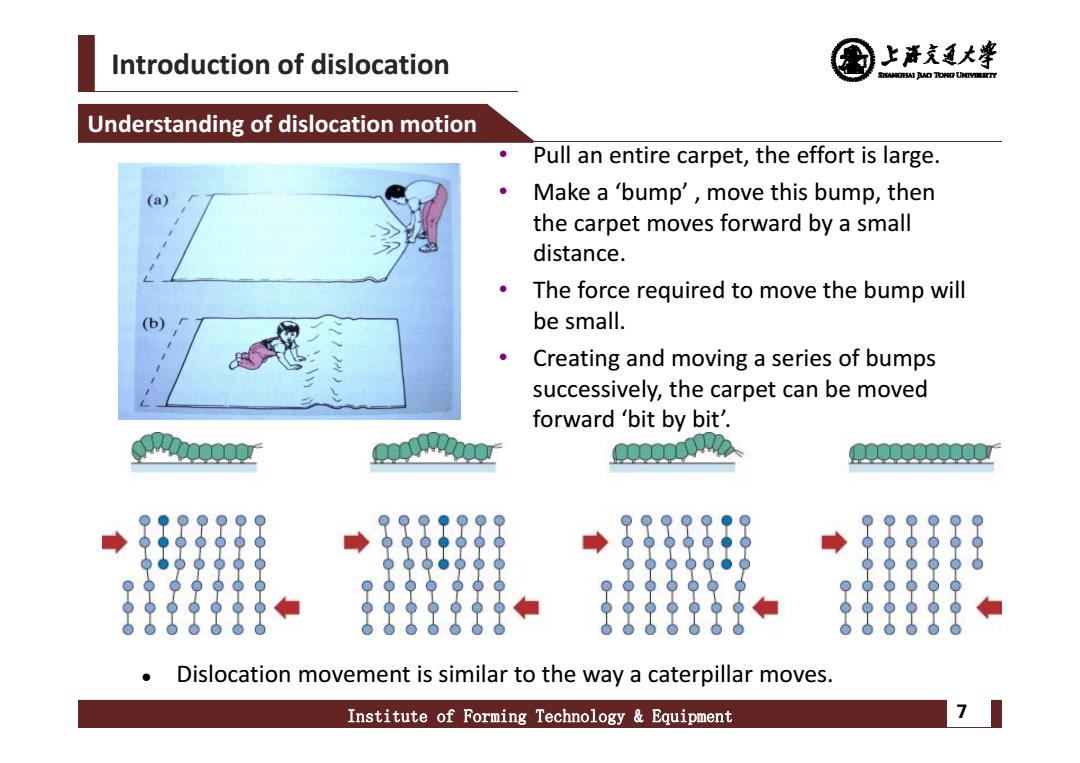
Introduction of dislocation 上清充通大学 SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Understanding of dislocation motion Pull an entire carpet,the effort is large. (a) Make a 'bump',move this bump,then the carpet moves forward by a small distance. The force required to move the bump will be small. Creating and moving a series of bumps successively,the carpet can be moved forward 'bit by bit'. Dislocation movement is similar to the way a caterpillar moves. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 7
Introduction of dislocation Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 7 Understanding of dislocation motion • Pull an entire carpet, the effort is large. • Make a ‘bump’ , move this bump, then the carpet moves forward by a small distance. • The force required to move the bump will be small. • Creating and moving a series of bumps successively, the carpet can be moved forward ‘bit by bit’. Dislocation movement is similar to the way a caterpillar moves
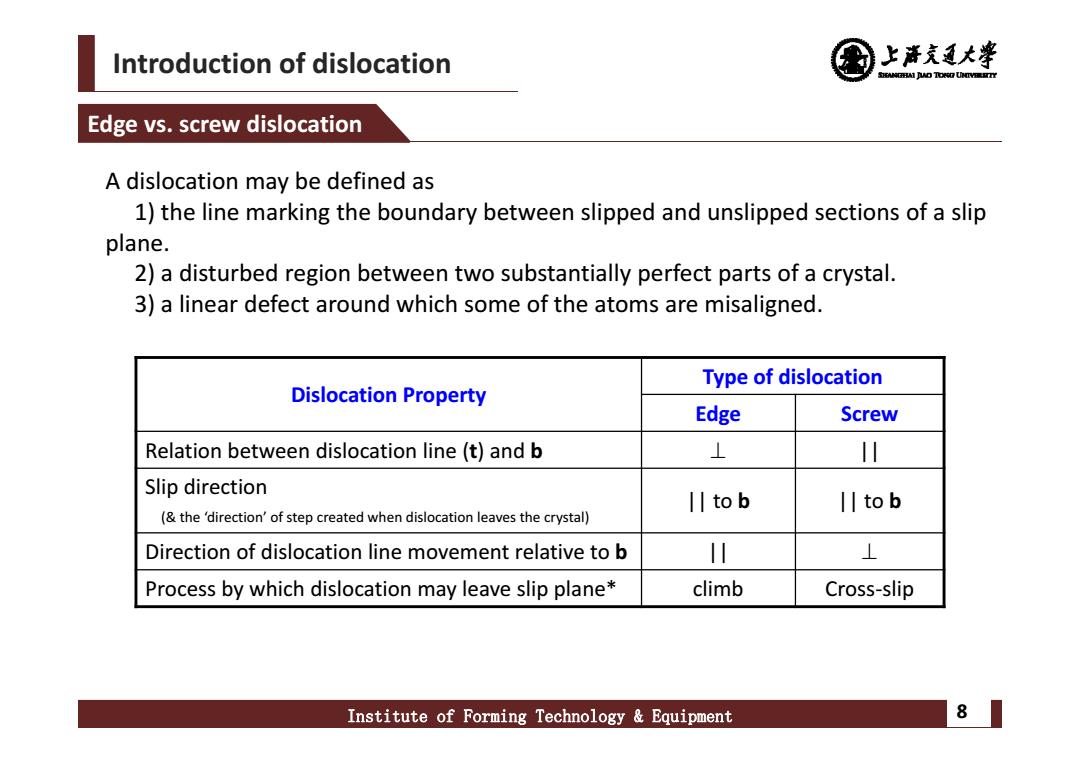
Introduction of dislocation 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Edge vs.screw dislocation A dislocation may be defined as 1)the line marking the boundary between slipped and unslipped sections of a slip plane. 2)a disturbed region between two substantially perfect parts of a crystal. 