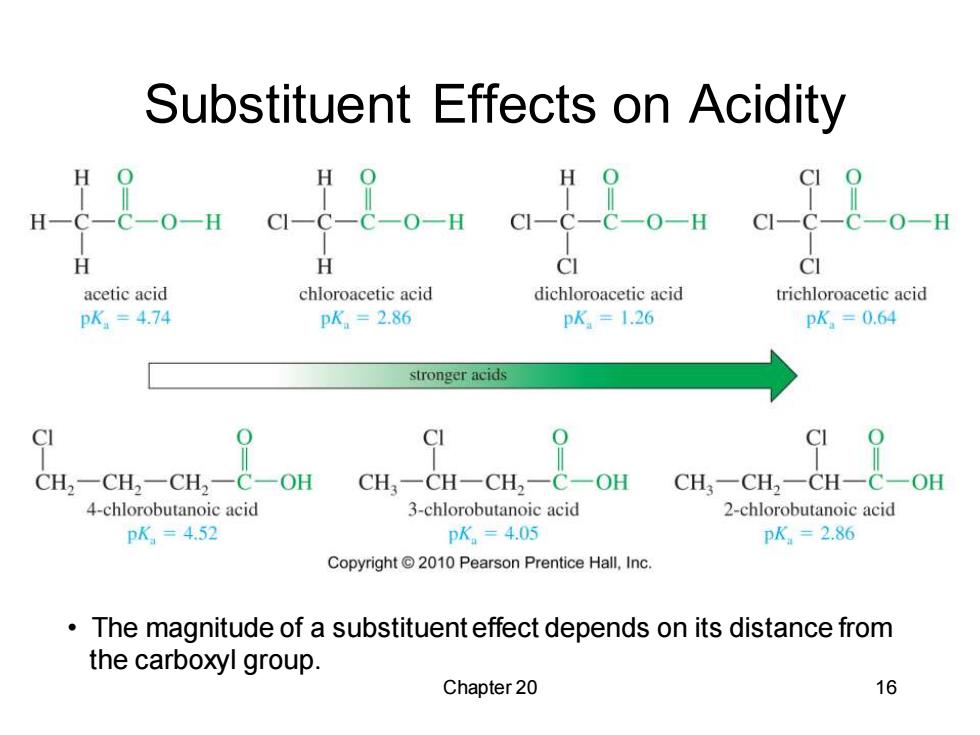
Substituent Effects on Acidity a-6_C-0-1 H H CI CI acetic acid chloroacetic acid dichloroacetic acid trichloroacetic acid pK=4.74 pK=2.86 pK=1.26 pK=0.64 stronger acids CI CI C CH2一CH2一CH2一C一OH CH一CH一CH2一C一OH CH3一CH2一CH一C一OH 4-chlorobutanoic acid 3-chlorobutanoic acid 2-chlorobutanoic acid pK=4.52 pK。=4.05 pK=2.86 Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The magnitude of a substituent effect depends on its distance from the carboxyl group. Chapter 20 16
Chapter 20 16 Substituent Effects on Acidity • The magnitude of a substituent effect depends on its distance from the carboxyl group
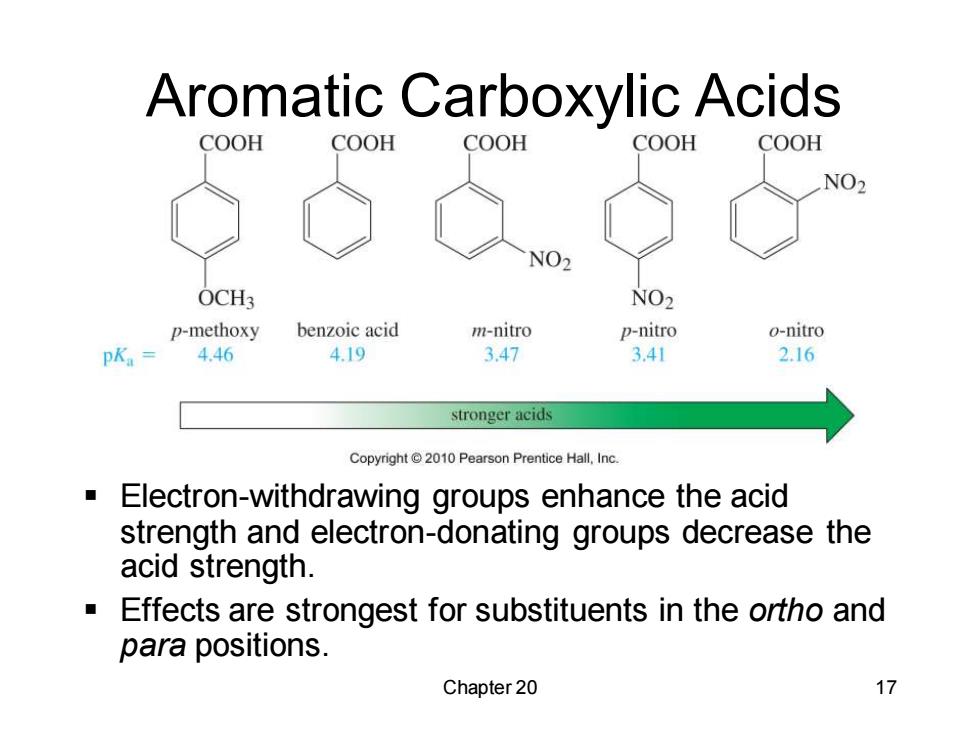
Aromatic Carboxylic Acids COOH COOH COOH COOH COOH NO2 NO2 OCH3 NO2 p-methoxy benzoic acid m-nitro p-nitro o-nitro pK.