
ECS Vireless oundations 8.MIMO II:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 1
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 1 8. MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures
8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures EECS Wireless oundations Outline Transceiver architectures for fast fading (V-BLAST family) Transceiver architecture for slow fading (D-BLAST) Multiple antennas in networks:SDMA Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 2
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 2 Outline • Transceiver architectures for fast fading (V-BLAST family) • Transceiver architecture for slow fading (D-BLAST) • Multiple antennas in networks: SDMA
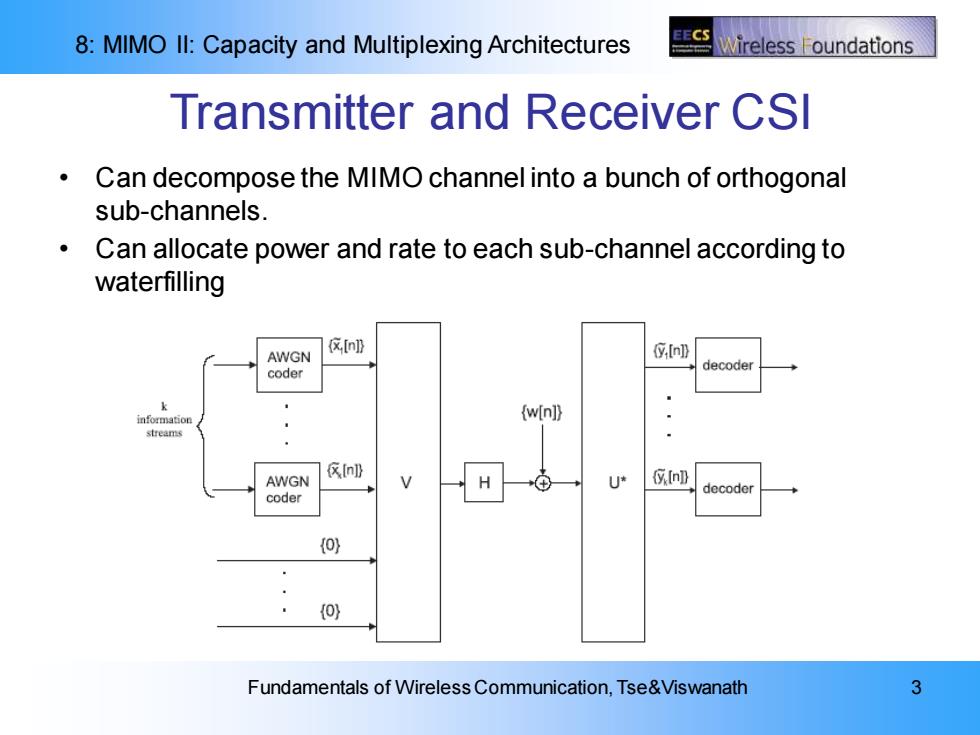
8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures ECS Nireless oundations Transmitter and Receiver CSI Can decompose the MIMO channel into a bunch of orthogonal sub-channels. Can allocate power and rate to each sub-channel according to waterfilling [n]) AWGN decode coder k information {wn》 streams 交nl AWGN U* In)) decoder coder (o) (o) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 3
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 3 Transmitter and Receiver CSI • Can decompose the MIMO channel into a bunch of orthogonal sub-channels. • Can allocate power and rate to each sub-channel according to waterfilling
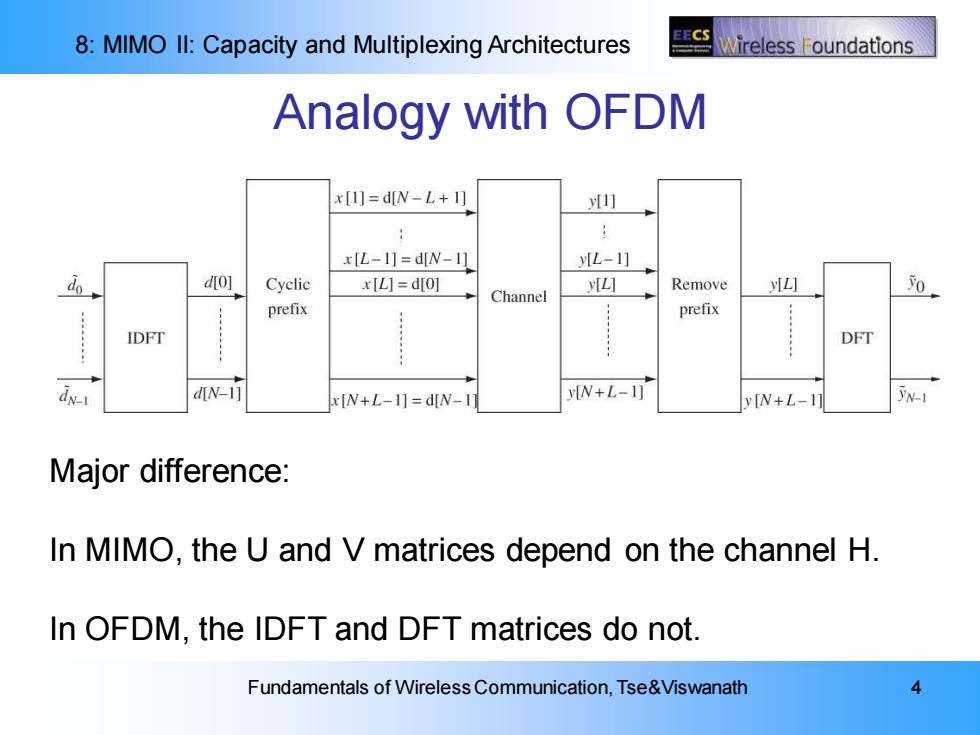
