
Number Theory Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
Number Theory Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University

How to compute gcd(x,y) Observation:gcd(x,y)=ged(x-y,y)=gcd(x-2y,y)=.... Suppose x>y,x=ky+d where d<y,thus gcd(x,y)=ged(ky+d,y)=gcd(ky+d-ky,y)=gcd(d,y) Euclid's Algorithm: integer euclid(pos.integer m,pos.integer n) x=m,y=n while(y>0) r=x mod y x=y y=r return x 2
2 How to compute gcd(x,y) Observation: gcd(x,y) = gcd(x-y, y) = gcd(x-2y, y) = …. Suppose x>y, x=ky+d where d<y, thus gcd(x,y)=gcd(ky+d, y)=gcd(ky+d-ky, y)=gcd(d,y) Euclid’s Algorithm: integer euclid(pos. integer m, pos. integer n) x = m, y = n while(y > 0) r = x mod y x = y y = r return x
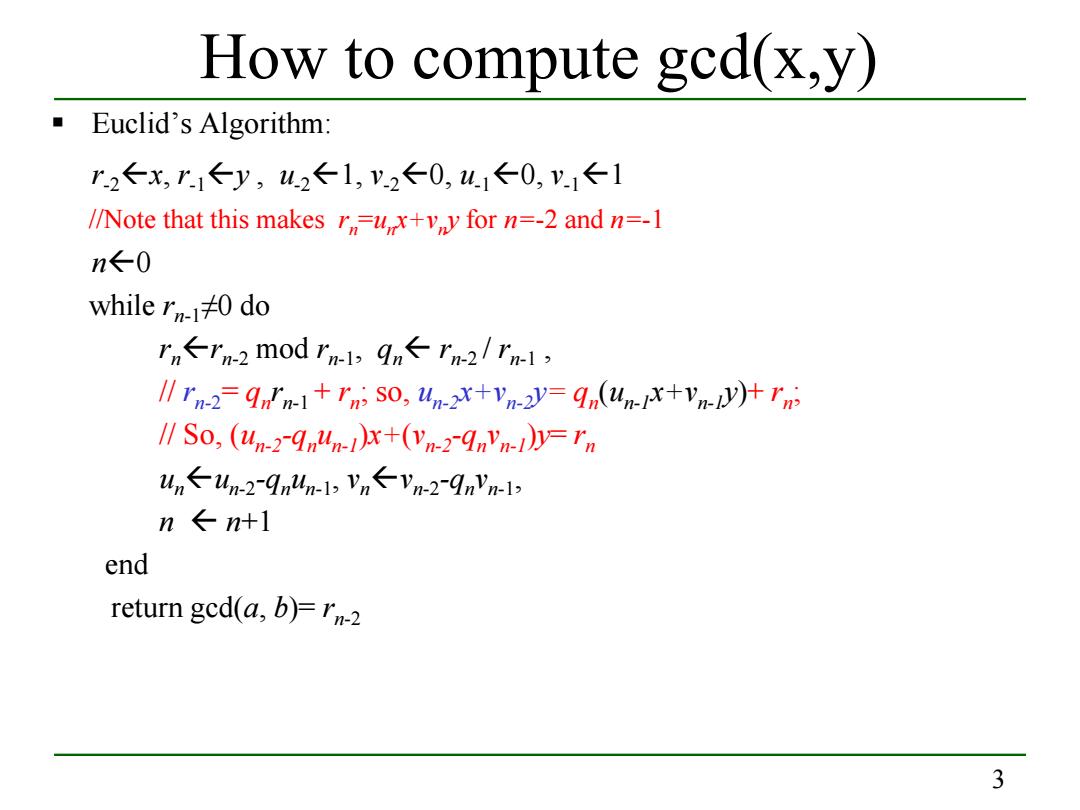
How to compute gcd(x,y) Euclid's Algorithm: r2←x,r1y,u2←1,V.2←0,u1←0,y1←1 //Note that this makes ru,x+vy for n=-2 and n=-1 n←0 while r140 do rn←n-2m0drn-l,9n←rm-2/Tnml, IIIn2=gm1+ni So,un-xx+Vn-2y=9nun-x+vn)+n ISo,(un-2-qnunx+(vn2-qnvn-Dyrn un←un-2-9n4n-l,Vn←Vn-2-9nyn-l n←nt1 end return gcd(a,b)=rn-2 3
3 How to compute gcd(x,y) Euclid’s Algorithm: r-2x, r-1y , u-21, v-20, u-10, v-11 //Note that this makes rn=unx+vny for n=-2 and n=-1 n0 while rn-1≠0 do rnrn-2 mod rn-1, qn rn-2 / rn-1 , // rn-2= qnrn-1 + rn; so, un-2x+vn-2y= qn(un-1x+vn-1y)+ rn; // So, (un-2-qnun-1)x+(vn-2-qnvn-1)y= rn unun-2-qnun-1, vnvn-2-qnvn-1, n n+1 end return gcd(a, b)= rn-2
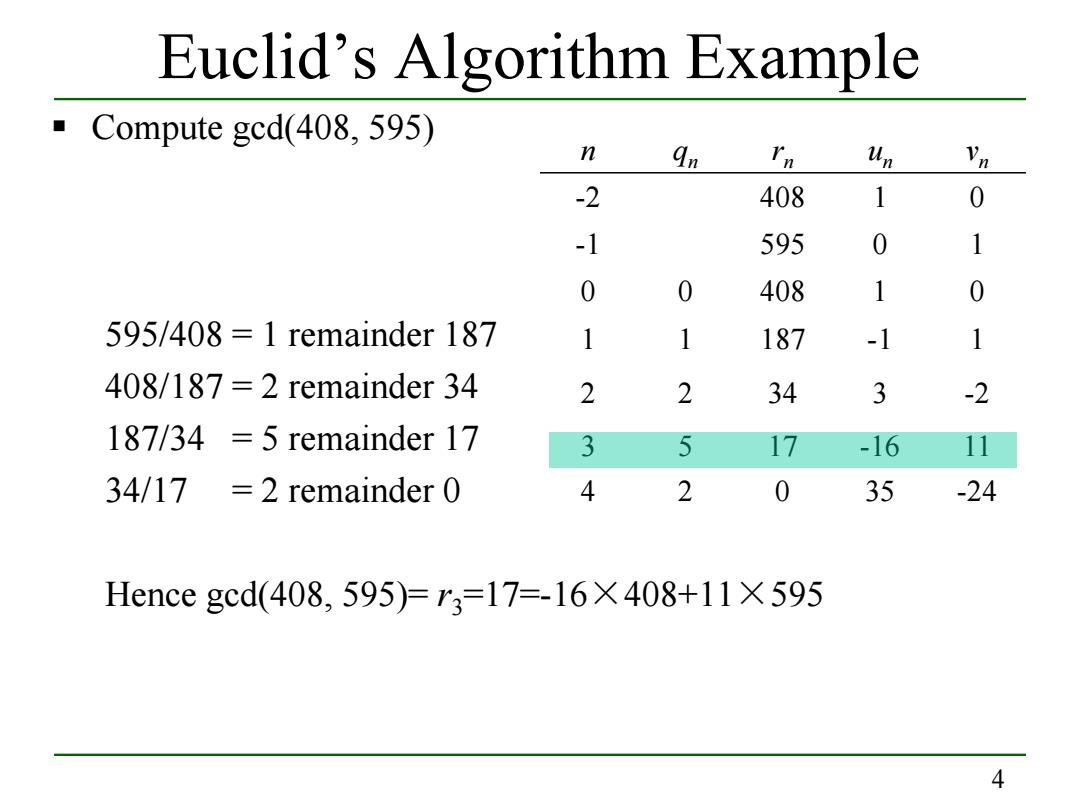