=4.46 4.19 3.47 3.41 2.16 stronger acids Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Electron-withdrawing groups enhance the acid strength and electron-donating groups decrease the acid strength. a Effects are strongest for substituents in the ortho and para positions. Chapter 20 17
Chapter 20 17 Aromatic Carboxylic Acids ▪ Electron-withdrawing groups enhance the acid strength and electron-donating groups decrease the acid strength. ▪ Effects are strongest for substituents in the ortho and para positions
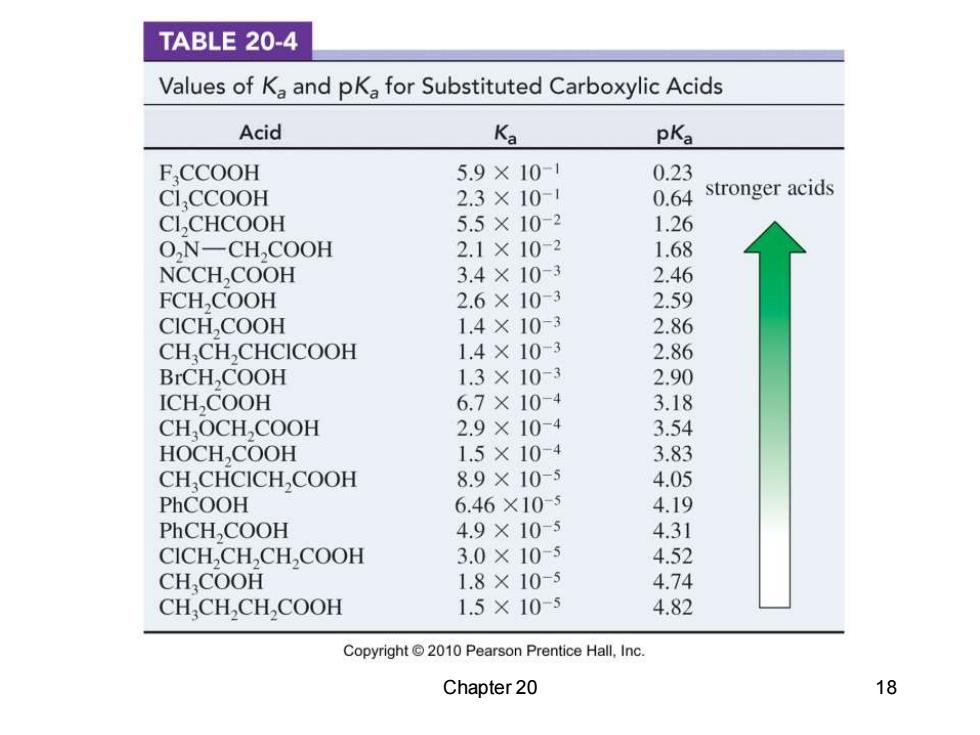
TABLE 20-4 Values of Ka and pKa for Substituted Carboxylic Acids Acid K pKa FCCOOH 5.9×10-1 0.23 CI.CCOOH 2.3×10-1 0.64 stronger acids CL,CHCOOH 5.5×10-2 1.26 O,N-CH,COOH 2.1×10-2 1.68 NCCH,COOH 3.4×10-3 2.46 FCH,COOH 2.6×10-3 2.59 CICH,COOH 1.4×10-3 2.86 CH,CH,CHCICOOH 1.4×10-3 2.86 BrCH,COOH 1.3×10-3 2.90 