
NANJING UNIVERSITY Timed Automata
Timed Automata
效绵鼎 Aim of the Lecture knowledge of a basic formalism for modeling timed systems basic understanding of verification algorithms for timed systems (useful for practical modeling and verification)
Aim of the Lecture ◼ knowledge of a basic formalism for modeling timed systems ◼ basic understanding of verification algorithms for timed systems (useful for practical modeling and verification)
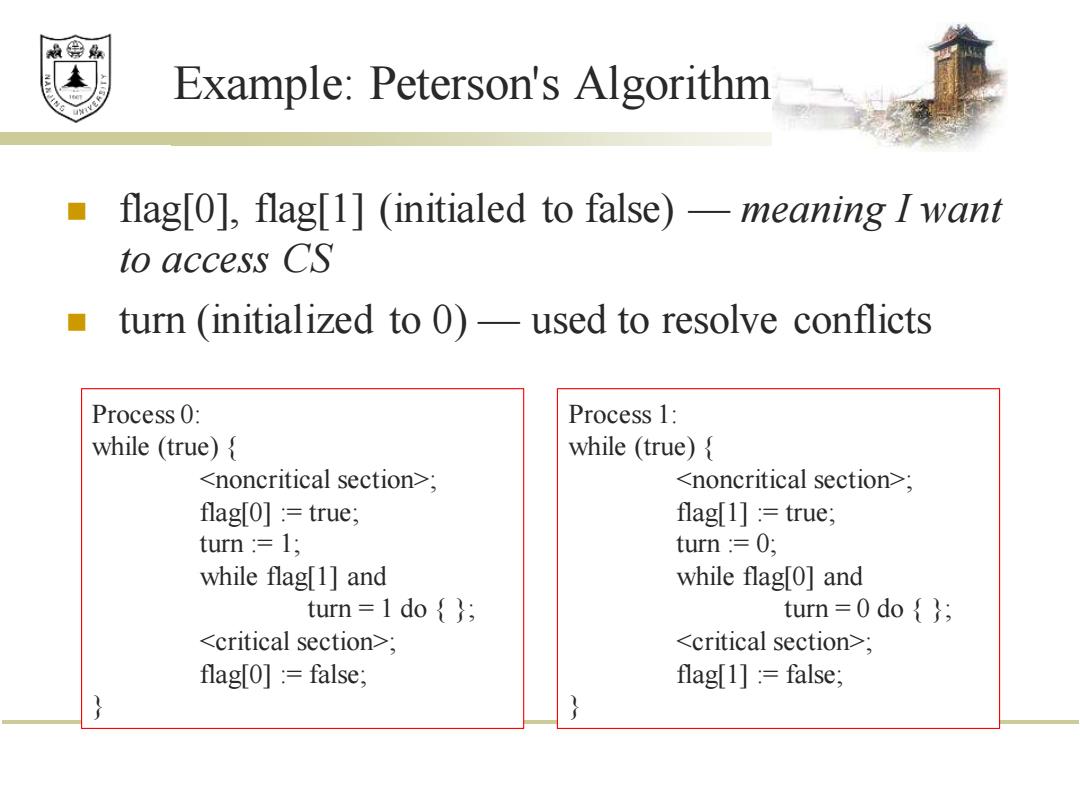
效绵鼎 Example:Peterson's Algorithm flag[0],flag[1](initialed to false)-meaning I want to access CS turn (initialized to 0)-used to resolve conflicts Process 0: Process 1: while (true){ while (true){ <noncritical section>; <noncritical section>; flag[0]:true; flag[1]:true; turn :1; turn :0; while flag[1]and while flag[0]and turn =1 do {} turn =0 do; <critical section>; <critical section>; flag[o]:false; flag[1]:false;
