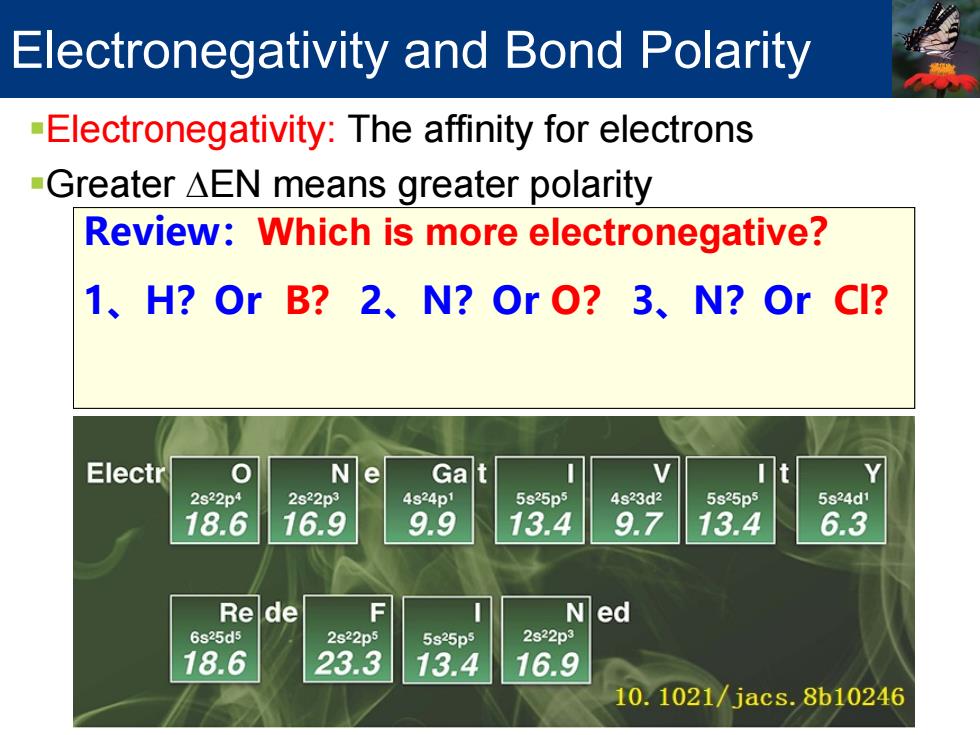
Electronegativity and Bond Polarity -Electronegativity:The affinity for electrons -Greater AEN means greater polarity Review:Which is more electronegative? 1、H?OrB?2、N?OrO?3、N?OrCI? Electr 0 Ne Gat 2s22p4 2s22p3 4s24p1 5s25p5 4s23d2 5s25p5 5s24d1 18.6 16.9 9.9 13.4 9.7 13.4 6.3 Rede F Ned 6s25d5 2s22p5 5s25p5 2s22p3 18.6 23.3 13.4 16.9 10.1021/jacs.8b10246
Electronegativity: H: 2.1 B: 2.0 C: 2.5 N: 3.0 O: 3.5 F: 4.0 Cl: 3.0 Br: 2.8 I: 2.5 Li: 1.0 Mg: 1.2 Review:Which is more electronegative? 1、H?Or B? 2、N?Or O? 3、N?Or Cl? Electronegativity and Bond Polarity Electronegativity: The affinity for electrons Greater ∆EN means greater polarity

Electronegativity and Bond Polarity 电负性 元素周期表第三维度,衡量不同原子吸引电子的强度; 定义 分子中原子吸引电子的能力(19世纪瑞典永斯~贝采利鸟斯Jòns Jacob B erzelius及美国莱纳斯•鲍林Linus Pauling) √电子亲合性和第一电离势的平均值(同期,诺贝尔化学奖得主罗伯特·马 利肯Robert Mulliken) √电负性是费米能量的负值(化学家Robert Parr) ·问题 √标度只对周期表中部分元素适用;预言化学反应或键极性时偶尔失效。 新定义和标度 √价电子平均构型能(M.Rahm副教授2019.2;诺奖得主R.Hoffmann19981) https://pubs.acs.org.ccindex.cn/doi/pdf/10.1021/jacs.8b10246
