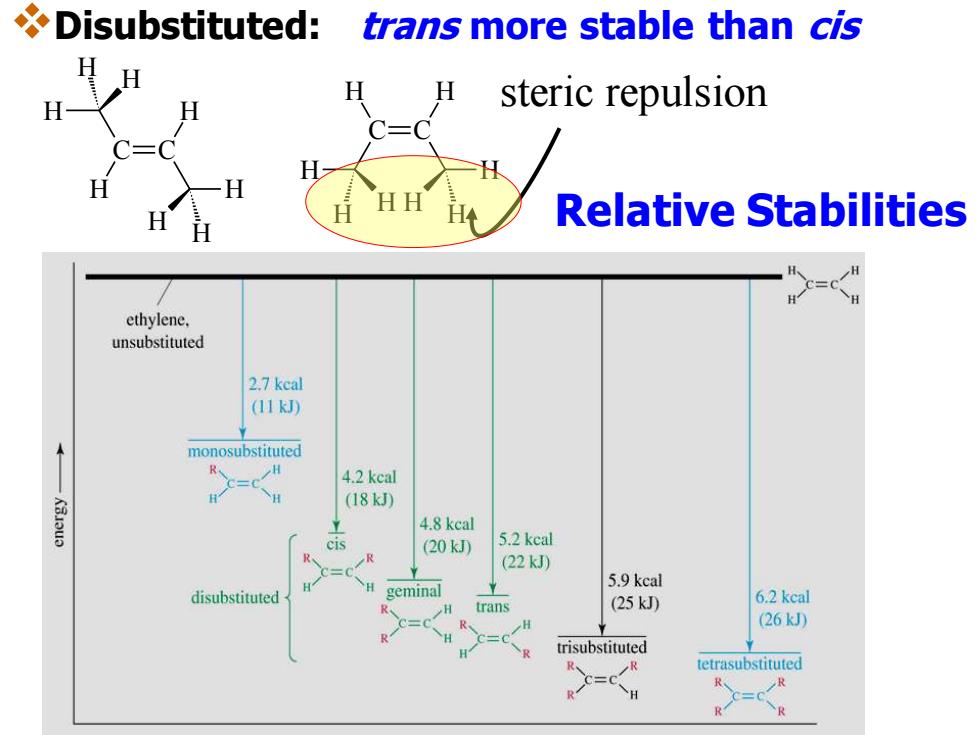
Disubstituted: trans more stable than cis H H steric repulsion HH Relative Stabilities ethylene. unsubstituted 2.7 keal (11kJ) monosubstituted R H C=C 4.2 kcal (18kJ 4.8 kcal cis (20kJ 5.2 keal R (22kJ) 5.9 kcal disubstituted geminal H trans (25kJ 6.2 keal 26kJ) =C trisubstituted 、 tetrasubstituted C=c R R R
❖Disubstituted: trans more stable than cis steric repulsion C C H H H H H H H H C C H H H H H H H H Relative Stabilities
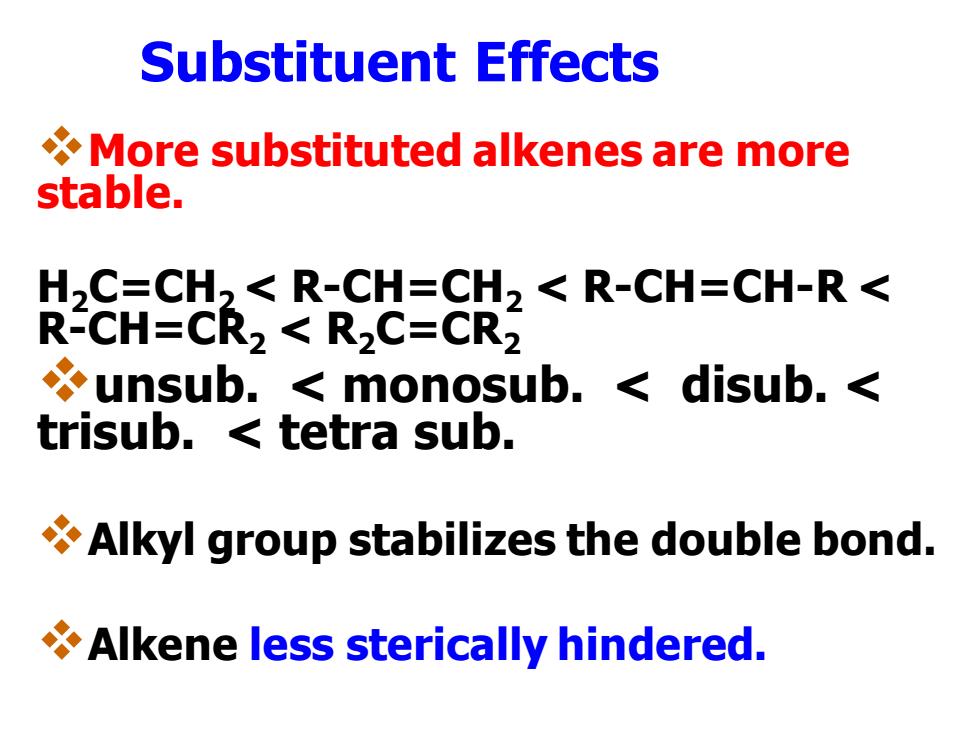
Substituent Effects More substituted alkenes are more stable. H,C=CH2<R-CH=CH2<R-CH=CH-R< R-CH=CR2 R2C=CR2 unsub.monosub.disub.< trisub.tetra sub. Alkyl group stabilizes the double bond. Alkene less sterically hindered
Substituent Effects ❖More substituted alkenes are more stable. H2C=CH2 < R-CH=CH2 < R-CH=CH-R < R-CH=CR2 < R2C=CR2 ❖unsub. < monosub. < disub. < trisub. < tetra sub. ❖Alkyl group stabilizes the double bond. ❖Alkene less sterically hindered