Euclid's Algorithm Example Compute ged(408,595) n Un -2 408 1 0 -1 595 0 1 0 0 408 1 0 595/408 =1 remainder 187 1 1 187 -1 1 408/187=2 remainder 34 2 2 34 3 -2 187/34 5 remainder 17 3 5 17 -16 11 34/17 =2 remainder 0 4 2 0 35 -24 Hence gcd(408,595)=r3=17=-16×408+11×595 4
4 Euclid’s Algorithm Example Compute gcd(408, 595) 595/408 = 1 remainder 187 408/187 = 2 remainder 34 187/34 = 5 remainder 17 34/17 = 2 remainder 0 Hence gcd(408, 595)= r3=17=-16×408+11×595 n qn rn un vn -2 408 1 0 -1 595 0 1 0 0 408 1 0 4 2 0 35 -24 3 5 17 -16 11 2 2 34 3 -2 1 1 187 -1 1

Finding Multiplicative Inverses Compute the multiplicative inverse al mod n It is equivalent to find a number u such that ua 1 mod n In other words,there is an integer y such that ua vn=1 Using Euclid's algorithm,we can compute ged(a,n)to find a and v such that ua vn 1 Fact:a and n are relatively prime iff there are integers u and v such that ua vn=1. Proof:If ged(a,n)=1,then we can find u and v such that ua vn=1 according to Euclid's algorithm.If gcd(a,n)=m>1,suppose a=km,n=k'm,then for any integers u and v,ua+yn ukm+vk'm=(uk+vk)mt1. 5
5 Finding Multiplicative Inverses Compute the multiplicative inverse a-1 mod n It is equivalent to find a number u such that ua = 1 mod n In other words, there is an integer v such that ua + vn = 1 Using Euclid’s algorithm, we can compute gcd(a, n) to find u and v such that ua + vn = 1 Fact: a and n are relatively prime iff there are integers u and v such that ua + vn=1. Proof: If gcd(a,n)=1, then we can find u and v such that ua + vn = 1 according to Euclid’s algorithm. If gcd(a, n)=m>1, suppose a=km, n=k’m, then for any integers u and v, ua+vn = ukm+vk’m=(uk+vk’)m≠1