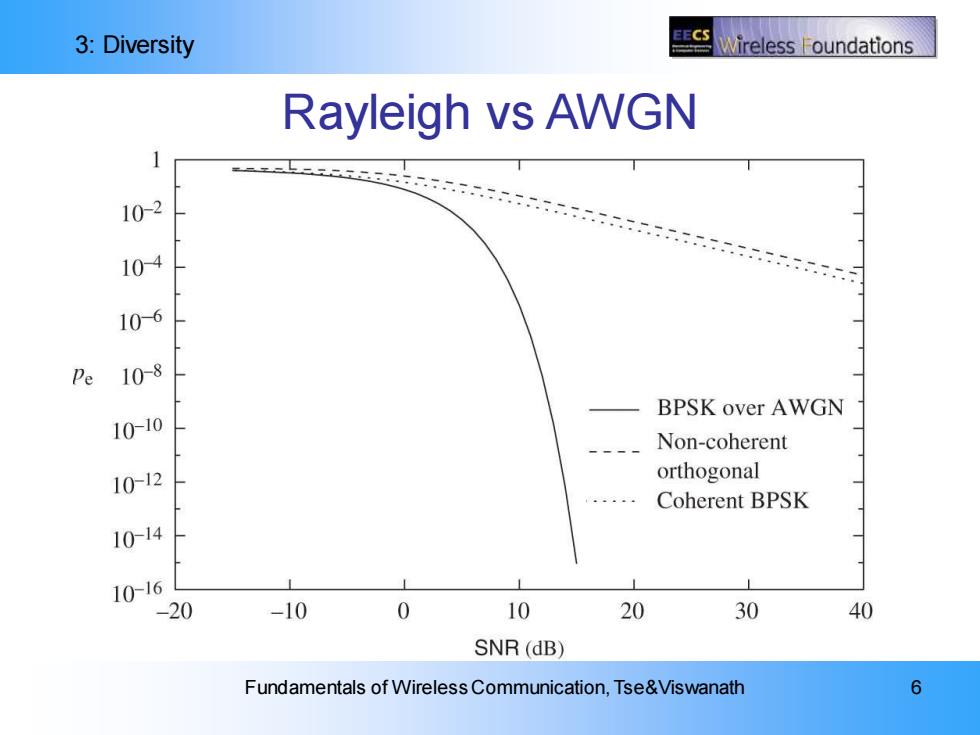
3:Diversity ireless oundations Rayleigh vs AWGN 102 104 106 Pe 10-8 BPSK over AWGN 1010 Non-coherent 1012 orthogonal Coherent BPSK 1014 10-16 1 20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 SNR(dB) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 6
3: Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 6 Rayleigh vs AWGN

3:Diversity EECS Wireless Foundations Typical Error Event Conditional on h, Pe=Q(V2IhI2SNR Whenerror probability is very small. When<NR,error probability is large: (R) SNR |h2exp(1). Typical error event is due to channel being in deep fade rather than noise being large. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath
3: Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 7 Conditional on h, When error probability is very small. When error probability is large: Typical error event is due to channel being in deep fade rather than noise being large. Typical Error Event
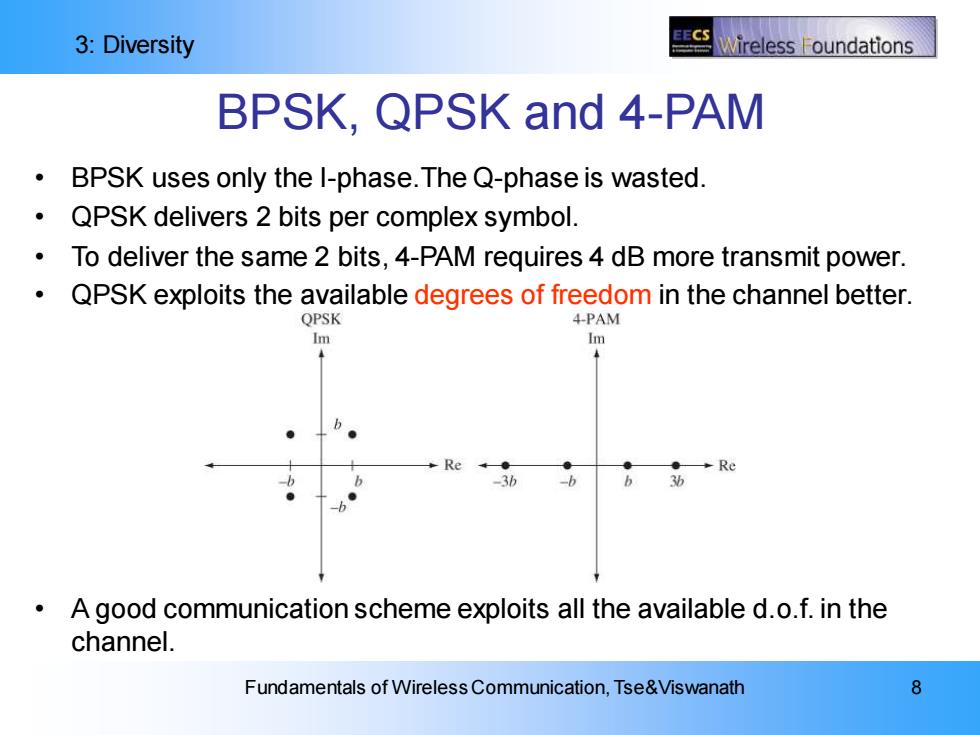
3:Diversity EECS Vireless oundations BPSK,QPSK and 4-PAM 。 