Stability of Cycloalkene ring connects CH CH,H CH,-CH2 behind the double bond. CH: CH: CH. CH. CH, H CH2 H CH, H CH2 CH,-CH, trans cyclic system trans-cycloheptene trans-cyclooctene cis-cyclooctene marginally stable stable more stable Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Cis isomer more stable Small rings have additional ring strain. Must have at least eight carbons to form a stable trans double bond. For cyclodecene (and larger),the trans double bond is almost as stable as the cis
Stability of Cycloalkene ❖Cis isomer more stable ❖Small rings have additional ring strain. ❖Must have at least eight carbons to form a stable trans double bond. ❖For cyclodecene (and larger), the trans double bond is almost as stable as the cis

Sec 2 Preparation of alkenes Alkenes can be synthesized by the reduction of alkynes,or by the elimination of alkyl halides and alcohols. -E2 dehydrohalogenation (-HX);E1 dehydrohalogenation (-HX);Dehydration of alcohols (-H2O) Dehalogenation of vicinal dibromides(-X2)
Sec 2 Preparation of alkenes Alkenes can be synthesized ❖by the reduction of alkynes, or ❖by the elimination of alkyl halides and alcohols. ◼E2 dehydrohalogenation (-HX);E1 dehydrohalogenation (-HX);Dehydration of alcohols (-H2O) ❖Dehalogenation of vicinal dibromides(-X2 )

Reduction of alkynes Lindlar's催化剂法: C2HsC=CC2H5 Pd/BaSO. H 喹啉 顺式烯烃 硼氢化方法 C2H5 C2H5C=CCH3+1/2(BH3)2 C2H5 CH3 顺式烯烃 H Z-2-戊烯 液氨法 CH3-C=C-CH3 2Na+NH 液氨 2NaNH2 CH3 反式烯烃
顺式烯烃 C2H5 C CC2H5 + H2 Pd/BaSO4 喹啉 C C H5 C2 C2 H5 H H Lindlar’s催化剂法: 硼氢化方法 C2 H5 C C CH3 + 1/2(BH3 )2 o 0 C C C C2H5 CH3 H B o 0 C CH3COOH C C C2H5 CH3 H H Z-2-戊烯 顺式烯烃 Reduction of alkynes CH3 C C CH3 + 2Na + NH3 液氨 C C + 2NaNH2 H H CH3 H3C 反式烯烃 液氨法