Example: Peterson's Algorithm ◼ flag[0], flag[1] (initialed to false) — meaning I want to access CS ◼ turn (initialized to 0) — used to resolve conflicts Process 0: while (true) { <noncritical section>; flag[0] := true; turn := 1; while flag[1] and turn = 1 do { }; <critical section>; flag[0] := false; } Process 1: while (true) { <noncritical section>; flag[1] := true; turn := 0; while flag[0] and turn = 0 do { }; <critical section>; flag[1] := false; }
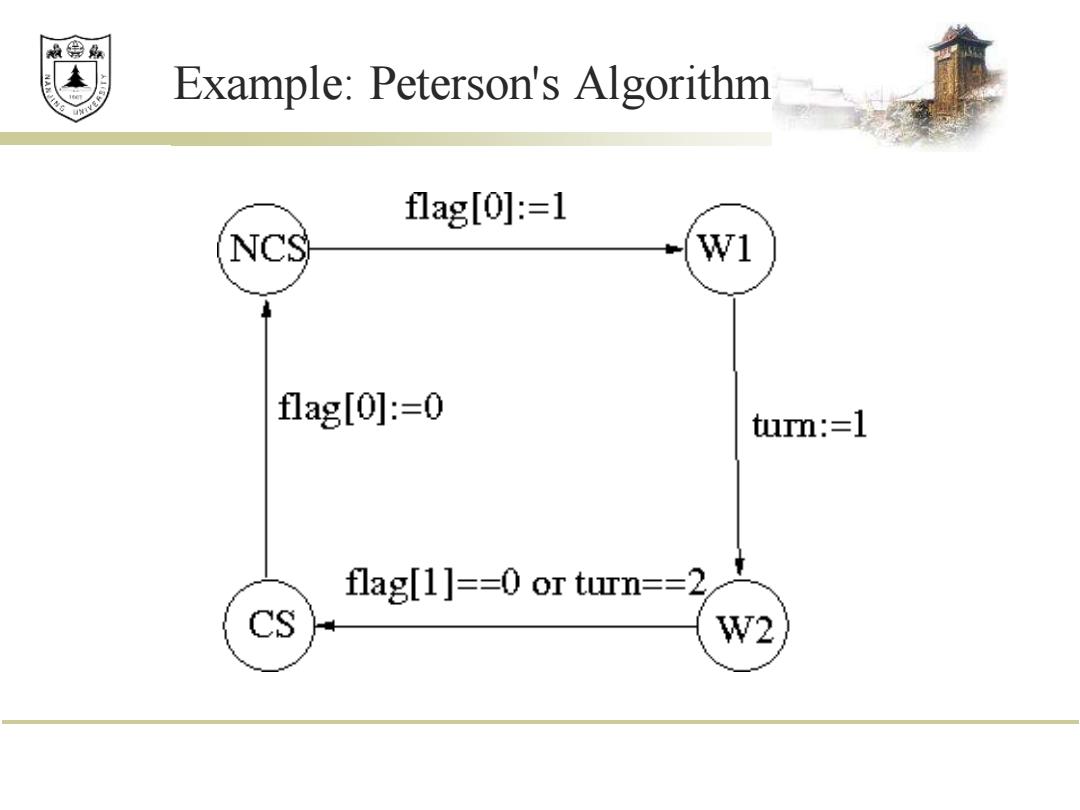
赖绵县 Example:Peterson's Algorithm flag[0]:=1 NCS w1 flag[0]小:=0 turn:=1 flag[1]==0 or turn==2 CS W2
Example: Peterson's Algorithm
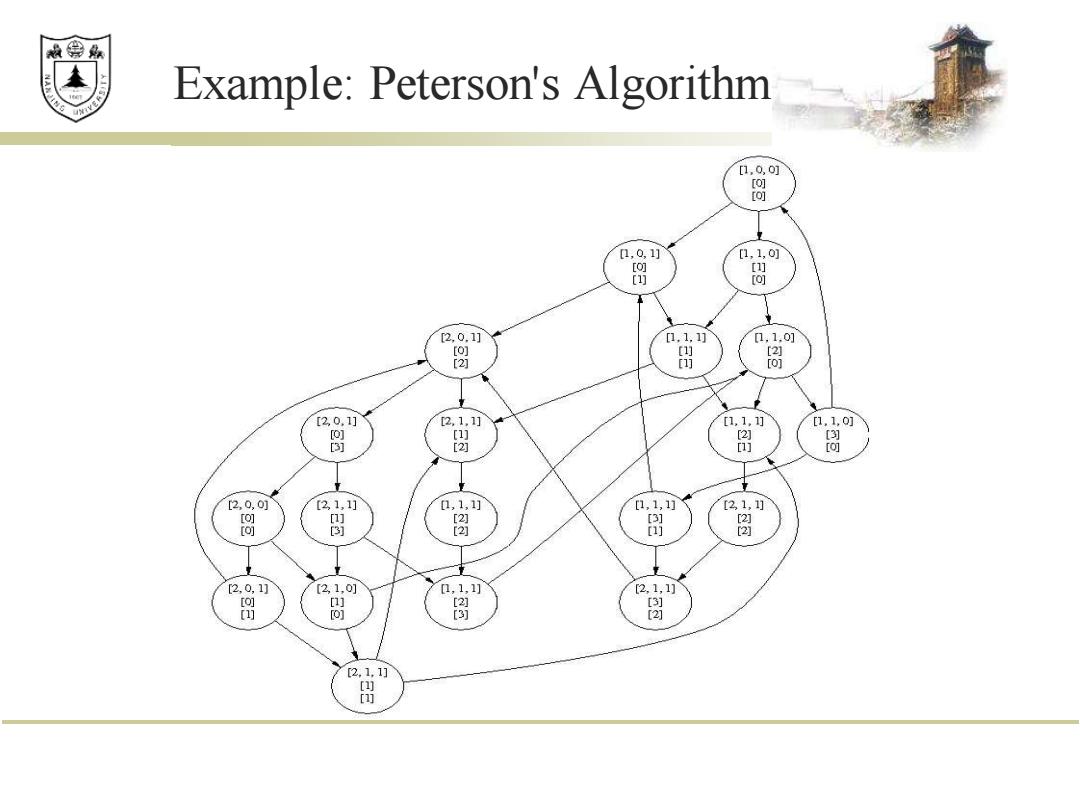
效绵鼎 Example:Peterson's Algorithm [1.0,0j [o] [o] 0,0,1] 1,1,0 [ [ [) [o] 2,0.1] [1,1,1 1,1.0] [O] [ [ [2] n [o] [2,0.1] 2,1.1] [1,1,1] [1,1,] [2 3) [3 [2 j [2,0,0j [2,1,1] 1,1,1] [1,1,1] 2,1,1] [o] [2 3 图 2 [20,1] [2,1,0] 1,1,1] [2,1,1 [o] [] [2☒ [ ] [o] [3) 2] [2,1,1] [ [
Example: Peterson's Algorithm