ICH,COOH 6.7×10-4 3.18 CH,OCH,COOH 2.9×10-4 3.54 HOCH,COOH 1.5×10-4 3.83 CH CHCICH,COOH 8.9×10-5 4.05 PhCOOH 6.46×10-5 4.19 PhCH,COOH 4.9×10-5 4.31 CICH,CH,CH,COOH 3.0×10-5 4.52 CH,COOH 1.8×10-5 4.74 CH,CH,CH,COOH 1.5×10-5 4.82 Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 20 18
Chapter 20 18
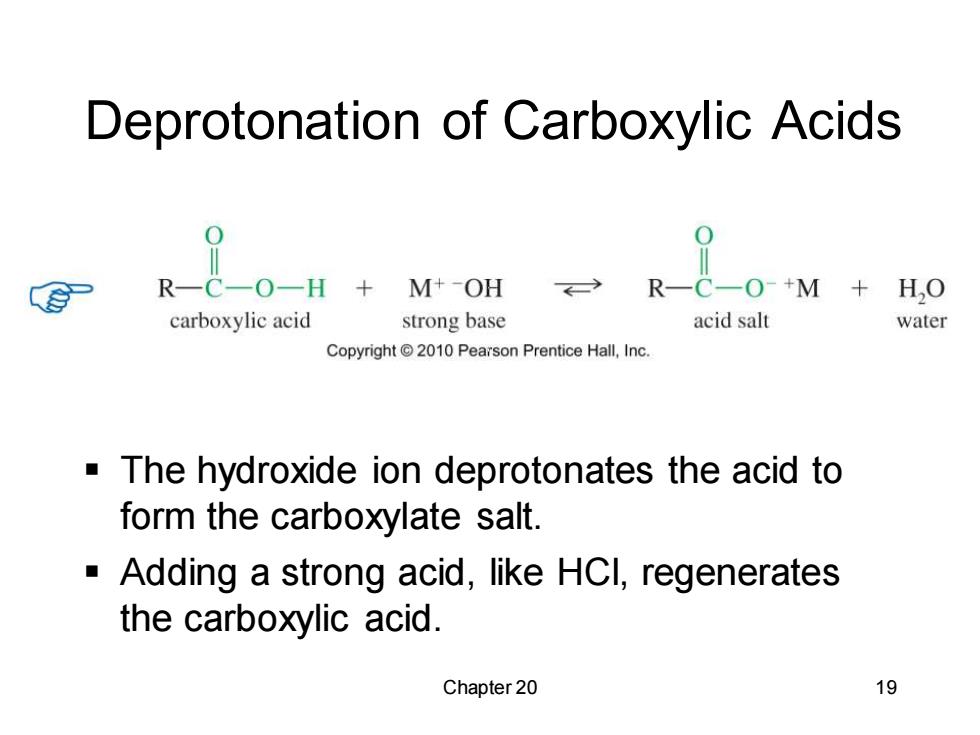
Deprotonation of Carboxylic Acids R一C一O-H+M+-OH R一C一O-+M+H,O carboxylic acid strong base acid salt water Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The hydroxide ion deprotonates the acid to form the carboxylate salt. Adding a strong acid,like HCI,regenerates the carboxylic acid. Chapter 20 19
Chapter 20 19 Deprotonation of Carboxylic Acids ▪ The hydroxide ion deprotonates the acid to form the carboxylate salt. ▪ Adding a strong acid, like HCl, regenerates the carboxylic acid