3)a linear defect around which some of the atoms are misaligned. Type of dislocation Dislocation Property Edge Screw Relation between dislocation line(t)and b ⊥ 川 Slip direction l川tob II tob (the 'direction'of step created when dislocation leaves the crystal) Direction of dislocation line movement relative to b 1 ⊥ Process by which dislocation may leave slip plane* climb Cross-slip Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 8
Introduction of dislocation Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 8 Edge vs. screw dislocation Dislocation Property Type of dislocation Edge Screw Relation between dislocation line (t) and b || Slip direction (& the ‘direction’ of step created when dislocation leaves the crystal) || to b || to b Direction of dislocation line movement relative to b || Process by which dislocation may leave slip plane* climb Cross‐slip A dislocation may be defined as 1) the line marking the boundary between slipped and unslipped sections of a slip plane. 2) a disturbed region between two substantially perfect parts of a crystal. 3) a linear defect around which some of the atoms are misaligned
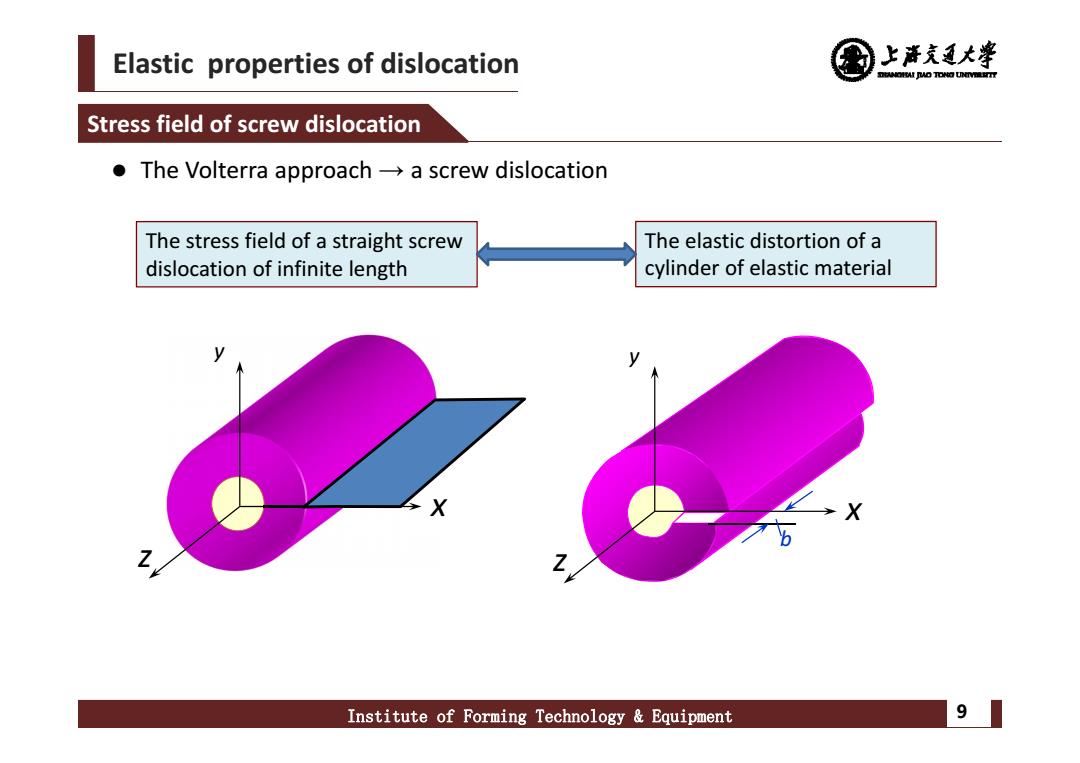
Elastic properties of dislocation 上清充通大学 DREANOIAI AO TONG UNTVEREITT Stress field of screw dislocation ●The Volterra approach→a screw dislocation The stress field of a straight screw The elastic distortion of a dislocation of infinite length cylinder of elastic material Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 9
Elastic properties of dislocation Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 9 The Volterra approach → a screw dislocation Stress field of screw dislocation z x y z x y b The stress field of a straight screw dislocation of infinite length The elastic distortion of a cylinder of elastic material

