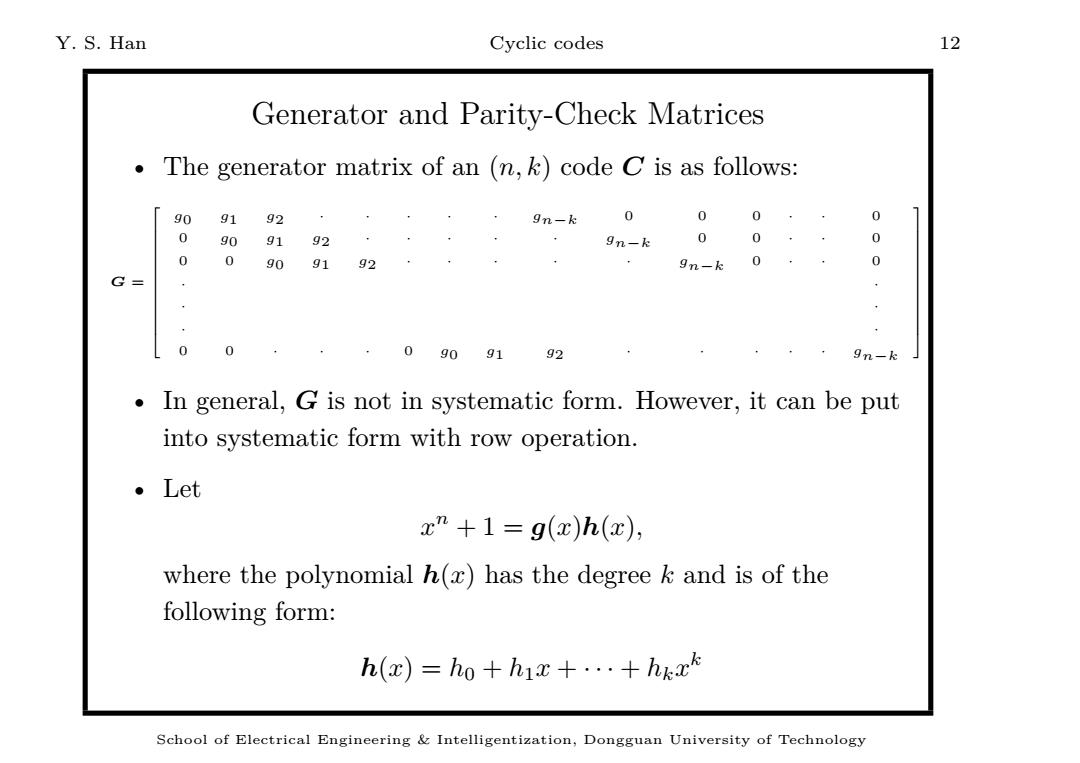
Y.S.Han Cyclic codes 12 Generator and Parity-Check Matrices The generator matrix of an (n,k)code C is as follows: 90 9192 9n-k 0 0 0 0 0 909192 9n-k 0 0 0 0 0909192 9n-k0 0 G- 0 0909192 9n-k In general,G is not in systematic form.However,it can be put into systematic form with row operation. 。Let x"+1=g(x)h(x), where the polynomial h(x)has the degree k and is of the following form: h(x)=ho+hix+...+hkxk School of Electrical Engineering Intelligentization,Dongguan University of Technology
Y. S. Han Cyclic codes 12 Generator and Parity-Check Matrices • The generator matrix of an (n, k) code C is as follows: G = g0 g1 g2 · · · · · g n−k 0 0 0 · · 0 0 g0 g1 g2 · · · · · g n−k 0 0 · · 0 0 0 g0 g1 g2 · · · · · g n−k 0 · · 0 · · · · · · 0 0 · · · 0 g0 g1 g2 · · · · · g n−k • In general, G is not in systematic form. However, it can be put into systematic form with row operation. • Let x n + 1 = g(x)h(x), where the polynomial h(x) has the degree k and is of the following form: h(x) = h0 + h1 x + · · · + hk x k School of Electrical Engineering & Intelligentization, Dongguan University of Technology
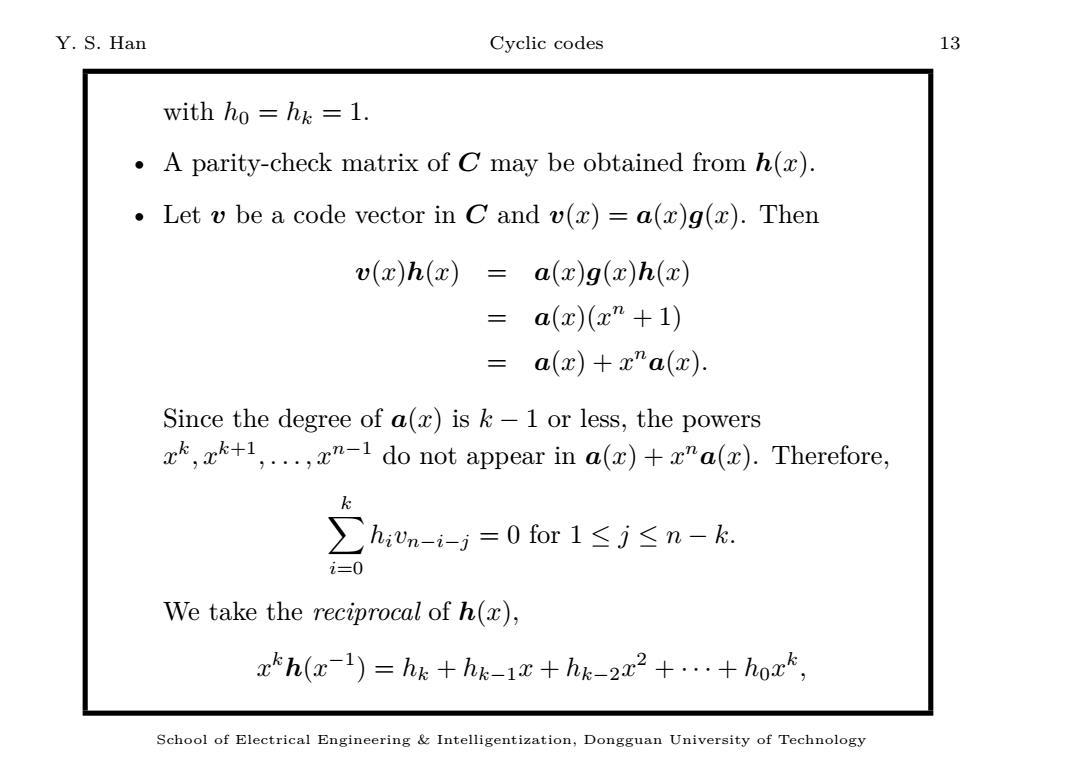
