
Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications,3r Edition John McMurry Chapter 2 Polar covalent Bonds;acids and Bases Understanding organic and biological chemistry means knowing not just what happens but also why and how it happens at the molecular level. By Junru Wang College of Chemistry and Pharmacy Room C206,Science Building Tel:15109273921;Email:wangjr07@163.com
By Junru Wang College of Chemistry and Pharmacy Room C206, Science Building Tel: 15109273921; Email: wangjr07@163.com Chapter 2 Polar covalent Bonds; acids and Bases Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3rd Edition John McMurry Understanding organic and biological chemistry means knowing not just what happens but also why and how it happens at the molecular level
Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications,3r Edition John McMurry Chapter 2 Polar covalent Bonds;acids and Bases Homework:2-2 (P31),2-6, 2-22P58d)2-26,2-34,2-38 Key Notes Electronegativity,Dipole Moments,Formal Charges Resonance,Acids and Bases
Chapter 2 Polar covalent Bonds; acids and Bases Organic Chemistry with Biological Applications, 3rd Edition John McMurry Key Notes Electronegativity , Dipole Moments, Formal Charges Resonance, Acids and Bases Homework: 2-2 (P31),2-6, 2-22(P58d), 2-26,2-34,2-38
Main Contents Polarity of Bonds Molecules √Electronegativity √Dipole Moments ☐Formal Charges ResonanceResonance Forms ■Acids and Bases The Bronsted-Lowry Definition √The Lewis Definition Noncovalent Interactions Between Molecules
Main Contents Polarity of Bonds & Molecules Electronegativity Dipole Moments Formal Charges Resonance & Resonance Forms Acids and Bases The Brønsted–Lowry Definition The Lewis Definition Noncovalent Interactions Between Molecules
Sec 1 Polarity of Bonds Molecules Chemical bonds lonic bonds Bond in sodium chloride is ionic -Sodium transfers an electron to chlorine to give Na*and CI lons held together by electrostatic attractions between unlike charges Nonpolar Covalent bonds Two electrons are shared equally by the two bonding atoms Carbon-carbon bond in ethane -Symmetrical electron distribution in the bond Most bonds are neither fully ionic or covalent
Chemical bonds Ionic bonds Bond in sodium chloride is ionic Sodium transfers an electron to chlorine to give Na+ and Cl- Ions held together by electrostatic attractions between unlike charges Nonpolar Covalent bonds Two electrons are shared equally by the two bonding atoms Carbon-carbon bond in ethane Symmetrical electron distribution in the bond Most bonds are neither fully ionic or covalent ! Sec 1 Polarity of Bonds & Molecules
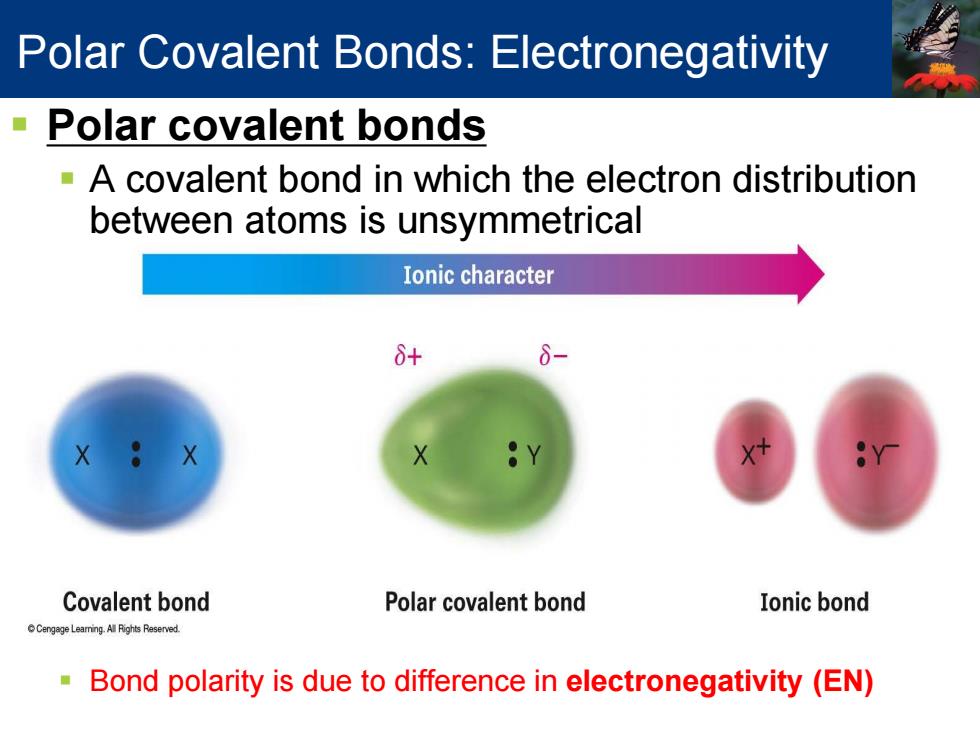
Polar Covalent Bonds:Electronegativity Polar covalent bonds -A covalent bond in which the electron distribution between atoms is unsymmetrical Ionic character 8+ Covalent bond Polar covalent bond Ionic bond Cengage Leaming.Al Rights Reserved. Bond polarity is due to difference in electronegativity (EN)
Polar covalent bonds A covalent bond in which the electron distribution between atoms is unsymmetrical Bond polarity is due to difference in electronegativity (EN) Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity