
Organic Chemistry with BiologicalApplications,3 Edition JOHN MCMURRY John McMurry Chapter 12 Organohalides:Nucleophilic Organic Chemistry Substitutions and Eliminations wth Biological Applications Nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations are frequently involved in the biochemical pathways of terrestrial organisms and alkyl halide chemistry acts as a relatively simple model of biomolecules. By Junru Wang College of Chemistry and Pharmacy Room C206,Science Building Tel:87092829(O);Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang College of Chemistry and Pharmacy Room C206, Science Building Tel: 87092829(O);Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 12 Organohalides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3 rd Edition John McMurry Nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations—are frequently involved in the biochemical pathways of terrestrial organisms and alkyl halide chemistry acts as a relatively simple model of biomolecules
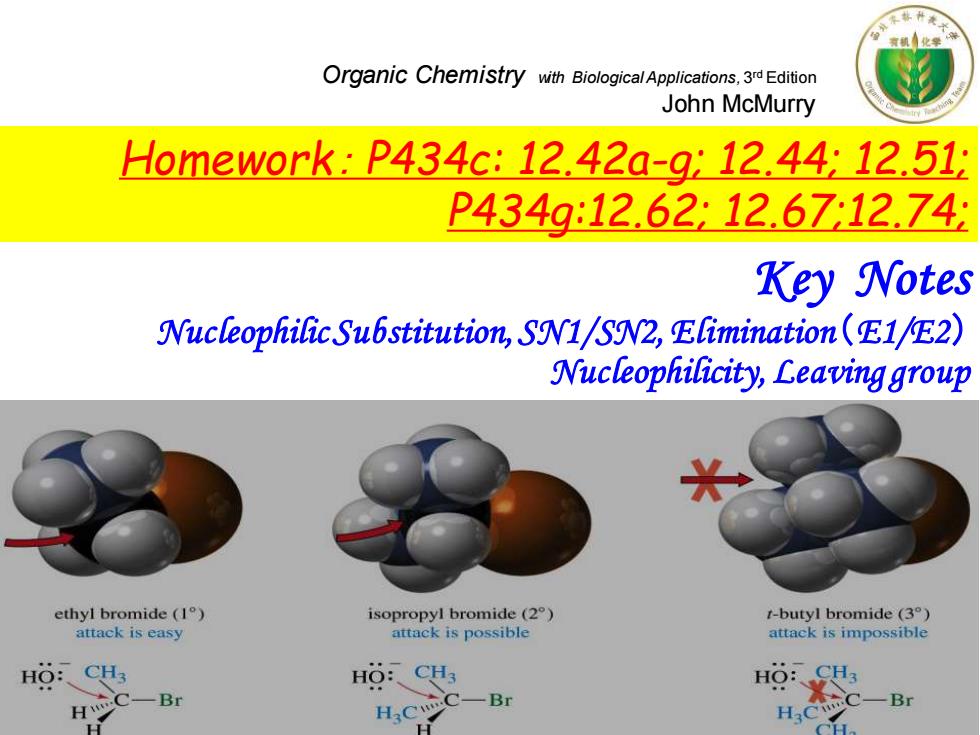
Organic Chemistry with BiologicalApplications.3Edition John McMurry Hdomework:P434c:12.42a-912.44:12.51: P434g:12.62:12.67:12.74 Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution,SN1/SN2,Elimination(E1/E2) Nucleophilicity,Leaving group ethyl bromide (1) isopropyl bromide (2) t-butyl bromide(3°) attack is easy attack is possible attack is impossible HO:CH3 HO:CH3 HO: -Br -Br H H3C H
Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3 rd Edition John McMurry Key Notes Nucleophilic Substitution, SN1/SN2, Elimination(E1/E2) Nucleophilicity, Leaving group Homework: P434c: 12.42a-g; 12.44; 12.51; P434g:12.62; 12.67;12.74;

Main Contents Preparing Alkyl Halides Reactions of Alkyl Halides Organometallic Coupling Reactions Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction √SN2 Reaction SN1 Reaction Biological Substitution Reactions Elimination Reactions:E1 E2
