
Organic Chemistry with BiologicalApplications,3 Edition John McMurry Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions The principles of all chemical reactions follow the same rules". To understand both organic and biological chemistry,it's necessary to know not just what occurs but also why and how chemical reactions take place. Homework:P145c:5.43:5.44. P162:6.9:P178:6.216.23:6.24 Key Notes Addition reactions;Elimination reactions;Substitution reactions;Rearrangement reactions;Mechanisms;Radical Reactions;Polar Reactions
Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3 rd Edition John McMurry Key Notes Addition reactions;Elimination reactions;Substitution reactions;Rearrangement reactions;Mechanisms;Radical Reactions;Polar Reactions The principles of all chemical reactions follow the same “rules” . To understand both organic and biological chemistry, it’s necessary to know not just what occurs but also why and how chemical reactions take place. Chapter 06 An Overview of Organic Reactions Homework: P145c:5.43; 5.44; P162:6.9; P178:6.21; 6.23; 6.24

6-1 Kinds of Organic Reactions Organic chemical reactions broadly organized in two ways: 1.What kinds of reactions occur 2.How those reactions occur
Organic chemical reactions broadly organized in two ways: 1. What kinds of reactions occur 2. How those reactions occur 6-1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
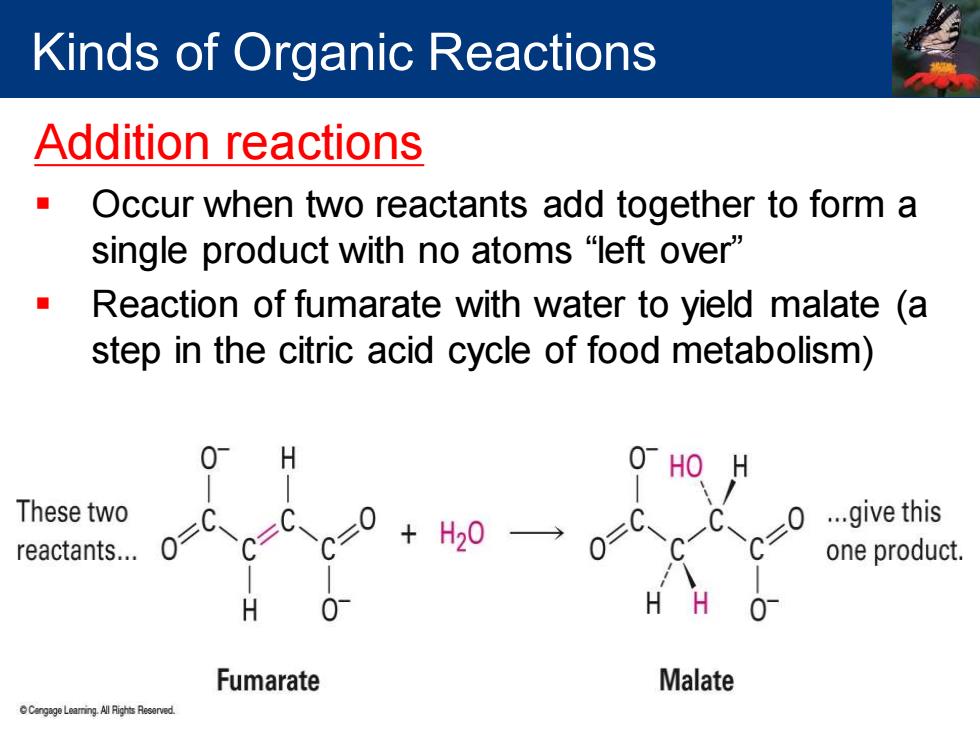
Kinds of Organic Reactions Addition reactions Occur when two reactants add together to form a single product with no atoms“left over'” Reaction of fumarate with water to yield malate (a step in the citric acid cycle of food metabolism) H 0 HO H These two ...give this reactants... 0 H20 one product. H H 01 Fumarate Malate n Leaming All Rights Reserved
