
The Offshoring Decision:Total Cost ■ Many companies have taken advantage of cost reduction through offshoring However,the benefits of offshoring to low-cost countries to be far less than anticipated. The reason: focusing exclusively on unit cost rather than total cost when making the offshoring decision ignoring critical risk factors SEIEE AU406 6-6
+ - SEIEE AU406 Many companies have taken advantage of cost reduction through offshoring However, the benefits of offshoring to low-cost countries to be far less than anticipated. The reason: focusing exclusively on unit cost rather than total cost when making the offshoring decision ignoring critical risk factors 6-6 The Offshoring Decision: Total Cost

The Offshoring Decision:Total Cost Dimensions to Consider When Evaluating Total Cost from Offshoring Performance Dimension Activity Impacting Performance Impact of Offshoring Order communication Order placement More difficult communication Supply chain visibility Scheduling and expediting Poorer visibility It is important to Raw material costs Sourcing of raw material Could go either way quantify these factors depending on raw material sourcing carefully when making Unit cost Production,quality (production and Labor/fixed costs decrease; transportation) quality may suffer the offshoring decision Freight costs Transportation modes and quantity Higher freight costs The benefits:unit cost Taxes and tariffs Border crossing Could go either way Supply lead time Order communication,supplier Lead time increase results reduction from low production scheduling,production time, in poorer forecasts and customs,transportation,receiving higher inventories labor and fixed costs; On-time delivery/lead Production,quality,customs, Poorer on-time delivery time uncertainty transportation,receiving and increased uncertainty tax advantages resulting in higher inventory and lower ▣almost every other product availability Minimum order quantity factor getting worse Production,transportation Larger minimum quantities increase inventory Product returns Quality Increased returns likely Inventories Lead times,inventory in transit and Increase production Working capital Inventories and financial reconciliation Increase Hidden costs Order communication,invoicing Higher hidden costs errors,managing exchange rate risk Stock-outs Ordering,production,transportation Increase with poorer visibility 6-7
+ - SEIEE AU406 6-7 The Offshoring Decision: Total Cost It is important to quantify these factors carefully when making the offshoring decision The benefits: unit cost reduction from low labor and fixed costs; tax advantages almost every other factor getting worse