Main Contents ◼Preparing Alkyl Halides ◼Reactions of Alkyl Halides ◼Organometallic Coupling Reactions ◼Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction ✓SN2 Reaction ✓SN1 Reaction ◼Biological Substitution Reactions ◼Elimination Reactions: E1 & E2
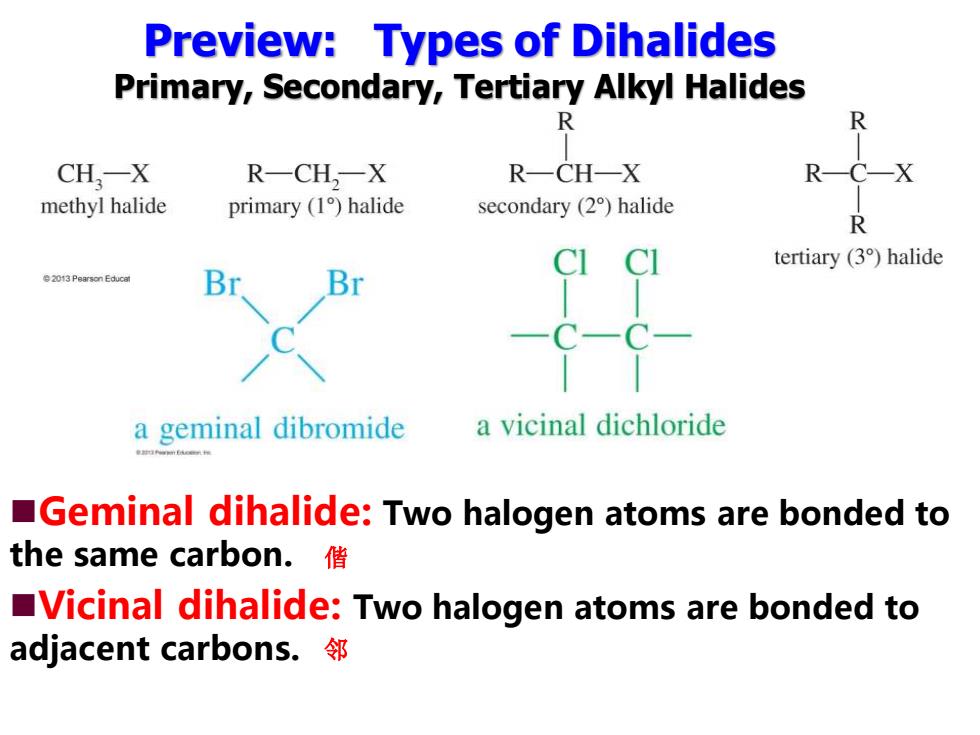
Preview:Types of Dihalides Primary,Secondary,Tertiary Alkyl Halides 个 R CH,-X R-CH,一X R-CH-X RC-X methyl halide primary (1)halide secondary (2)halide R CI tertiary (3)halide 2013 Pearson Educat Br a geminal dibromide a vicinal dichloride Geminal dihalide:Two halogen atoms are bonded to the same carbon.偕 Vicinal dihalide:Two halogen atoms are bonded to adjacent carbons..邻
Preview: Types of Dihalides Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Alkyl Halides ◼Geminal dihalide: Two halogen atoms are bonded to the same carbon. ◼Vicinal dihalide: Two halogen atoms are bonded to adjacent carbons. 偕 邻
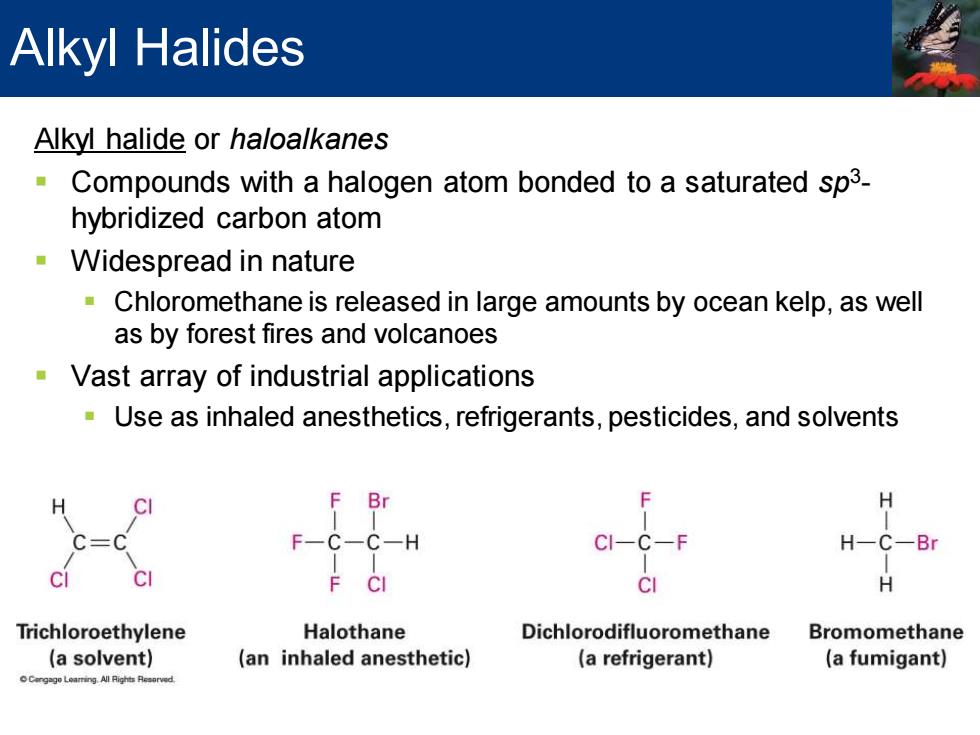
Alkyl Halides Alkyl halide or haloalkanes -Compounds with a halogen atom bonded to a saturated sp3- hybridized carbon atom Widespread in nature Chloromethane is released in large amounts by ocean kelp,as well as by forest fires and volcanoes Vast array of industrial applications Use as inhaled anesthetics,refrigerants,pesticides,and solvents Br F-C-C-H Cl- C- H-C-Br F CI H Trichloroethylene Halothane Dichlorodifluoromethane Bromomethane (a solvent) (an inhaled anesthetic) (a refrigerant) (a fumigant) Leaing All Rights Reaorved
Alkyl halide or haloalkanes ▪ Compounds with a halogen atom bonded to a saturated sp3 - hybridized carbon atom ▪ Widespread in nature ▪ Chloromethane is released in large amounts by ocean kelp, as well as by forest fires and volcanoes ▪ Vast array of industrial applications ▪ Use as inhaled anesthetics, refrigerants, pesticides, and solvents Alkyl Halides