Addition reactions ▪ Occur when two reactants add together to form a single product with no atoms “left over” ▪ Reaction of fumarate with water to yield malate (a step in the citric acid cycle of food metabolism) Kinds of Organic Reactions
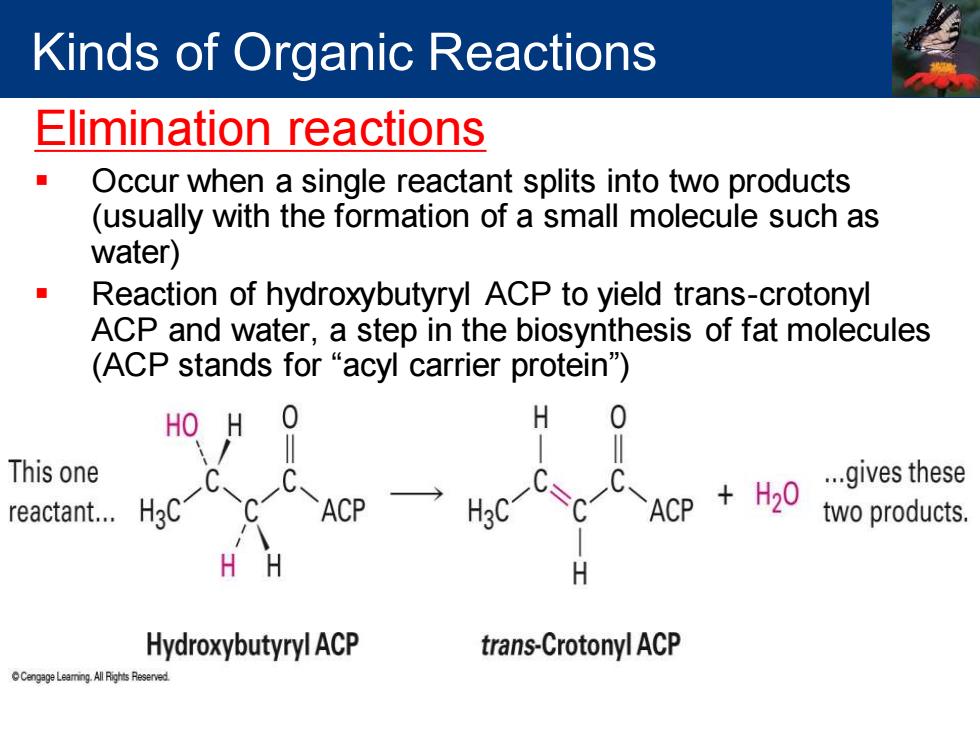
Kinds of Organic Reactions Elimination reactions Occur when a single reactant splits into two products (usually with the formation of a small molecule such as water) Reaction of hydroxybutyryl ACP to yield trans-crotonyl ACP and water,a step in the biosynthesis of fat molecules (ACP stands for "acyl carrier protein) HO H 0 H 0 This one reactant.… ACP H3C ACP H20 ...gives these two products. H H Hydroxybutyryl ACP trans-Crotonyl ACP
Elimination reactions ▪ Occur when a single reactant splits into two products (usually with the formation of a small molecule such as water) ▪ Reaction of hydroxybutyryl ACP to yield trans-crotonyl ACP and water, a step in the biosynthesis of fat molecules (ACP stands for “acyl carrier protein”) Kinds of Organic Reactions
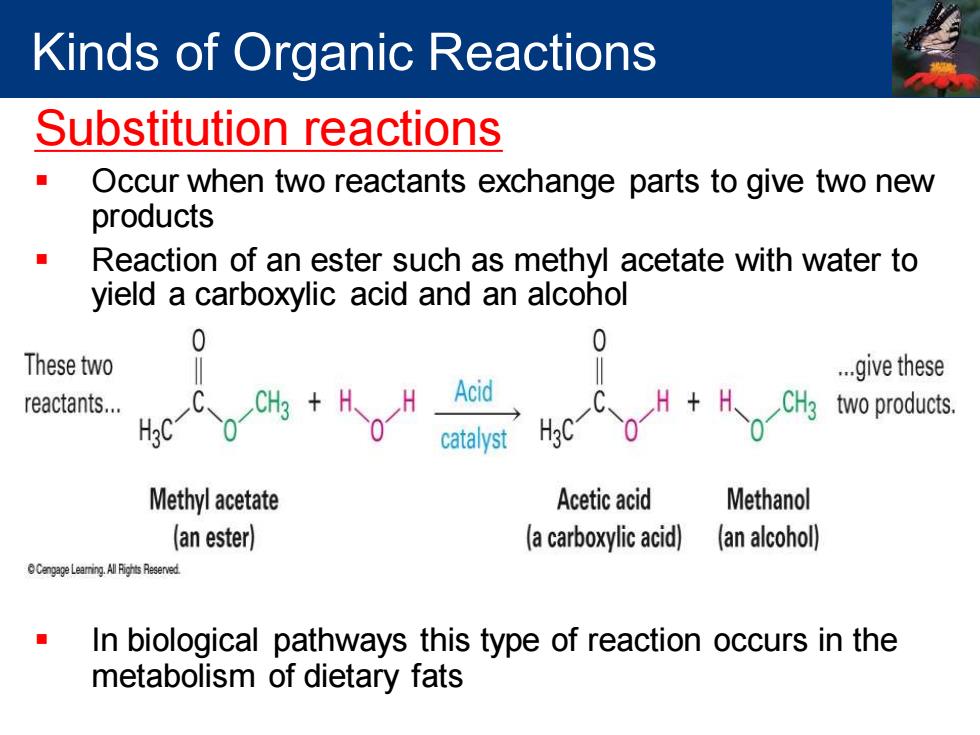
Kinds of Organic Reactions Substitution reactions Occur when two reactants exchange parts to give two new products Reaction of an ester such as methyl acetate with water to yield a carboxylic acid and an alcohol 0 0 These two ..give these reactants... Hc-Co Acid CH3 two products. catalyst H3C Methyl acetate Acetic acid Methanol (an ester) (a carboxylic acid) (an alcohol) npeLeaming Alih Resered In biological pathways this type of reaction occurs in the metabolism of dietary fats
Substitution reactions ▪ Occur when two reactants exchange parts to give two new products ▪ Reaction of an ester such as methyl acetate with water to yield a carboxylic acid and an alcohol ▪ In biological pathways this type of reaction occurs in the metabolism of dietary fats Kinds of Organic Reactions