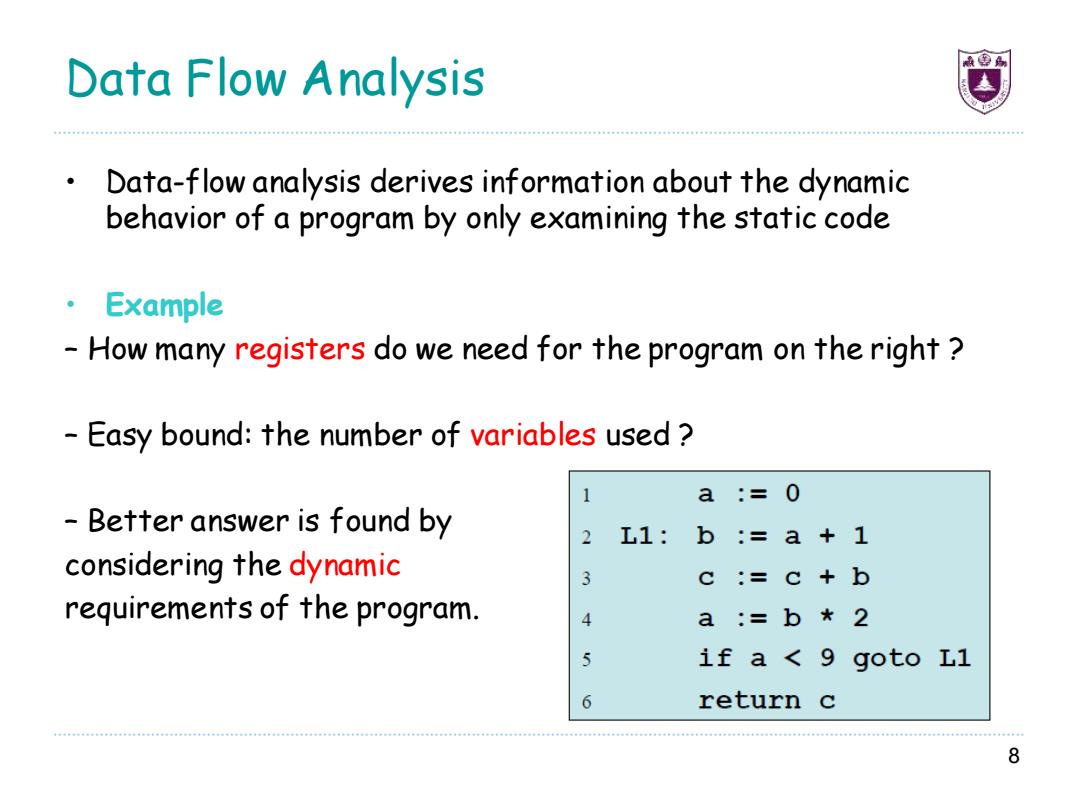
Data Flow Analysis Data-flow analysis derives information about the dynamic behavior of a program by only examining the static code Example How many registers do we need for the program on the right Easy bound:the number of variables used a:=0 Better answer is found by 2 L1:b:= :a+1 considering the dynamic 3 :=C+b requirements of the program. 4 a:=b*2 5 if a <9 goto Ll return c 8
Data Flow Analysis • Data-flow analysis derives information about the dynamic behavior of a program by only examining the static code • Example – How many registers do we need for the program on the right ? – Easy bound: the number of variables used ? – Better answer is found by considering the dynamic requirements of the program. 8

Basic Techniques Basic Approaches A simple way to perform data-flow analysis of programs is to set up data-flow equations for each node of the control flow graph and solve them by repeatedly calculating the output from the input locally at each node until the whole system stabilizes,i.e.,it reaches a fixpoint. The above general approach was developed by Gary Kildall while teaching at the Naval Postgraduate School 9
Basic Techniques Basic Approaches A simple way to perform data-flow analysis of programs is to set up data-flow equations for each node of the control flow graph and solve them by repeatedly calculating the output from the input locally at each node until the whole system stabilizes, i.e., it reaches a fixpoint. The above general approach was developed by Gary Kildall while teaching at the Naval Postgraduate School 9

