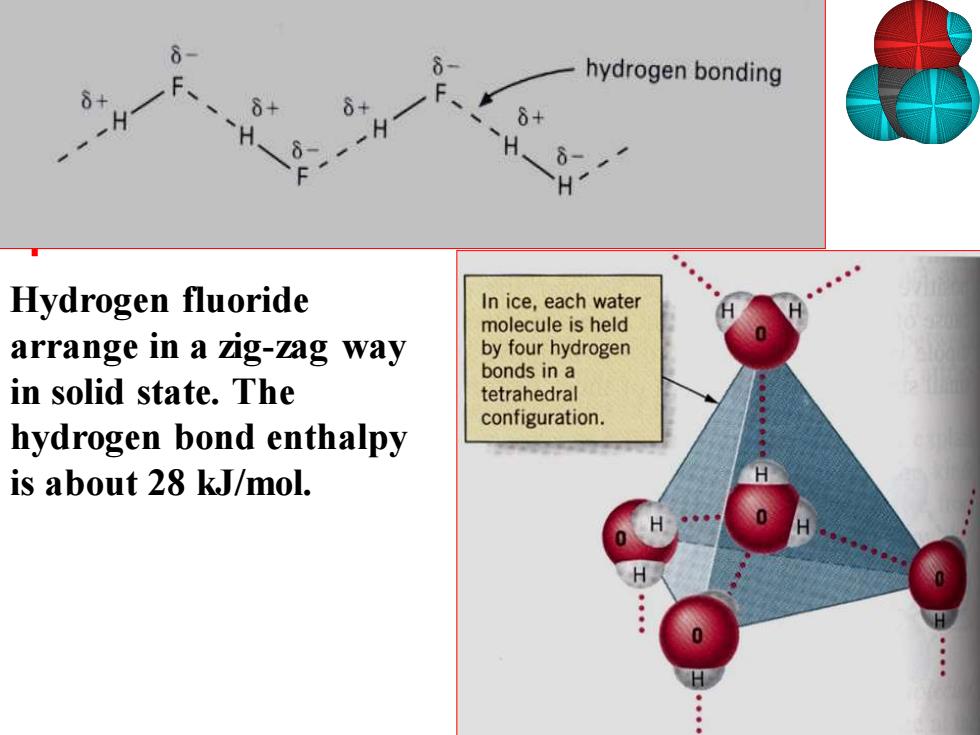
hydrogen bonding Hydrogen fluoride In ice,each water molecule is held arrange in a zig-zag way by four hydrogen bonds in a in solid state.The tetrahedral configuration. hydrogen bond enthalpy is about 28 kJ/mol
Hydrogen fluoride arrange in a zig-zag way in solid state. The hydrogen bond enthalpy is about 28 kJ/mol
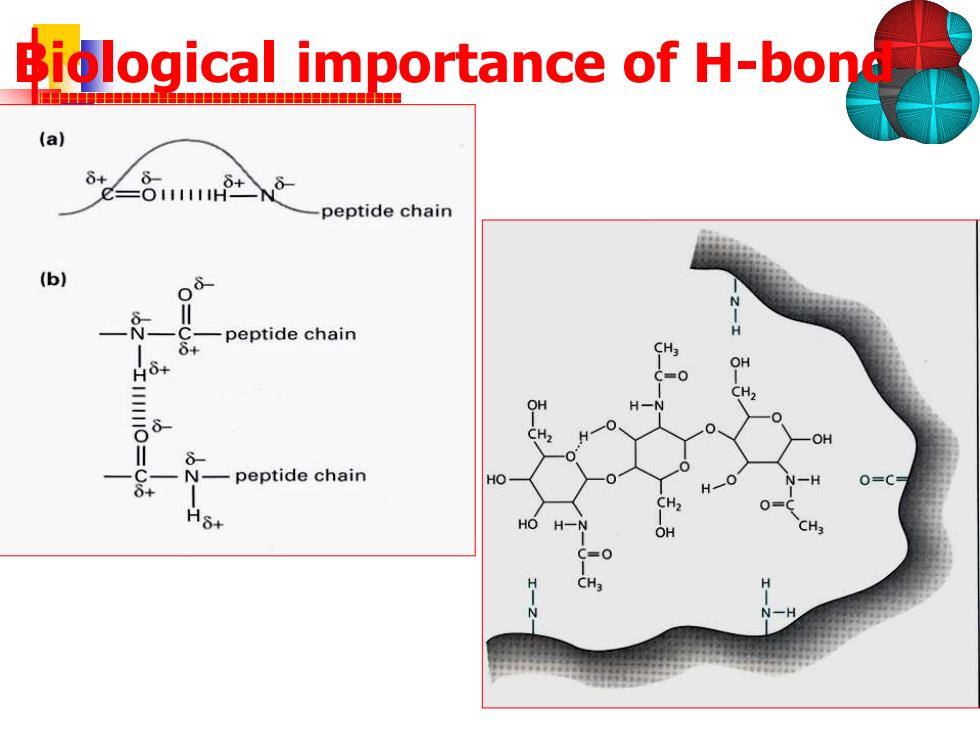
Biological importance of H-bon (a) δ+ =O11111H peptide chain (b) -peptide chain H6. N-peptide chain HO 0=C δ+
Biological importance of H-bond
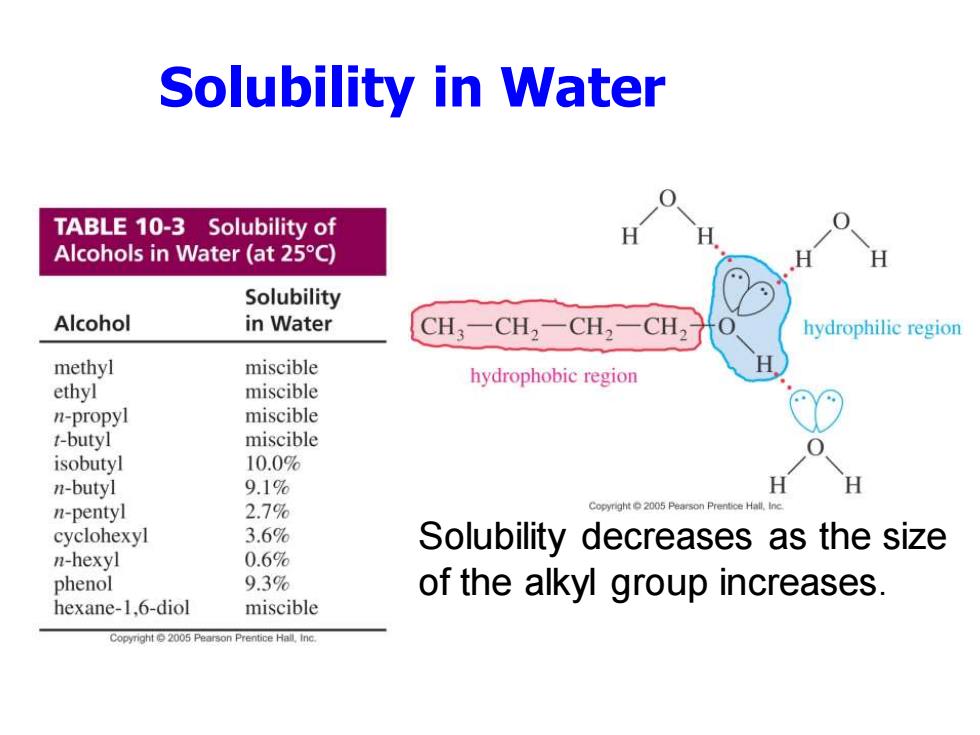
Solubility in Water TABLE 10-3 Solubility of Alcohols in Water (at 25C) H Solubility Alcohol in Water CH3一CH2-CH2一CH2 hydrophilic region methyl miscible hydrophobic region ethyl miscible n-propyl miscible t-butyl miscible isobutyl 10.0% n-butyl 9.1% H H n-pentyl 2.7% cyclohexyl 