电负性 元素周期表第三维度,衡量不同原子吸引电子的强度; 定义 分子中原子吸引电子的能力(19世纪瑞典永斯•贝采利乌斯Jöns Jacob B erzelius及美国莱纳斯•鲍林Linus Pauling) 电子亲合性和第一电离势的平均值(同期,诺贝尔化学奖得主罗伯特•马 利肯Robert Mulliken) 电负性是费米能量的负值(化学家Robert Parr) 问题 标度只对周期表中部分元素适用;预言化学反应或键极性时偶尔失效。 新定义和标度 价电子平均构型能(M.Rahm副教授2019.2;诺奖得主R. Hoffmann1981) https://pubs.acs.org.ccindex.cn/doi/pdf/10.1021/jacs.8b10246 Electronegativity and Bond Polarity

Electronegativity and Bond Types Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by less than 0.5 are nonpolar covalent Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by 0.5 to 2.0 are polar covalent Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by more than 2.0 are largely ionic Carbon hydrogen bonds are nonpolar.Bonds between carbon(EN 2.5)and more electronegative elements,such as oxygen(EN 3.5)and nitrogen (EN 3.0)are polar covalent bonds with the bonding electrons drawn towards the more electronegative atoms
Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by less than 0.5 are nonpolar covalent Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by 0.5 to 2.0 are polar covalent Bonds between atoms whose electronegativities differ by more than 2.0 are largely ionic Carbon hydrogen bonds are nonpolar. Bonds between carbon (EN = 2.5) and more electronegative elements, such as oxygen (EN = 3.5) and nitrogen (EN = 3.0) are polar covalent bonds with the bonding electrons drawn towards the more electronegative atoms Electronegativity and Bond Types