Control Flow Graphs (CFGs) ·Simplification For now,we will use CFG's in which nodes represent program statements rather than basic blocks Example a=0 1 a:=0 2b=a+1 2 L1:b:= a+1 Y 3 c= c+b 3 c :=c+b V 4 a:=b*2 4a=b*2 5 if a <9 goto Ll 7 5 a<9 6 return c No Yes 6 return c 10
Control Flow Graphs (CFGs) • Simplification – For now, we will use CFG’s in which nodes represent program statements rather than basic blocks 10

At Different Program Points At Different Program Points Which assignment statements produced value of variable at this point? Which variables contain values that are no longer used after this program point? What is the range of possible values of variable at this program point? 11
At Different Program Points • At Different Program Points ➢ Which assignment statements produced value of variable at this point? ➢ Which variables contain values that are no longer used after this program point? ➢ What is the range of possible values of variable at this program point? ➢ …… 11
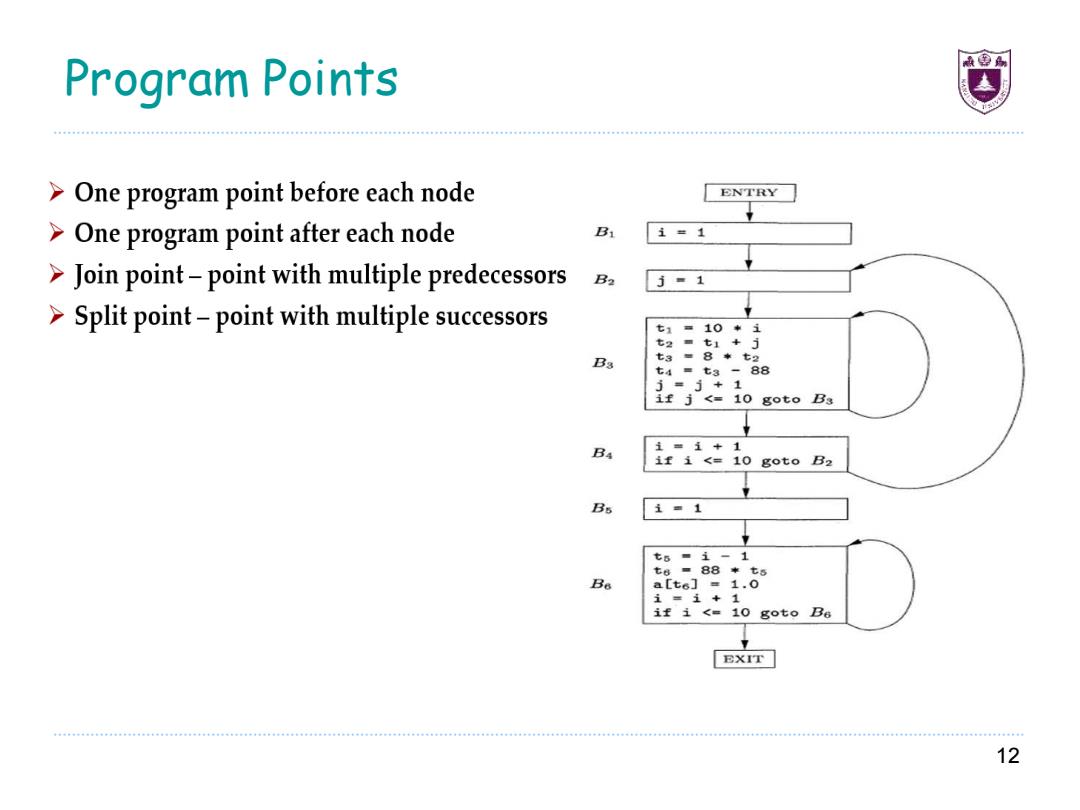
Program Points >One program point before each node ENTRY >One program point after each node B 1=1 >Join point-point with multiple predecessors B2 j=1 >Split point-point with multiple successors 七1=10*1 七2■ ti+j t3■8*七2 t4=t3 -88 j=j+1 if j<=10 goto Ba B4 1=1+1 1f1<=10got0B2 Bs 1=1 t5■1-1 =88*七5 a[t6]=1.0 1=i+1 if i <10 goto Be EXIT 12
Program Points 12