BPSK uses only the l-phase.The Q-phase is wasted. QPSK delivers 2 bits per complex symbol. To deliver the same 2 bits,4-PAM requires 4 dB more transmit power. QPSK exploits the available degrees of freedom in the channel better. QPSK 4-PAM Im Im A good communication scheme exploits all the available d.o.f.in the channel. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 8
3: Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 8 BPSK, QPSK and 4-PAM • BPSK uses only the I-phase.The Q-phase is wasted. • QPSK delivers 2 bits per complex symbol. • To deliver the same 2 bits, 4-PAM requires 4 dB more transmit power. • QPSK exploits the available degrees of freedom in the channel better. • A good communication scheme exploits all the available d.o.f. in the channel
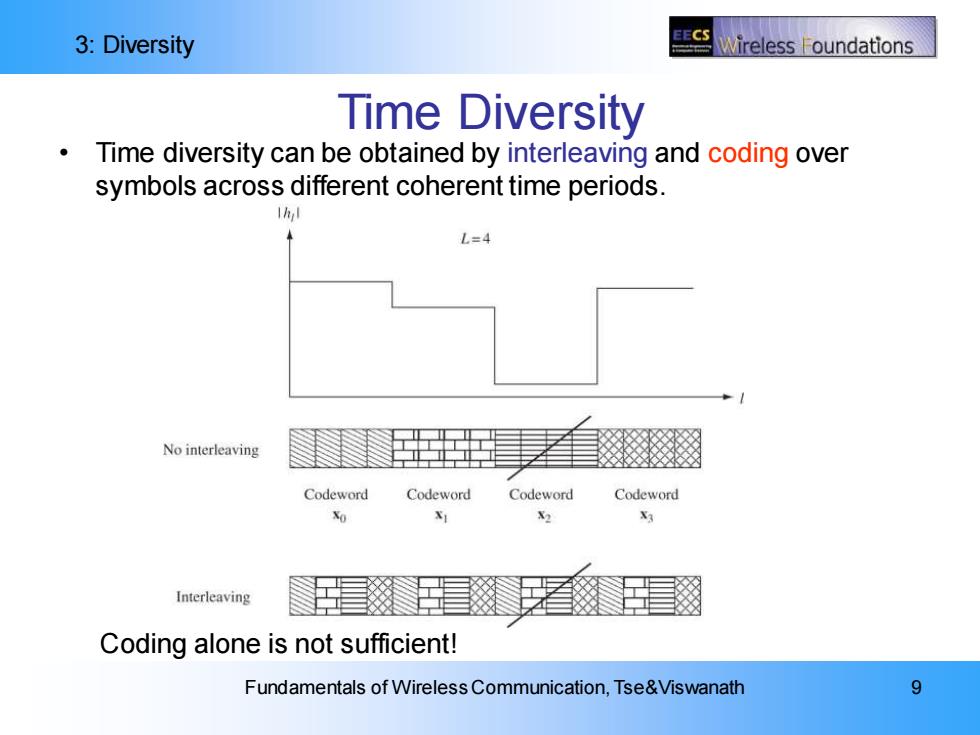
3:Diversity EECS Wireless oundations Time Diversity Time diversity can be obtained by interleaving and coding over symbols across different coherent time periods. 1hal L=4 No interleaving Codeword Codeword Codeword Codeword X3 Interleaving Coding alone is not sufficient! Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 9
3: Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 9 Time Diversity • Time diversity can be obtained by interleaving and coding over symbols across different coherent time periods. Coding alone is not sufficient!