Y.S.Han Cyclic codes 13 with ho =hk=1. A parity-check matrix of C may be obtained from h(x). Let v be a code vector in C and v(x)=a(x)g(z).Then v(x)h(x)=a(x)g(x)h(x) = a(x)(xn+1) =a(x)+x”a(x). Since the degree of a(x)is k-1 or less,the powers ,1,...,x"-1 do not appear in a(x)+x"a(x).Therefore, ∑:mi=0for1≤j≤n-k i= We take the reciprocal of h(x), xhh(x-1)=hk+hk-1x+hk-232+...+hoxk, School of Electrical Engineering Intelligentization,Dongguan University of Technology
Y. S. Han Cyclic codes 13 with h0 = hk = 1. • A parity-check matrix of C may be obtained from h(x). • Let v be a code vector in C and v(x) = a(x)g(x). Then v(x)h(x) = a(x)g(x)h(x) = a(x)(x n + 1) = a(x) + x n a(x). Since the degree of a(x) is k − 1 or less, the powers x k , xk+1, . . . , xn−1 do not appear in a(x) + x n a(x). Therefore, ∑ k i=0 hi vn−i−j = 0 for 1 ≤ j ≤ n − k. We take the reciprocal of h(x), x k h(x −1 ) = hk + hk−1 x + hk−2 x 2 + · · · + h0 x k , School of Electrical Engineering & Intelligentization, Dongguan University of Technology
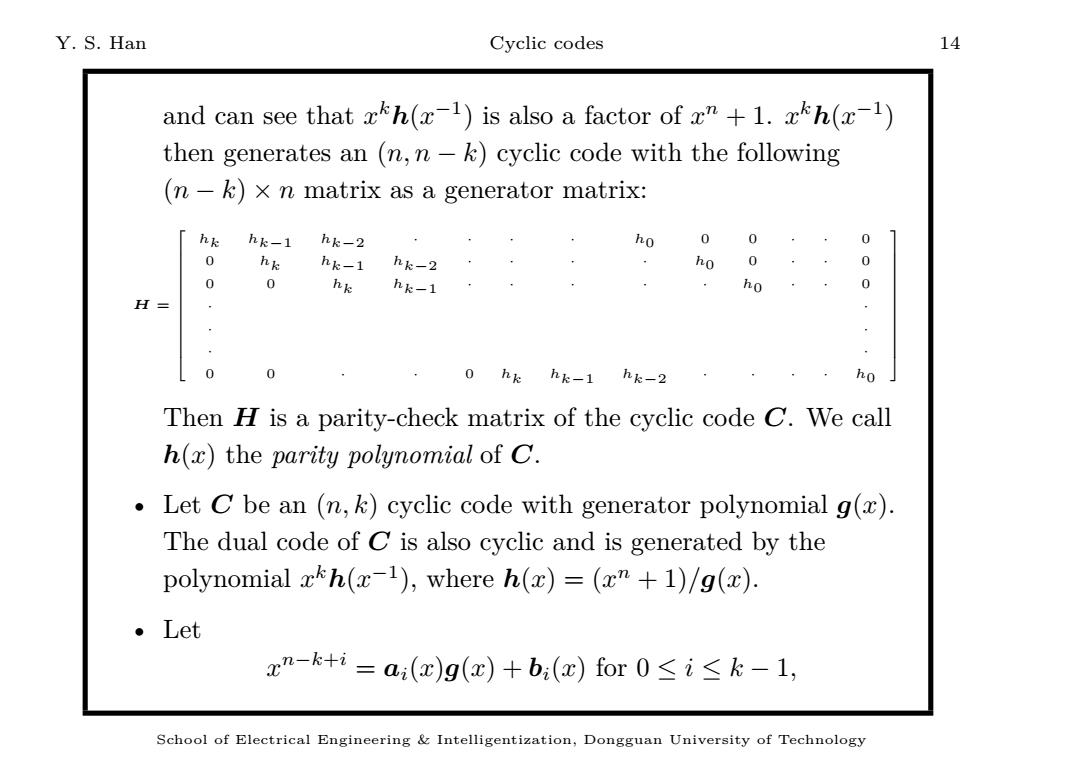
