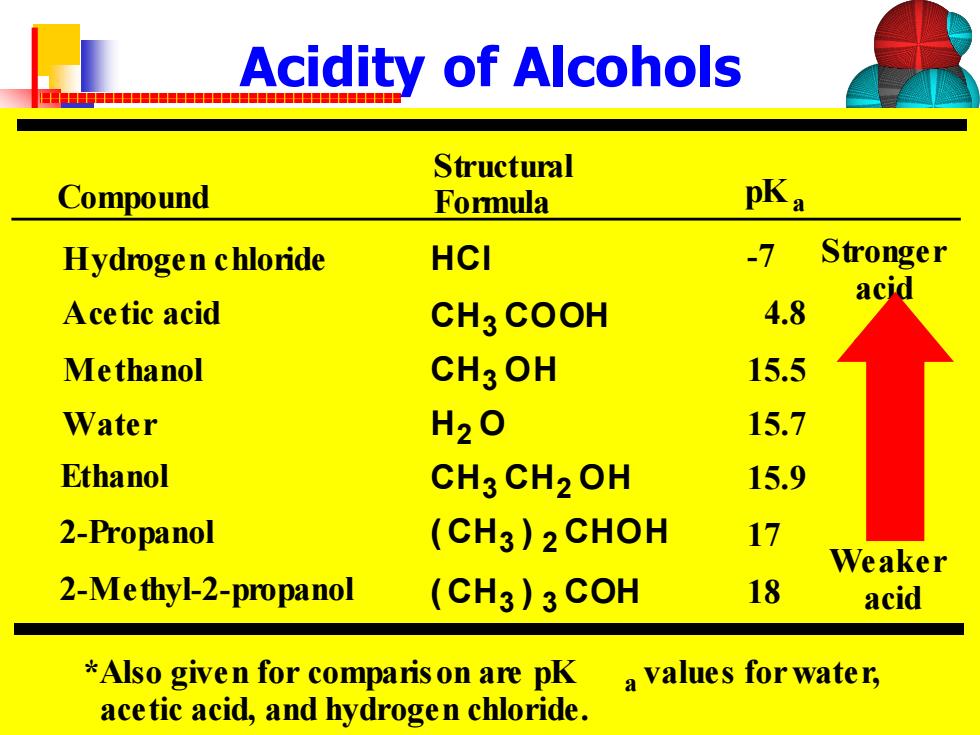
Acidity of Alcohols 品中器用 Structural Compound Formula pKa Hydrogen chloride HCI -7 Stronger acid Acetic acid CH3 COOH 4.8 Methanol CH3OH 15.5 Water H2O 15.7 Ethanol CH3 CH2OH 15.9 2-Propanol (CH3)2CHOH 17 Weaker 2-Me thyl-2-propanol (CH3)3COH 18 acid *Also given for comparis on are pK a values for water, acetic acid,and hydrogen chloride
Acidity of Alcohols ( CH3 ) 3 COH ( CH3 ) 2 CHOH CH3 CH2 OH H2 O CH3 OH CH3 COOH Hydrogen chloride HCl Acetic acid Methanol Water Ethanol 2-Propanol 2-Methyl-2-propanol Structural Formula Stronger acid Weaker acid *Also given for comparison are pK a values for water, acetic acid, and hydrogen chloride. Compound pKa -7 15.5 15.7 15.9 17 18 4.8
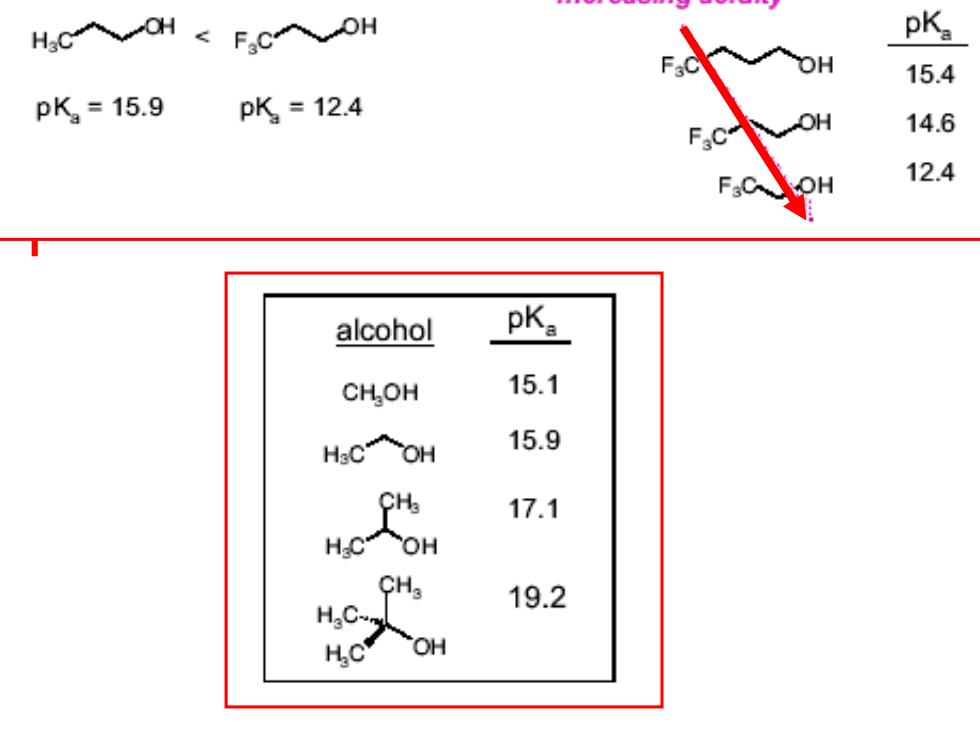
H,C入OH<F,C入DH 15.4 pK2=15.9 pK=12.4 14.6 12.4 alcohol pKa CH,OH 15.1 HCOH 15.9 17.1 CHa 19.2

Sec 2 Preparation of alcohols(REV Functional group transformation: -Functional groups such as alkyl halides,carboxylic acids,esters,alkenes,aldehydes,ketones,and ethers can be transformed into alcohols. C-C bond formation -Alcohols can be formed from epoxides,aldehydes, ketones,esters,and acid chlorides as a consequence of C-C bond formation with Grignard or organolithium reagents Reduction of Carbonyl Reduction of aldehyde yields 1 alcohol. .Reduction of ketone yields 2 alcohol. .Reagents:Sodium borohydride,NaBH4:Lithium aluminum hydride,LiAlH4:Raney nickel