8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures ECS Wireless oundations Analogy with OFDM x[1]=d[N-L+1] 山 xL-1]=dW-1 yL-1] d0] Cyelic x[L]=d[o] ☑ Remove yILl Channel 0 prefix prefix IDFT DFT dy-1 dN-1] x[N+L-1]=d[N-1] y[N+L-1] [N+L-1 Major difference: In MIMO,the U and V matrices depend on the channel H. In OFDM,the IDFT and DFT matrices do not. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 4 Analogy with OFDM Major difference: In MIMO, the U and V matrices depend on the channel H. In OFDM, the IDFT and DFT matrices do not
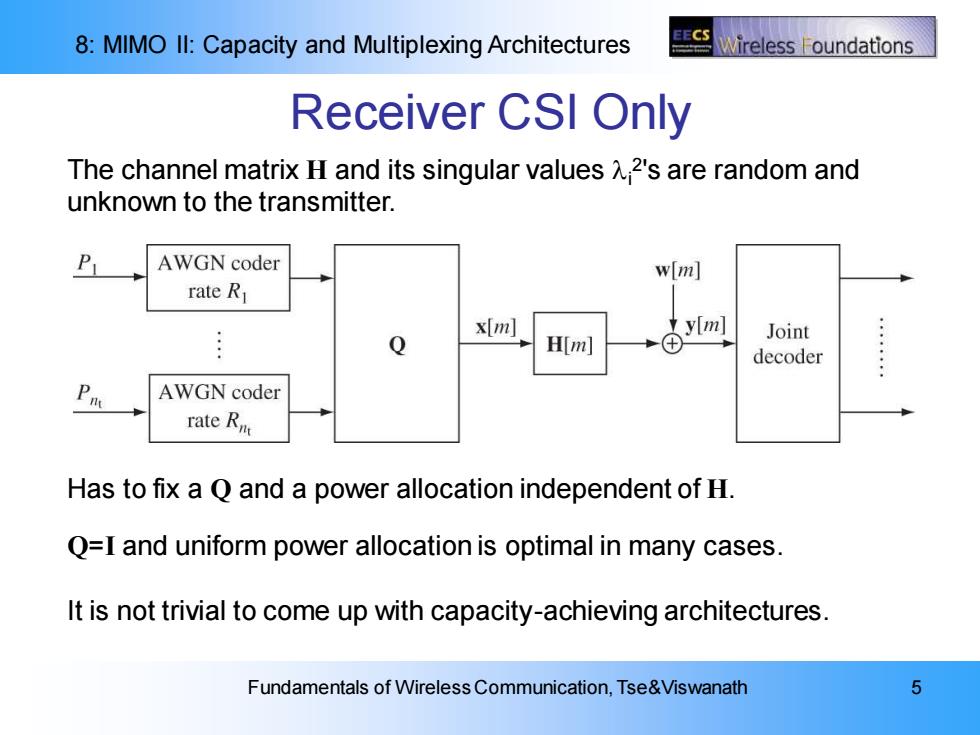
8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures vireless oundations Receiver CSI Only The channel matrix H and its singular values 2's are random and unknown to the transmitter. P AWGN coder w[m] rate R x[m] 文y[m] .... H(m] Joint decoder AWGN coder rate Rm Has to fix a Q and a power allocation independent of H. Q=I and uniform power allocation is optimal in many cases. It is not trivial to come up with capacity-achieving architectures. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 5
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 5 Receiver CSI Only The channel matrix H and its singular values i 2 's are random and unknown to the transmitter. Has to fix a Q and a power allocation independent of H. Q=I and uniform power allocation is optimal in many cases. It is not trivial to come up with capacity-achieving architectures