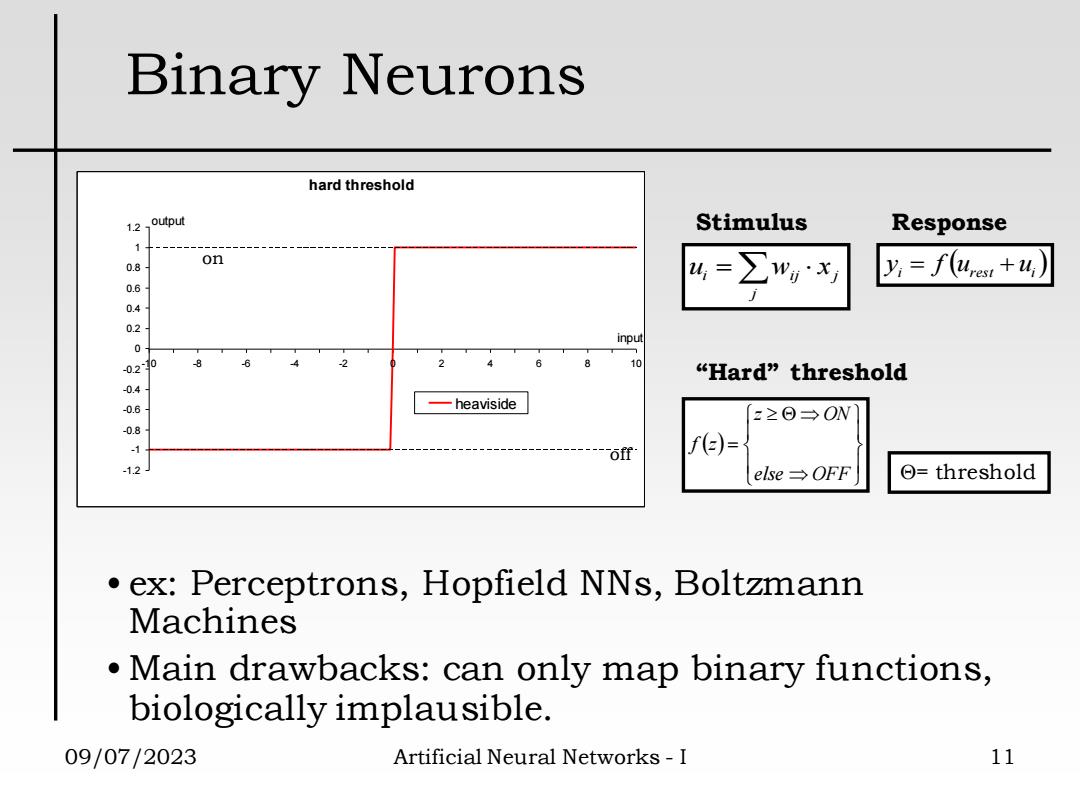
Binary Neurons hard threshold 1.2output Stimulus Response 0.8 on 4=∑wx y=f(ue1+4,) 0.6 0.2 input 020 10 “Hard”threshold 411 -heaviside z≥日→ON ōff f()= 12 ese→OFF O=threshold ex:Perceptrons,Hopfield NNs,Boltzmann Machines Main drawbacks:can only map binary functions, biologically implausible. 09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks-I 11
09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks - I 11 Binary Neurons ( ) = else OFF z ON f z “Hard” threshold = threshold hard threshold -1.2 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 input output heaviside • ex: Perceptrons, Hopfield NNs, Boltzmann Machines • Main drawbacks: can only map binary functions, biologically implausible. off on = j i ij j u w x Stimulus ( ) i urest ui y = f + Response
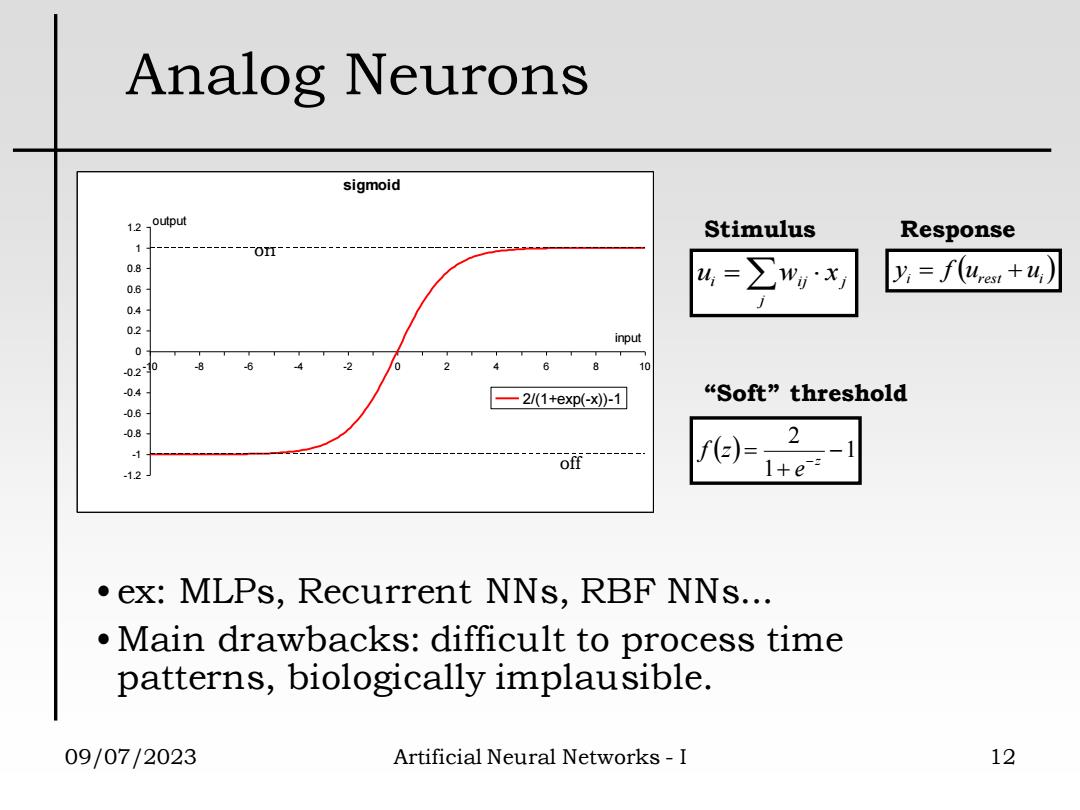
Analog Neurons sigmoid 12 output Stimulus Response 4= ∑wx y=f(u,e1+4) 04 input .10 6 8 10 8 2/(1+exp(-x)-1 “Soft”threshold 1 off f)= 2-1 -1.2 1+e: .ex:MLPs,Recurrent NNs,RBF NNs... Main drawbacks:difficult to process time patterns,biologically implausible. 09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks-I 12