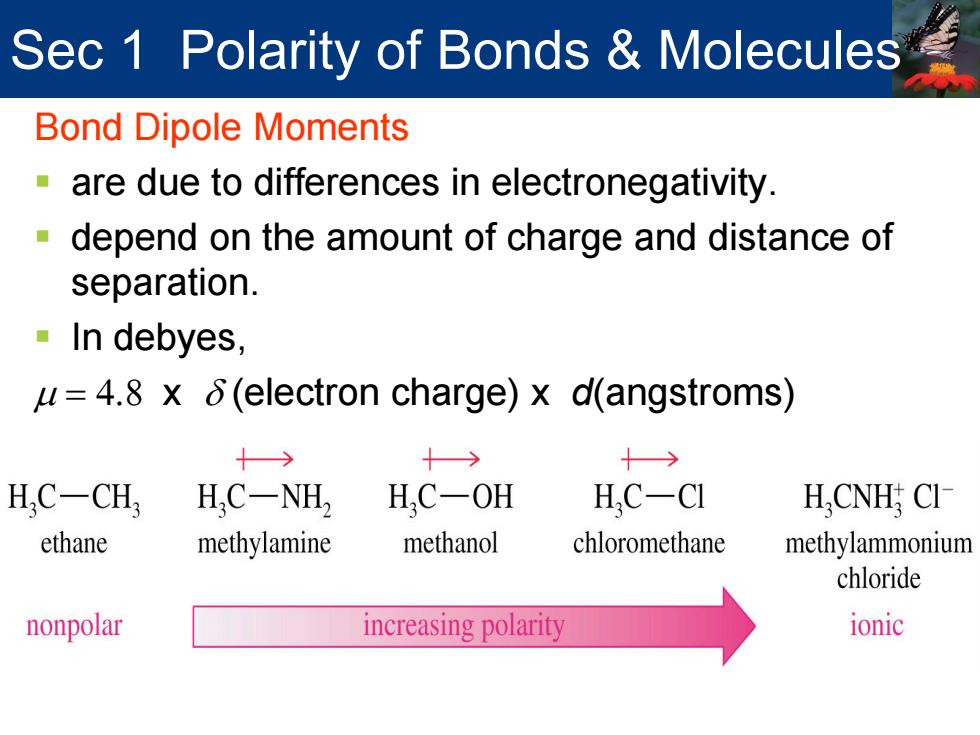
Sec 1 Polarity of Bonds Molecules Bond Dipole Moments are due to differences in electronegativity. -depend on the amount of charge and distance of separation. In debyes, u=4.8 x 6(electron charge)x d(angstroms) 十→ 十→ H.C-CH, H,C-NH2 H,C-OH H.C-CI H,CNH CI ethane methylamine methanol chloromethane methylammonium chloride nonpolar increasing polarity ionic
Sec 1 Polarity of Bonds & Molecules Bond Dipole Moments are due to differences in electronegativity. depend on the amount of charge and distance of separation. In debyes, µ = 4.8 x δ (electron charge) x d(angstroms)
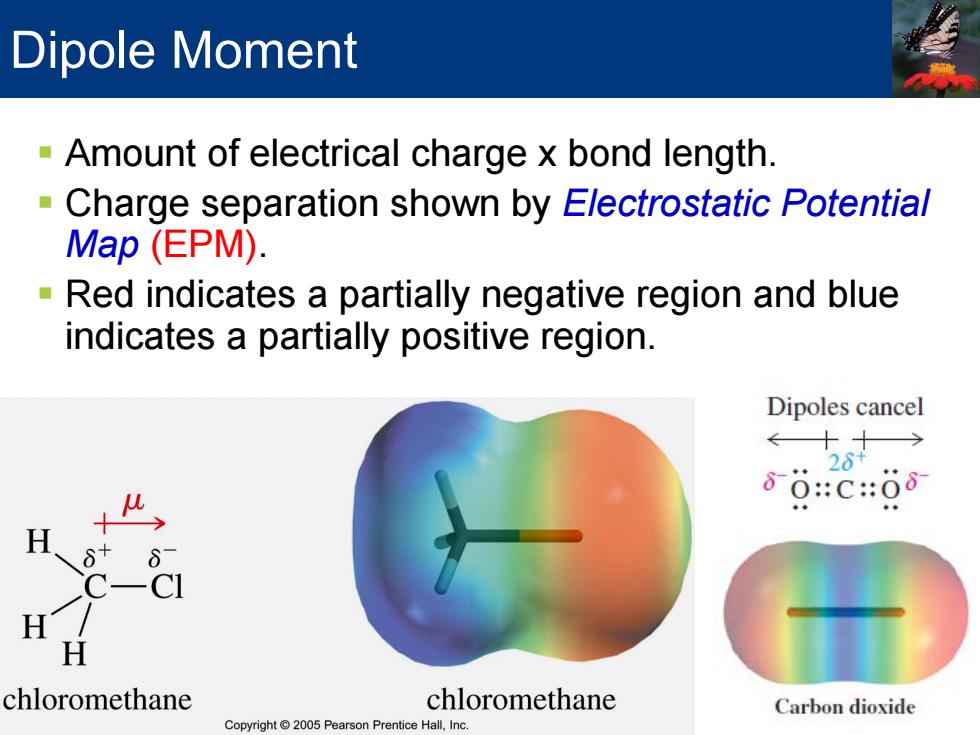
Dipole Moment Amount of electrical charge x bond length. -Charge separation shown by Electrostatic Potential Map (EPM). Red indicates a partially negative region and blue indicates a partially positive region. Dipoles cancel ←十十→ 26+ 80:c:08 H H chlo omethane chloromethane Carbon dioxide Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Dipole Moment Amount of electrical charge x bond length. Charge separation shown by Electrostatic Potential Map (EPM). Red indicates a partially negative region and blue indicates a partially positive region