
先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Kinematic viscosity Also called "momentum diffusivity",is the ratio of the dynamic viscosity n to the density of the fluid p. anced Materials 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Kinematic viscosity Also called “momentum diffusivity”, is the ratio of the dynamic viscosity η to the density of the fluid ρ

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Newtonian fluids:A fluid that behaves according to Newton's law,with a viscosity that is independent of the stress,is said to be Newtonian.Gases, water and many common liquids can be considered Newtonian in ordinary conditions and contexts. Non-Newtonian fluids,a fluid significantly deviate from that law in some way or other.For example: Shear-thickening liquids,whose viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain. 。 Shear-thinning liquids,whose viscosity decreases with the rate of shear strain. ● Thixotropic liquids,that become less viscous over time when shaken,agitated, or otherwise stressed. Rheopectic liquids,that become more viscous over time when shaken, agitated,or otherwise stressed. Bingham plastics that behave as a solid at low stresses but flow as a viscous fluid at high stresses. 上海充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Newtonian fluids: A fluid that behaves according to Newton’s law, with a viscosity that is independent of the stress, is said to be Newtonian. Gases, water and many common liquids can be considered Newtonian in ordinary conditions and contexts. Non-Newtonian fluids, a fluid significantly deviate from that law in some way or other. For example: • Shear-thickening liquids, whose viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain. • Shear-thinning liquids, whose viscosity decreases with the rate of shear strain. • Thixotropic liquids, that become less viscous over time when shaken, agitated, or otherwise stressed. • Rheopectic liquids, that become more viscous over time when shaken, agitated, or otherwise stressed. • Bingham plastics that behave as a solid at low stresses but flow as a viscous fluid at high stresses. Viscosity of liquid metal

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Physically,viscosity can be expressed as: 2tokeT./k 3 where kg is Boltzmann constant, U is the internal bonding energy without external force. to is the vibration period of the atoms at equilibrium position 10-13s for liquid metal. 6 is the distance between atomic layers in liquid. nced Ma 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Physically, viscosity can be expressed as: where kB is Boltzmann constant, U is the internal bonding energy without external force. τ0 is the vibration period of the atoms at equilibrium position 10-13s for liquid metal. δ is the distance between atomic layers in liquid. U / k T 3 B 0 B e 2 k T = ⋅ δ τ η
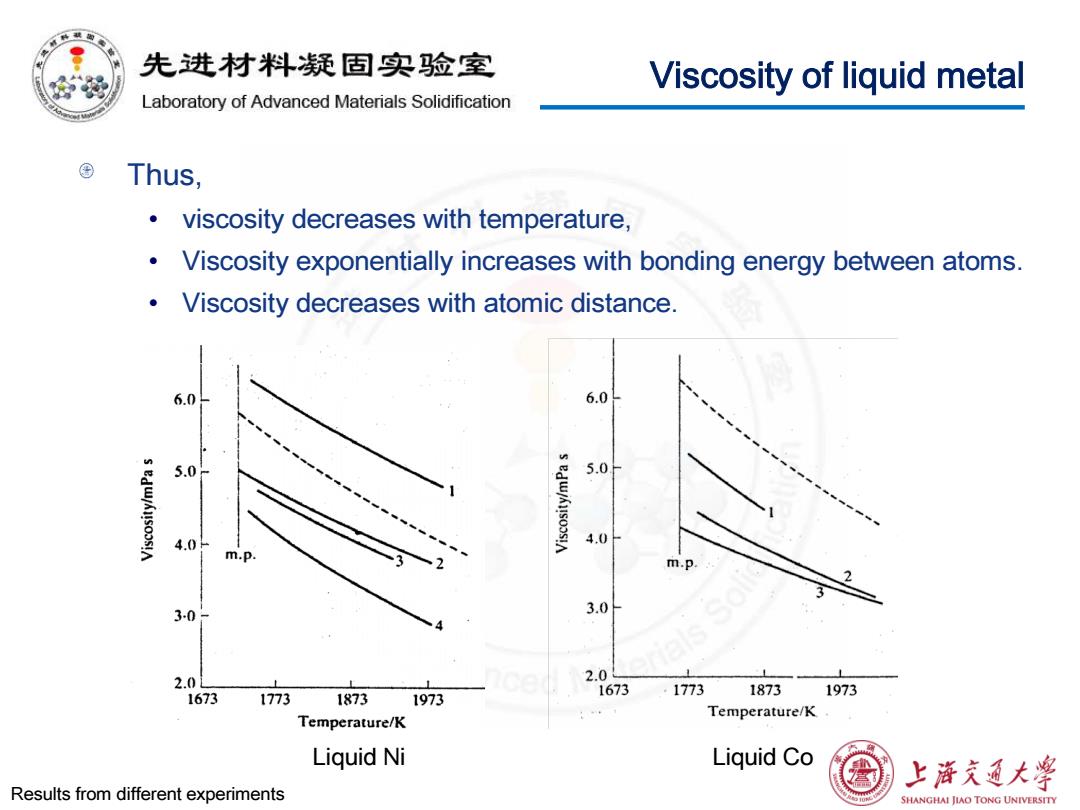
先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Thus, viscosity decreases with temperature, Viscosity exponentially increases with bonding energy between atoms. Viscosity decreases with atomic distance. 6.0 6.0 5.0 5.0 4.0- 4.0 m.p m.p. 3-0 3.0 2.0L 2. 1673 1773 1873 1673 1773 1873 1973 1973 Temperature/K Temperature/K Liquid Ni Liquid Co 上游文通大学 Results from different experiments SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Thus, • viscosity decreases with temperature, • Viscosity exponentially increases with bonding energy between atoms. • Viscosity decreases with atomic distance. Liquid Ni Liquid Co Results from different experiments

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Alloy composition effect on viscosity of alloys(Moelwyn-Hughes model,M-H model) 9=0xn+xm- Where y,and u,are the viscosity of pure element,x,and x2 are the mole fraction of the elements.R is the gas constant and /is the mixing enthalpy of two elements. vanced Mater 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Alloy composition effect on viscosity of alloys (Moelwyn-Hughes model, M-H model) Where μ1 and μ2 are the viscosity of pure element, x1 and x2 are the mole fraction of the elements. R is the gas constant and Hm is the mixing enthalpy of two elements. = + − RT H X X m η ( 1 η1 2 η2 ) 1 2