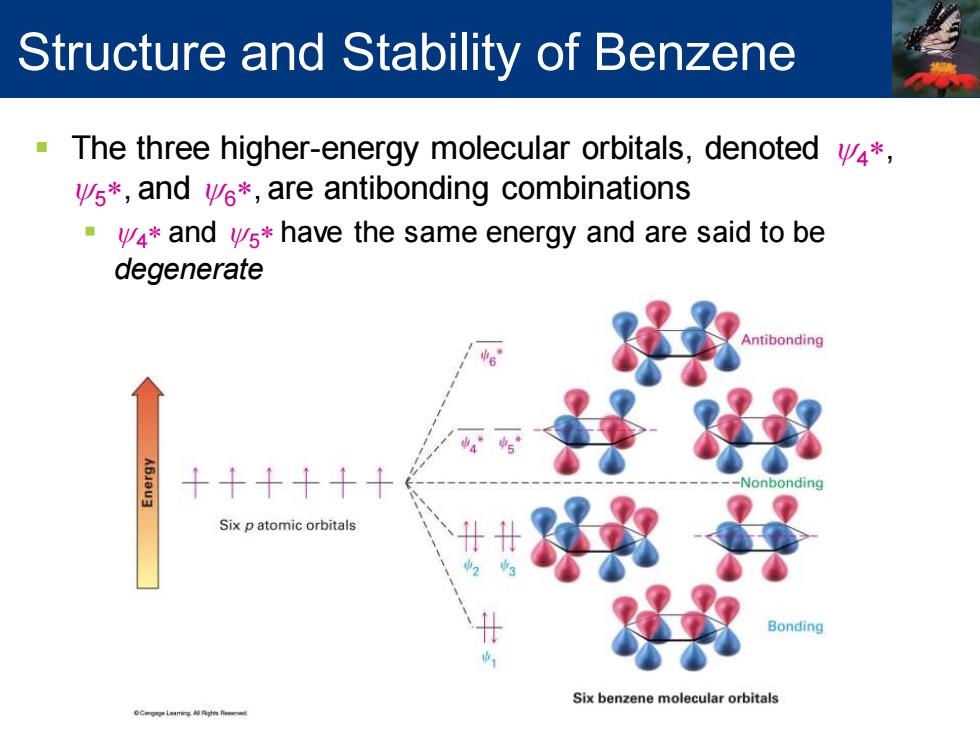
Structure and Stability of Benzene The three higher-energy molecular orbitals,denoted v4*, vs*,and ve*,are antibonding combinations 4*and vs*have the same energy and are said to be degenerate Antibonding 移 +++++ Six p atomic orbitals 好的泽 Bonding Six benzene molecular orbitals
▪ The three higher-energy molecular orbitals, denoted y4* , y5* , and y6* , are antibonding combinations ▪ y4* and y5* have the same energy and are said to be degenerate Structure and Stability of Benzene

Structure and Stability of Benzene ya and y4*have nodes passing through ring carbon atoms, therefore no z electron density on these carbons The six p electrons occupy the three bonding molecular orbitals and are delocalized over the entire conjugated system Six p atomic orbitals Bonding Six benzene molecular orbitals
▪ y3 and y4* have nodes passing through ring carbon atoms, therefore no p electron density on these carbons ▪ The six p electrons occupy the three bonding molecular orbitals and are delocalized over the entire conjugated system Structure and Stability of Benzene
9-3 Aromaticity and the Huckel 4n 2 Rule Benzene and other benzene-like aromatic molecules share similar characteristics: Benzene is cyclic and conjugated Benzene is unusually stable,it is 150 kJ/mol (36 kcal/mol) more stable than might be expected Benzene is planar and has the shape of a regular hexagon. All bond angles are 120,all carbon atoms are sp2- hybridized,and all carbon-carbon bond lengths are 139 pm Benzene undergoes substitution reactions that retain the cyclic conjugation rather than electrophilic addition reactions that would destroy the conjugation Benzene is a resonance hybrid whose structure is intermediate between two line-bond structures
Benzene and other benzene-like aromatic molecules share similar characteristics: ▪ Benzene is cyclic and conjugated ▪ Benzene is unusually stable, it is 150 kJ/mol (36 kcal/mol) more stable than might be expected ▪ Benzene is planar and has the shape of a regular hexagon. All bond angles are 120º, all carbon atoms are