Risk Management in Global SCM Global supply chains today are subject to more risk factors than localized supply chains of the past. These risks include supply disruption,supply delays, demand fluctuations,price fluctuations,and exchange-rate fluctuations. Financial Crisis in 2008 SEIEE AU406 6-8
+ - SEIEE AU406 Global supply chains today are subject to more risk factors than localized supply chains of the past. These risks include supply disruption, supply delays, demand fluctuations, price fluctuations, and exchange-rate fluctuations. Financial Crisis in 2008 6-8 Risk Management in Global SCM
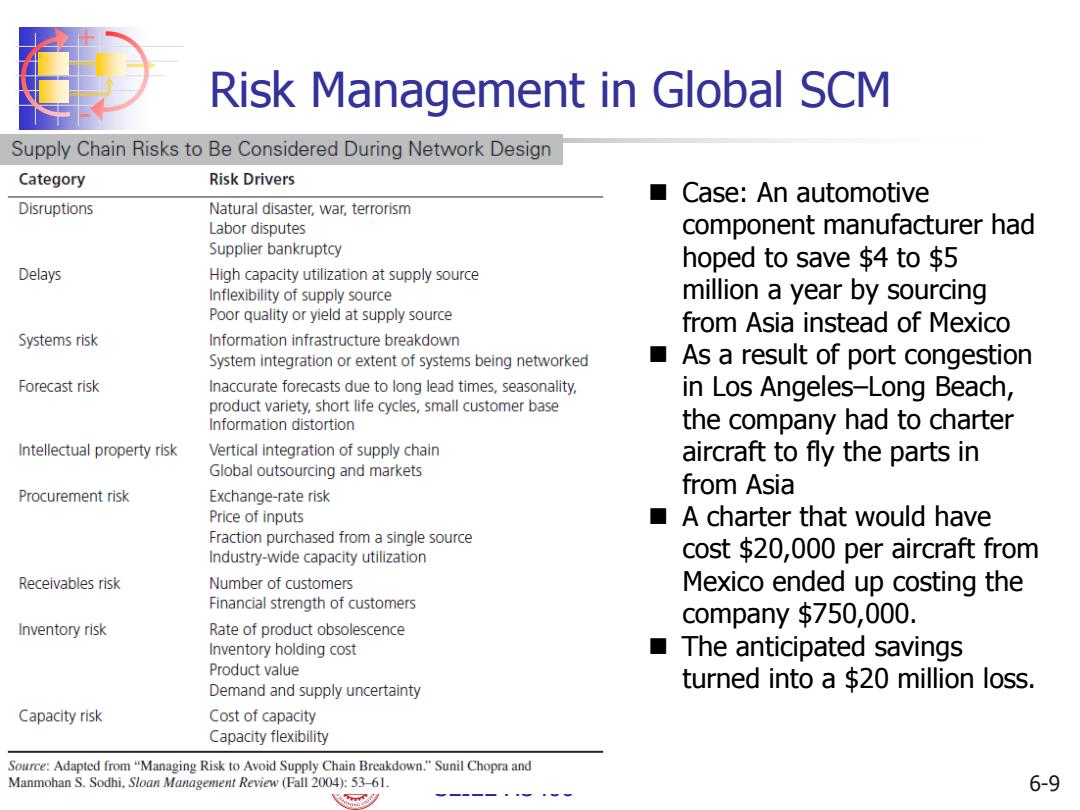
Risk Management in Global SCM Supply Chain Risks to Be Considered During Network Design Category Risk Drivers Case:An automotive Disruptions Natural disaster,war,terrorism Labor disputes component manufacturer had Supplier bankruptcy hoped to save $4 to $5 Delays High capacity utilization at supply source Inflexibility of supply source million a year by sourcing Poor quality or yield at supply source from Asia instead of Mexico Systems risk Information infrastructure breakdown System integration or extent of systems being networked As a result of port congestion Forecast risk Inaccurate forecasts due to long lead times,seasonality, in Los Angeles-Long Beach, product variety,short life cycles,small customer base Information distortion the company had to charter Intellectual property risk Vertical integration of supply chain aircraft to fly the parts in Global outsourcing and markets Procurement risk Exchange-rate risk from Asia Price of inputs A charter that would have Fraction purchased from a single source Industry-wide capacity utilization cost $20,000 per aircraft from Receivables risk Number of customers Mexico ended up costing the Financial strength of customers company $750,000. Inventory risk Rate of product obsolescence Inventory holding cost The anticipated savings Product value Demand and supply uncertainty turned into a $20 million loss. Capacity risk Cost of capacity Capacity flexibility Source:Adapted from "Managing Risk to Avoid Supply Chain Breakdown."Sunil Chopra and Manmohan S.Sodhi,Sloan Management Review (Fall 2004):53-61. 6-9 飞
+ - SEIEE AU406 Risk Management in Global SCM 6-9 Case: An automotive component manufacturer had hoped to save $4 to $5 million a year by sourcing from Asia instead of Mexico As a result of port congestion in Los Angeles–Long Beach, the company had to charter aircraft to fly the parts in from Asia A charter that would have cost $20,000 per aircraft from Mexico ended up costing the company $750,000. The anticipated savings turned into a $20 million loss

Risk Management in Global SCM Tailored Risk Mitigation Strategies During Network Design Risk Mitigation Strategy Tailored Strategies Increase capacity Focus on low-cost,decentralized capacity for predictable demand. Build centralized capacity for unpredictable demand.Increase decentralization as cost of capacity drops. Get redundant suppliers More redundant supply for high-volume products,less redundancy for low-volume products.Centralize redundancy for low-volume products in a few flexible suppliers. Increase responsiveness Favor cost over responsiveness for commodity products.Favor responsiveness over cost for short-life cycle products Increase inventory Decentralize inventory of predictable,lower value products. Centralize inventory of less predictable,higher value products. Increase flexibility Favor cost over flexibility for predictable,high-volume products. Favor flexibility for unpredictable,low-volume products.Centralize flexibility in a few locations if it is expensive. Pool or aggregate demand Increase aggregation as unpredictability grows. Increase source capability Prefer capability over cost for high-value,high-risk products.Favor cost over capability for low-value commodity products.Centralize high capability in flexible source if possible. Source:Adapted from "Managing Risk to Avoid Supply Chain Breakdown."Sunil Chopra and Manmohan S.Sodhi, Sloan Management Review (Fall 2004):53-61. SEIEE AU406 6-10
+ - SEIEE AU406 6-10 Risk Management in Global SCM