3.6% Solubility decreases as the size n-hexyl 0.6% phenol 9.3% of the alkyl group increases. hexane-1,6-diol miscible Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc
Solubility in Water Solubility decreases as the size of the alkyl group increases
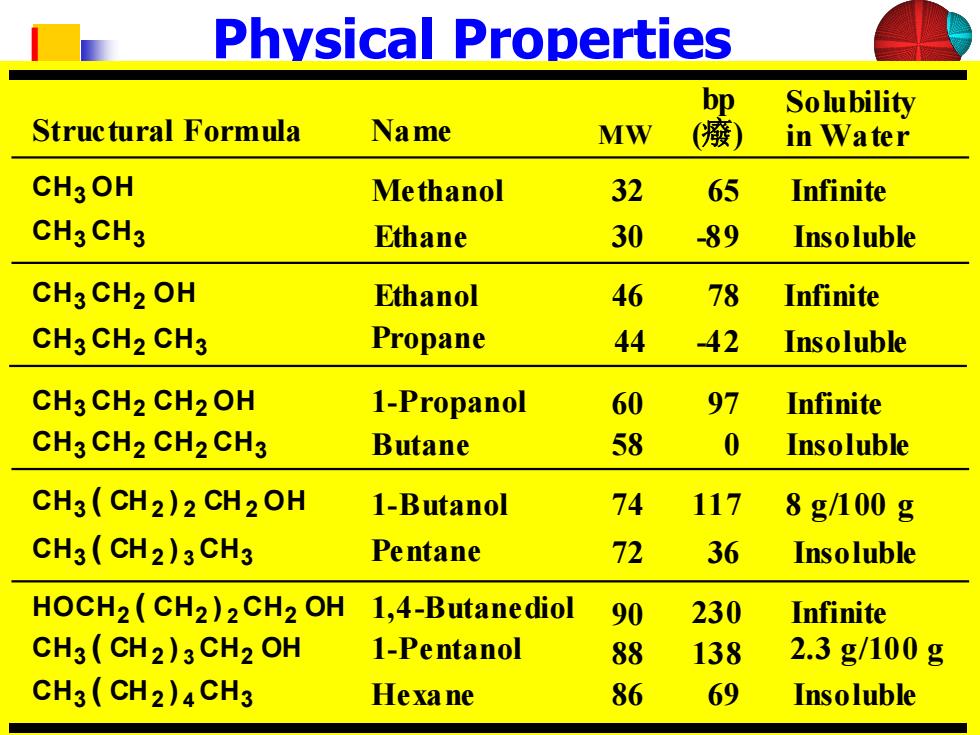
Physical Properties bp Solubility Structural Formula Name MW (癢) in Water CH3OH Methanol 32 65 Infinite CH3CH3 Ethane 30 -89 Insoluble CH3 CH2 OH Ethanol 46 78 Infinite CH3 CH2 CH3 Propane 44 42 Insoluble CH3 CH2CH2 OH 1-Propanol 60 97 Infinite CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 Butane 58 0 Insoluble CH3(CH2)2 CH2OH 1-Butanol 74 117 8g/100g CH3(CH2)3 CH3 Pentane 72 36 Insoluble HOCH2(CH2)2CH2 OH 1,4-Butanediol 90 230 Infinite CH3(CH2)3CH2 OH 1-Pentanol 88 138 2.3g/100g CH3(CH2)4CH3 Hexane 86 69 Insoluble