09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks - I 12 Analog Neurons ( ) 1 1 2 − + = −z e f z “Soft” threshold sigmoid -1.2 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 input output 2/(1+exp(-x))-1 • ex: MLPs, Recurrent NNs, RBF NNs... •Main drawbacks: difficult to process time patterns, biologically implausible. off on = j i ij j u w x Stimulus ( ) i urest ui y = f + Response
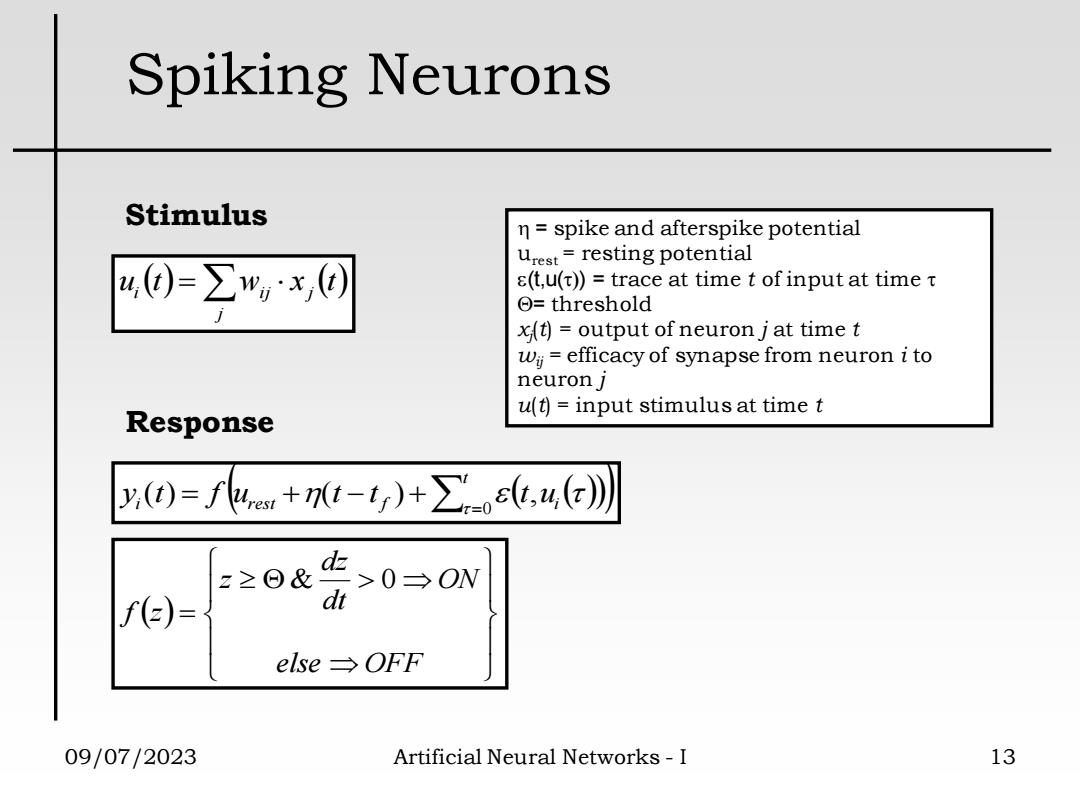
Spiking Neurons Stimulus n=spike and afterspike potential urest=resting potential u0=∑",x同 8(t,u(t))=trace at time t of input at timet ⊙=threshold x(t)=output of neuron j at time t wy=efficacy of synapse from neuron i to neuron j u(t)=input stimulus at time t Response y(0)=fke+7t-1)+∑st,4(女)川 z2⊙& >0→ON f)= dt else→OFF 09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks-I 13
09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks - I 13 Spiking Neurons ( ) = ( ) j i ij j u t w x t ( ( ( ))) = = + − + t i rest f ui y t f u t t t 0 ( ) ( ) , ( ) = else OFF ON dt dz z f z & 0 = spike and afterspike potential