Y.S.Han Cyclic codes 14 and can see that xh(-1)is also a factor of z"+1.xh(-1) then generates an (n,n-k)cyclic code with the following (n-k)x n matrix as a generator matrix: hk hk-1 hk-2 ho 0 0 0 hk hk-1 hk-2 ho 0 0 0 0 hk hk-1 ho H= 0 0 0 hk hk-1 hk-2 ho Then H is a parity-check matrix of the cyclic code C.We call h(x)the parity polynomial of C. Let C be an (n,k)cyclic code with generator polynomial g(x). The dual code of C is also cyclic and is generated by the polynomial xkh(x-1),where h(x)=(x"+1)/g(x). 。Let xn-k+i=a(x)g(c)+b:(c)for0≤i≤k-1, School of Electrical Engineering Intelligentization,Dongguan University of Technology
Y. S. Han Cyclic codes 14 and can see that x k h(x −1 ) is also a factor of x n + 1. x k h(x −1 ) then generates an (n, n − k) cyclic code with the following (n − k) × n matrix as a generator matrix: H = hk hk−1 hk−2 · · · · h0 0 0 · · 0 0 hk hk−1 hk−2 · · · · h0 0 · · 0 0 0 hk hk−1 · · · · · h0 · · 0 · · · · · · 0 0 · · 0 hk hk−1 hk−2 · · · · h0 Then H is a parity-check matrix of the cyclic code C. We call h(x) the parity polynomial of C. • Let C be an (n, k) cyclic code with generator polynomial g(x). The dual code of C is also cyclic and is generated by the polynomial x k h(x −1 ), where h(x) = (x n + 1)/g(x). • Let x n−k+i = ai (x)g(x) + bi (x) for 0 ≤ i ≤ k − 1, School of Electrical Engineering & Intelligentization, Dongguan University of Technology