Sec 2 Preparation of alcohols(REV) ❖Functional group transformation: ◼ Functional groups such as alkyl halides, carboxylic acids, esters, alkenes, aldehydes, ketones, and ethers can be transformed into alcohols. ❖C-C bond formation ◼ Alcohols can be formed from epoxides, aldehydes, ketones, esters, and acid chlorides as a consequence of C-C bond formation with Grignard or organolithium reagents ❖Reduction of Carbonyl ◼ Reduction of aldehyde yields 1ºalcohol. ◼ Reduction of ketone yields 2ºalcohol. ◼ Reagents:Sodium borohydride, NaBH4;Lithium aluminum hydride, LiAlH4;Raney nickel
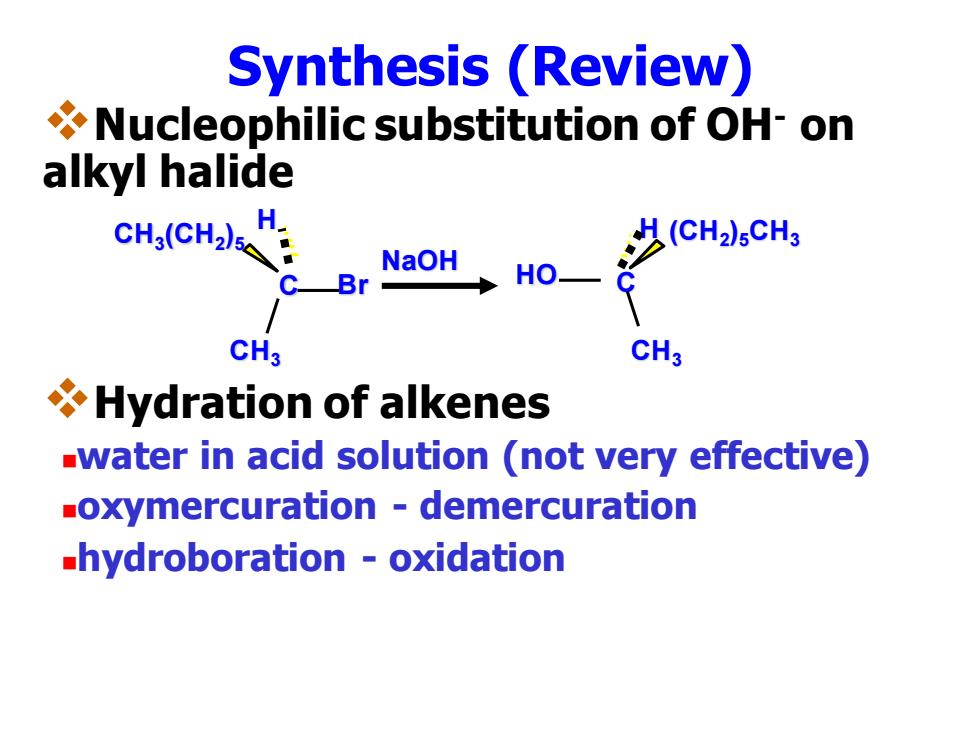
Synthesis (Review) Nucleophilic substitution of OH-on alkyl halide cH,c H(CH2)5CH3 NaOH C-Br HO- CH3 CH3 Hydration of alkenes -water in acid solution (not very effective) -oxymercuration demercuration hydroboration -oxidation
Synthesis (Review) ❖Nucleophilic substitution of OH- on alkyl halide ❖Hydration of alkenes ◼water in acid solution (not very effective) ◼oxymercuration - demercuration ◼hydroboration - oxidation NaOH C H CH3 HO (CH2 )5CH3 C H CH3 Br CH3 (CH2 )5

Glycols(Review) Syn hydroxylation of alkenes -osmium tetroxide,hydrogen peroxide -cold,dilute,basic potassium permanganate Anti hydroxylation of alkenes -peroxyacids,hydrolysis
Glycols (Review) ❖Syn hydroxylation of alkenes ◼osmium tetroxide, hydrogen peroxide ◼cold, dilute, basic potassium permanganate ❖Anti hydroxylation of alkenes ◼peroxyacids, hydrolysis