urest = resting potential (t,u()) = trace at time t of input at time = threshold xj (t) = output of neuron j at time t wij = efficacy of synapse from neuron i to neuron j u(t) = input stimulus at time t Response Stimulus
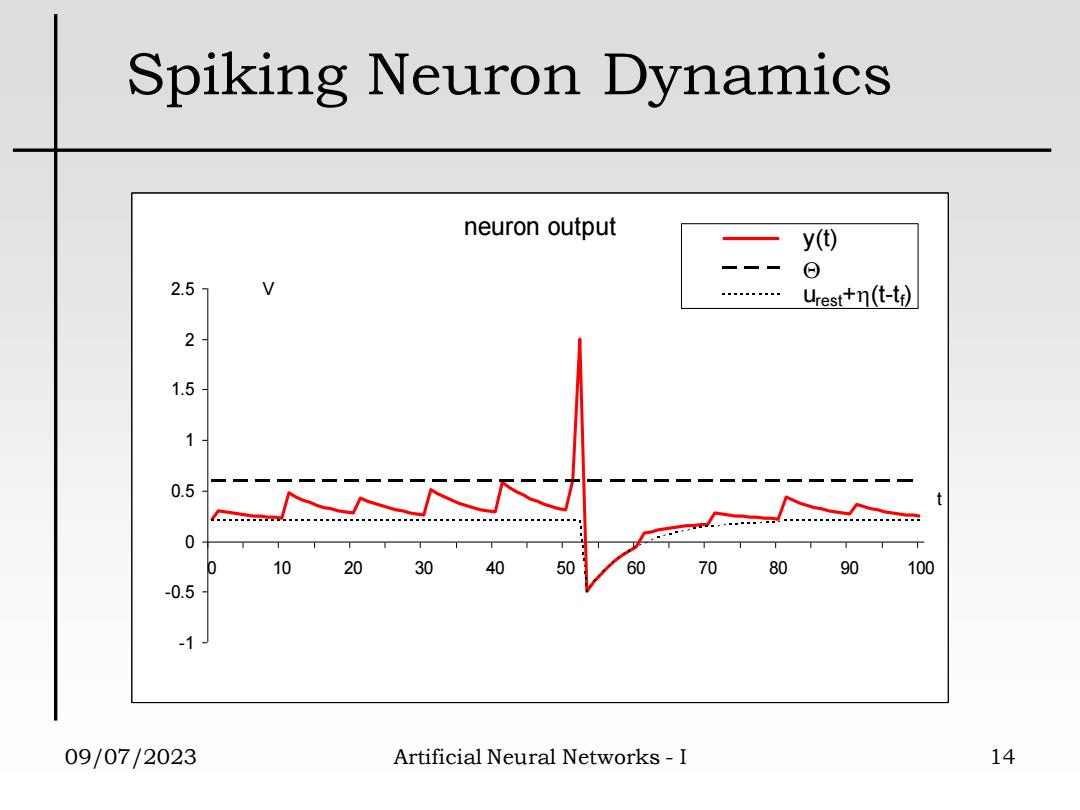
Spiking Neuron Dynamics neuron output y() Θ 2.57 V urest+n(t-t) 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 10 2030 40 50 60 70 8090 100 -0.5 -1 09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks-I 14
09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks - I 14 Spiking Neuron Dynamics neuron output - 1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 t V y(t) urest+(t-tf )

赫布律 加拿大心理学家Donald Hebb出版了《行为的组 织》一书,指出学习导致突触的联系强度和传 递效能的提高,即为“赫布律”。 在此基础上,人们提出了各种学习规则和算法, 以适应不同网络模型的需要。有效的学习算法, 使得神经网络能够通过连接权值的调整,构造 客观世界的内在表示,形成具有特色的信息处 理方法,信息存储和处理体现在网络的连接中。 09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks-I 15
09/07/2023 Artificial Neural Networks - I 15 赫布律 加拿大心理学家Donald Hebb出版了《行为的组 织》一书,指出学习导致突触的联系强度和传 递效能的提高,即为“赫布律” 。 在此基础上,人们提出了各种学习规则和算法, 以适应不同网络模型的需要。有效的学习算法, 使得神经网络能够通过连接权值的调整,构造 客观世界的内在表示,形成具有特色的信息处 理方法,信息存储和处理体现在网络的连接中