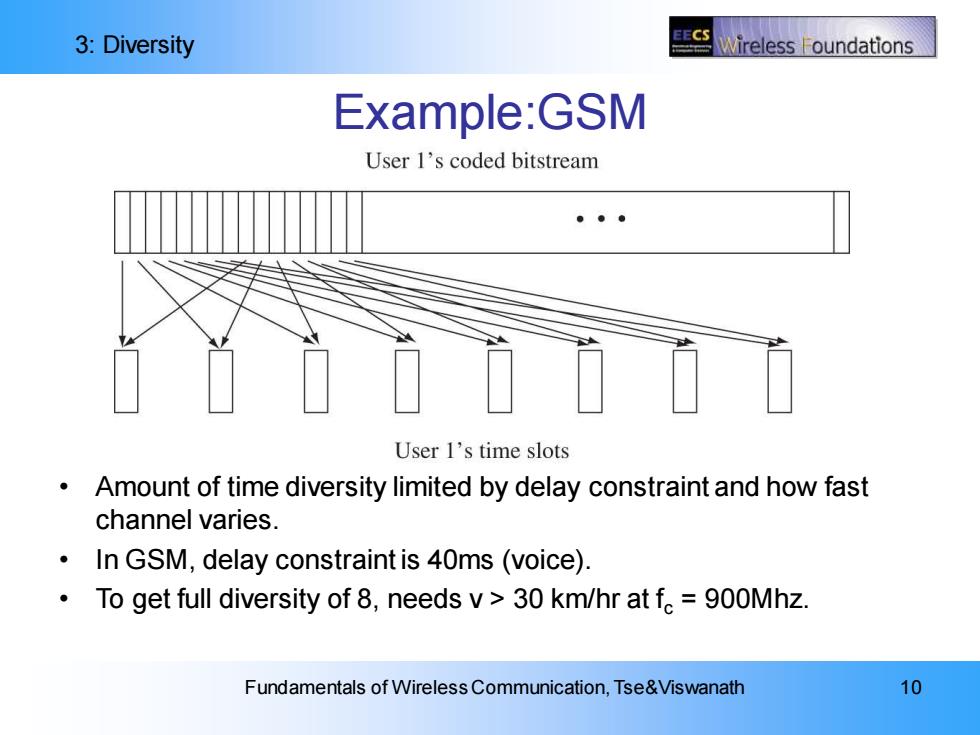
3:Diversity Wireless oundations Example:GSM User 1's coded bitstream User 1's time slots Amount of time diversity limited by delay constraint and how fast channel varies. In GSM,delay constraint is 40ms(voice). To get full diversity of 8,needs v>30 km/hr at fc=900Mhz. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 10
3: Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 10 Example:GSM • Amount of time diversity limited by delay constraint and how fast channel varies. • In GSM, delay constraint is 40ms (voice). • To get full diversity of 8, needs v > 30 km/hr at fc = 900Mhz