sp2 - hybridized, and all carbon-carbon bond lengths are 139 pm ▪ Benzene undergoes substitution reactions that retain the cyclic conjugation rather than electrophilic addition reactions that would destroy the conjugation ▪ Benzene is a resonance hybrid whose structure is intermediate between two line-bond structures 9-3 Aromaticity and the Hückel 4n + 2 Rule

Aromaticity and the Huckel 4n 2 Rule The Huckel 4n 2 rule -Theory devised in 1931 by the German physicist Erich Huckel A molecule is aromatic only if it has a planar, monocyclic system of conjugation and contains a total of 4n +2 zelectrons,where n is an integer(n=0,1, 2,3,…) Only molecules with 2,6,10,14,18,...zelectrons can be aromatic Molecules with 4n z electrons (4,8,12,16,...)can not be aromatic,said to be antiaromatic because delocalization of their zelectrons would lead to their destabilization
The Hückel 4n + 2 rule ▪ Theory devised in 1931 by the German physicist Erich Hückel ▪ A molecule is aromatic only if it has a planar, monocyclic system of conjugation and contains a total of 4n + 2 p electrons, where n is an integer (n = 0, 1, 2, 3,…) ▪ Only molecules with 2, 6, 10, 14, 18,… p electrons can be aromatic ▪ Molecules with 4n p electrons (4, 8, 12, 16,…) can not be aromatic, said to be antiaromatic because delocalization of their p electrons would lead to their destabilization Aromaticity and the Hückel 4n + 2 Rule
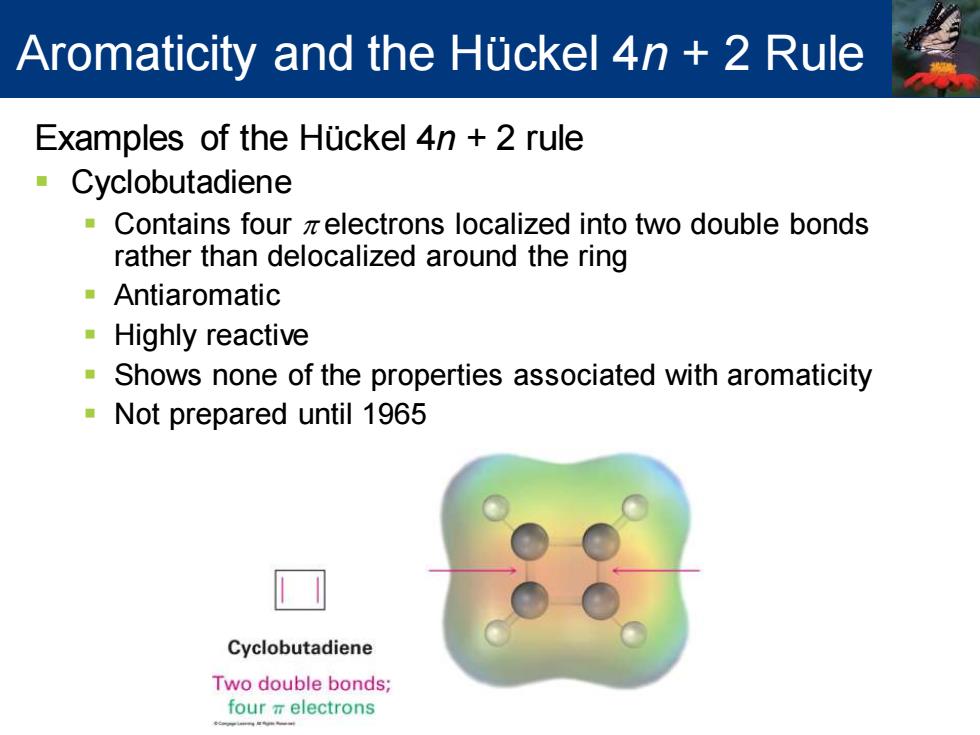
Aromaticity and the Huckel 4n 2 Rule Examples of the Huckel 4n 2 rule Cyclobutadiene Contains four zelectrons localized into two double bonds rather than delocalized around the ring Antiaromatic Highly reactive Shows none of the properties associated with aromaticity Not prepared until 1965 Cyclobutadiene Two double bonds; fourπelectrons
Examples of the Hückel 4n + 2 rule ▪ Cyclobutadiene ▪ Contains four p electrons localized into two double bonds rather than delocalized around the ring ▪ Antiaromatic ▪ Highly reactive ▪ Shows none of the properties associated with aromaticity ▪ Not prepared until 1965 Aromaticity and the Hückel 4n + 2 Rule