Elastic properties of dislocation 上清充通大学 SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Stress field of screw dislocation The elastic field in cylindrical polar coordinate 0 Note:No strain in radial direction 0 0 T-0 0 b L 2才 Z b z0 Y0:= 2·π·r Gb tg:=t:0=GY6:= 2π Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 10
Elastic properties of dislocation Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 10 The elastic field in cylindrical polar coordinate Note: No strain in radial direction Stress field of screw dislocation θ L r0 b z x y z z r P L b z z z z z 2 r P r b z 2 r Gb z z G z 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 z z
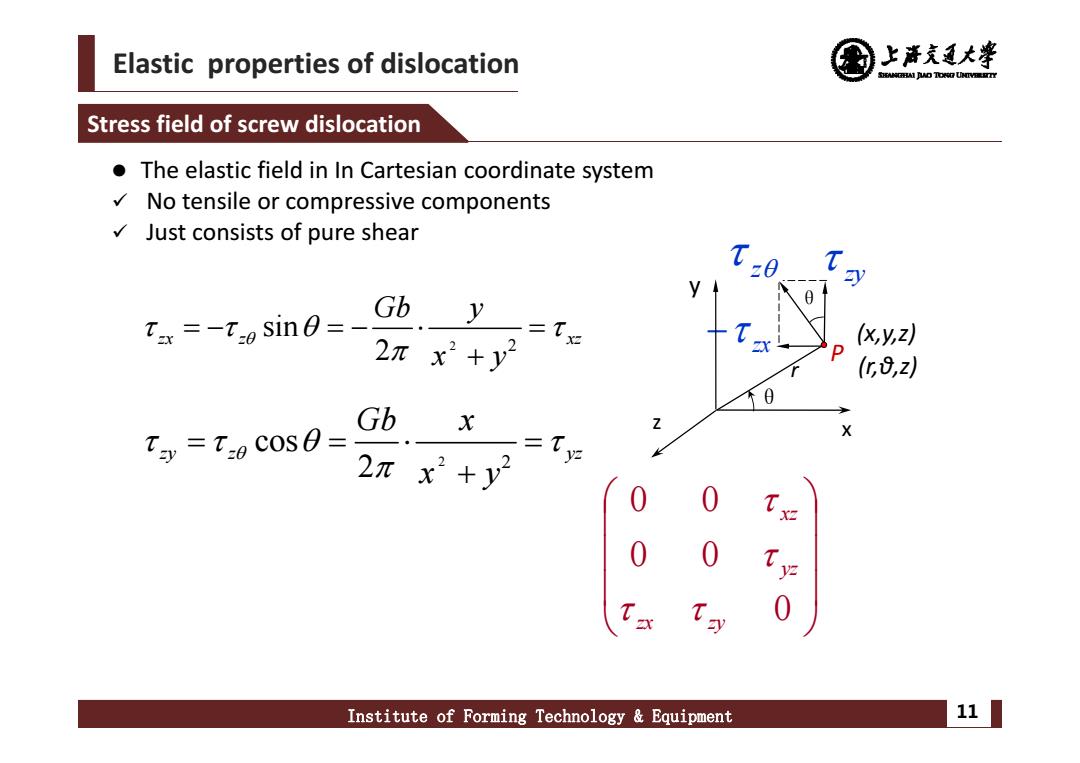
Elastic properties of dislocation 上产克大睾 SHANCBHAI JUAO TONO UNTVEEETTY Stress field of screw dislocation The elastic field inIn Cartesian coordinate system No tensile or compressive components Just consists of pure shear Gb Tax=-t:o sin0=- y 二T 2πx2+y2 (x,y,z) D (G8,z Gb x Ty=T:0 COS0= X 2πx2+y2 Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 11
Elastic properties of dislocation Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 11 Stress field of screw dislocation 2 2 sin 2 zx z xz Gb y x y 2 2 cos 2 zy z yz Gb x x y 0 0 0 0 0 zx zy yzxz zx θ z y x θ z zy r P (x,y,z) (r,θ,z) The elastic field in In Cartesian coordinate system No tensile or compressive components Just consists of pure shear