Physical Properties Structural Formula Name bp (癈) Solubility in Water Methanol 32 65 Infinite Ethane 30 -89 Insoluble Ethanol 46 78 Infinite Propane 44 -42 Insoluble 1-Propanol 60 97 Infinite Butane 58 0 Insoluble 1-Pentanol 88 138 2.3 g/100 g 1,4-Butanediol 90 230 Infinite Hexane 86 69 Insoluble 1-Butanol 74 117 8 g/100 g Pentane 72 36 Insoluble CH3 CH2 CH2 OH CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 CH3 OH CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 OH CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ( CH2 ) 3 CH2 OH HOCH2 ( CH2 ) 2 CH2 OH CH3 ( CH2 ) 4 CH3 CH3 ( CH2 ) 2 CH2 OH CH3 ( CH2 ) 3 CH3 MW
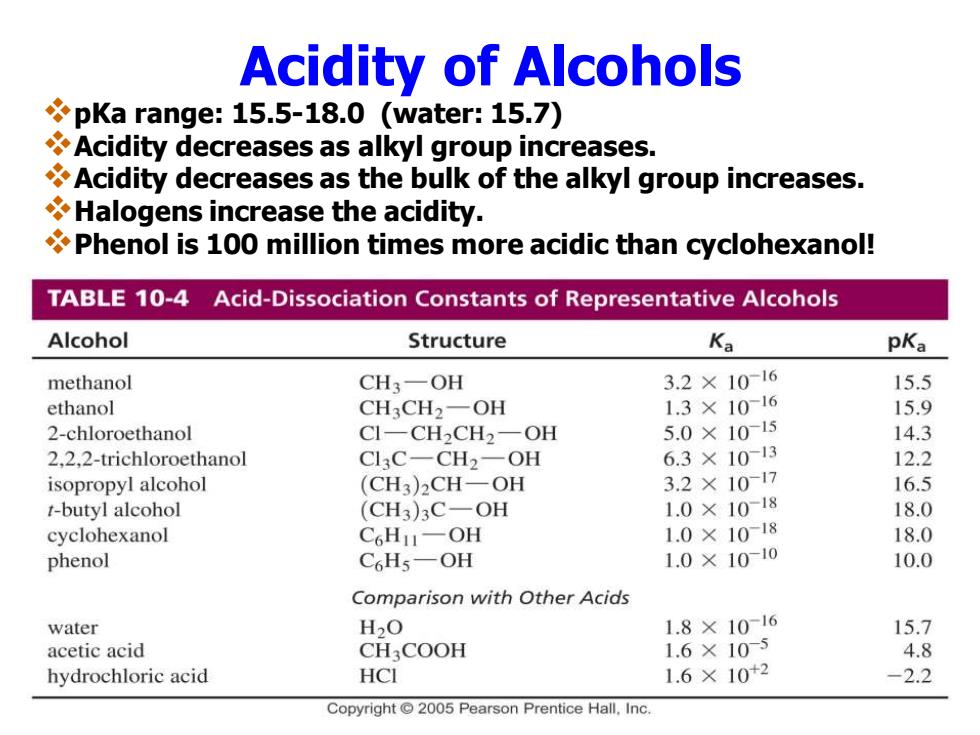
Acidity of Alcohols pKa range:15.5-18.0 (water:15.7) Acidity decreases as alkyl group increases. Acidity decreases as the bulk of the alkyl group increases. Halogens increase the acidity. Phenol is 100 million times more acidic than cyclohexanol! TABLE 10-4 Acid-Dissociation Constants of Representative Alcohols Alcohol Structure Ka pKa methanol CH3-OH 3.2×10-16 15.5 ethanol CH3CH2-OH 1.3×1016 15.9 2-chloroethanol CI-CH2CH2-OH 5.0×1015 14.3 2.2.2-trichloroethanol Cl3C-CH2-OH 6.3×1013 12.2 isopropyl alcohol (CH3)2CH-OH 3.2×1017 16.5 t-butyl alcohol (CH3)3C-OH 1.0×10-18 18.0 cyclohexanol C6HI-OH 1.0×1018 18.0 phenol C6Hs-OH 1.0×1010 10.0 Comparison with Other Acids water H2O 1.8×10-16 15.7 acetic acid CH3COOH 1.6×105 4.8 hydrochloric acid HCI 1.6×10+2 -2.2 Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc
Acidity of Alcohols ❖pKa range: 15.5-18.0 (water: 15.7) ❖Acidity decreases as alkyl group increases. ❖Acidity decreases as the bulk of the alkyl group increases. ❖Halogens increase the acidity. ❖Phenol is 100 million times more acidic than cyclohexanol!