
Organic Chemistry,7th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 8 Reactions of Alkenes Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
Chapter 8 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Reactions of Alkenes
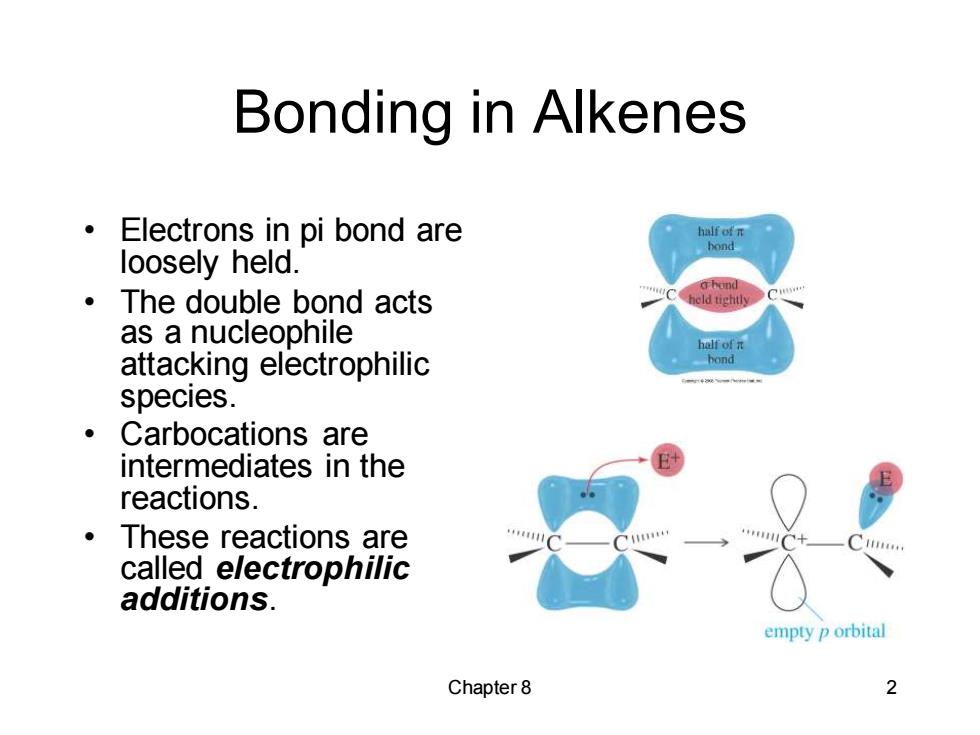
Bonding in Alkenes Electrons in pi bond are half of n loosely held. ·The double bond acts as a nucleophile hof元 attacking electrophilic hond species. ·Carbocations are intermediates in the reactions. ·These reactions are called electrophilic additions. empty p orbital Chapter 8 2
Chapter 8 2 Bonding in Alkenes • Electrons in pi bond are loosely held. • The double bond acts as a nucleophile attacking electrophilic species. • Carbocations are intermediates in the reactions. • These reactions are called electrophilic additions
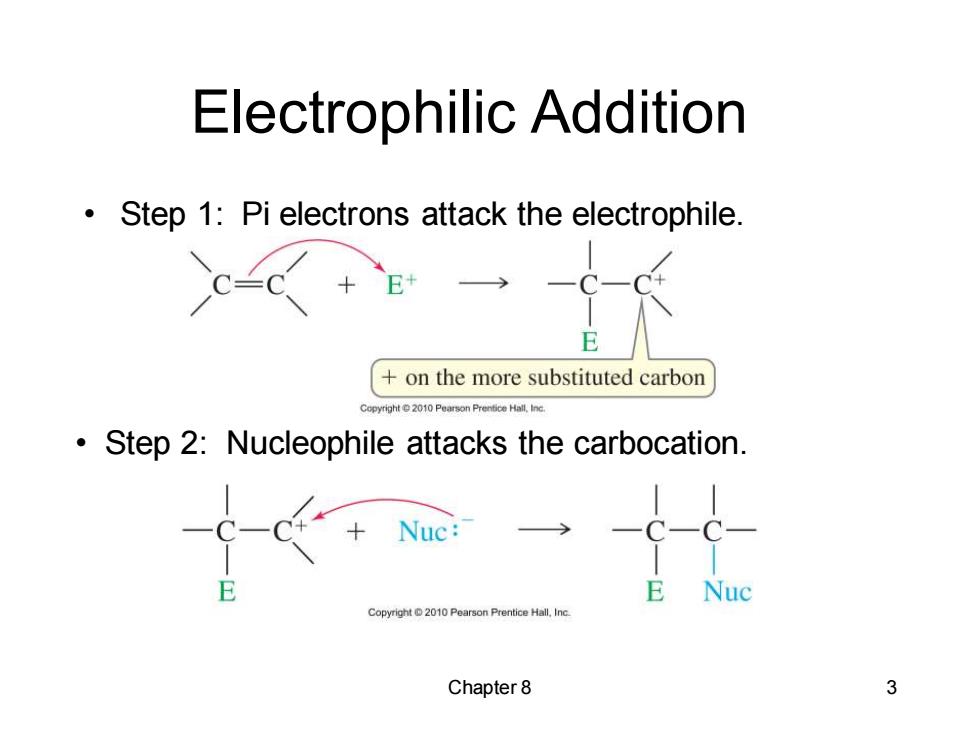
Electrophilic Addition Step 1:Pi electrons attack the electrophile. E on the more substituted carbon Step 2:Nucleophile attacks the carbocation. +Nuc:- E Nuc Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc. Chapter 8 3
Chapter 8 3 Electrophilic Addition • Step 1: Pi electrons attack the electrophile. • Step 2: Nucleophile attacks the carbocation

Types of Additions TABLE 8-1 Types of Additions to Alkenes C=C Type of Addition [Elements Added]a Product hydration halogenation [H.O [X.).an oxidation hydrogenation halohydrin formation [H.I.a reduction [HOX].an oxidation hydroxylation HX addition [HOOH],an oxidation HX灯 (hydrohalogenation) oxidative cleavage C=00=( [O.I.an oxidation cyclopropanation CH】 O].an oxidation These are not the reagents used but simply the groups that appear in the produc Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter8 4
Chapter 8 4 Types of Additions

Addition of HX to Alkenes Step 1 is the protonation of the double bond. The protonation step forms the most stable carbocation possible. In step 2,the nucleophile attacks the carbocation,forming an alkyl halide. HBr,HCI,and HI can be added through this reaction. Chapter8 5
Chapter 8 5 Addition of HX to Alkenes • Step 1 is the protonation of the double bond. • The protonation step forms the most stable carbocation possible. • In step 2, the nucleophile attacks the carbocation, forming an alkyl halide. • HBr, HCl, and HI can be added through this reaction