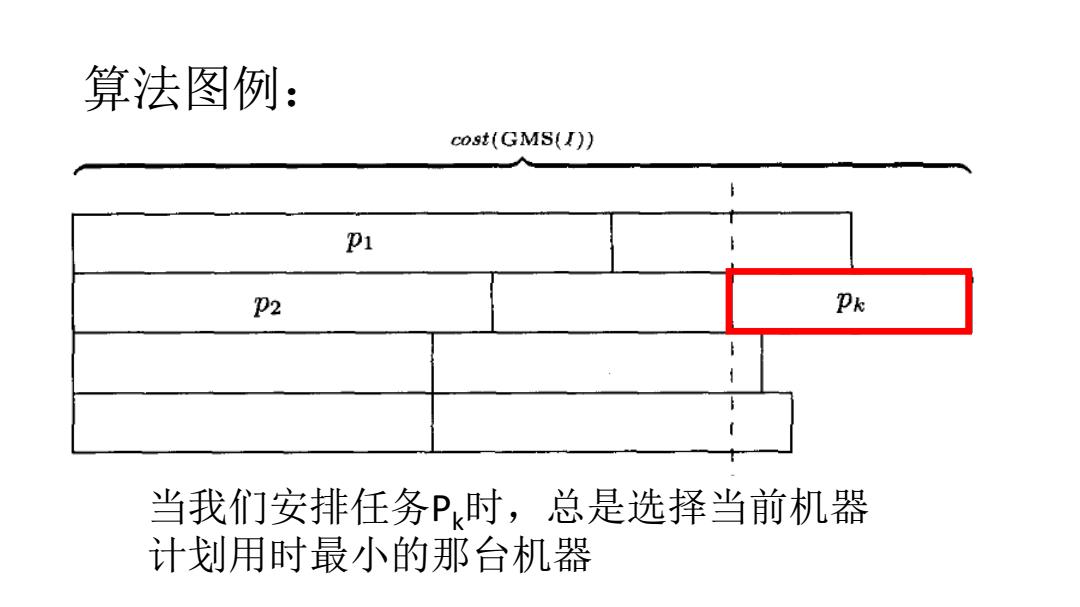
算法图例: cost(GMS(I)) P1 P2 Pk 当我们安排任务P时,总是选择当前机器 计划用时最小的那台机器
算法图例: 当我们安排任务Pk时,总是选择当前机器 计划用时最小的那台机器

生产调度问题的一个近似解 Algorithm 4.2.1.3 (GMS (GREEDY MAKESPAN SCHEDULE)). Input:I=(p1,...,Pn,m),n,m,p1,...,Pn positive integers and m 2. Step 1:Sort p1,...,Pn. To simplify the notation we assume p1≥p2≥·≥pn in the rest of the algorithm. Step 2:for i=1 to m do begin Ta:={i); Time(Ti):=pi end In the initialization step the m largest jobs are distributed to the m machines.At the end,Ti should contain the indices of all jobs assigned to the ith machine for i=1,...,m.} Step 3:for i=m+1 to n do begin compute an I such that Time(T)=min{Time(Til≤j≤m; T:=TUfi: Time(Ti):=Time(Ti)+pi end Output:(Ti,T2,...,Tm)
生产调度问题的一个近似解

生产调度问题的一个近似解 Algorithm 4.2.1.3 (GMS (GREEDY MAKESPAN SCHEDULE)). Input:I=(p1,...,pn,m),n,m,p1,...,p ositive integers and m 2. Step 1:Sort p1,...,Pn. To simplify the nota 2p2≥T≥pn in the rest of th hm. Step 2: for i 这个算法会 差到什么程 edistributed to the 度呢? dices of all jobs ,m.} 40 b compce an I such that me(T):=min{Time(T,)1≤j≤m}; T:=TU{}: Time(T):=Time(Ti)+pi end Output:(T,T2,.,Tm)为
生产调度问题的一个近似解 这个算法会 差到什么程 度呢?

问题是: eA(x)= cost(A())-Optu() Opt( 我们根本不知道最优解是多少!
问题是: 我们根本不知道最优解是多少!
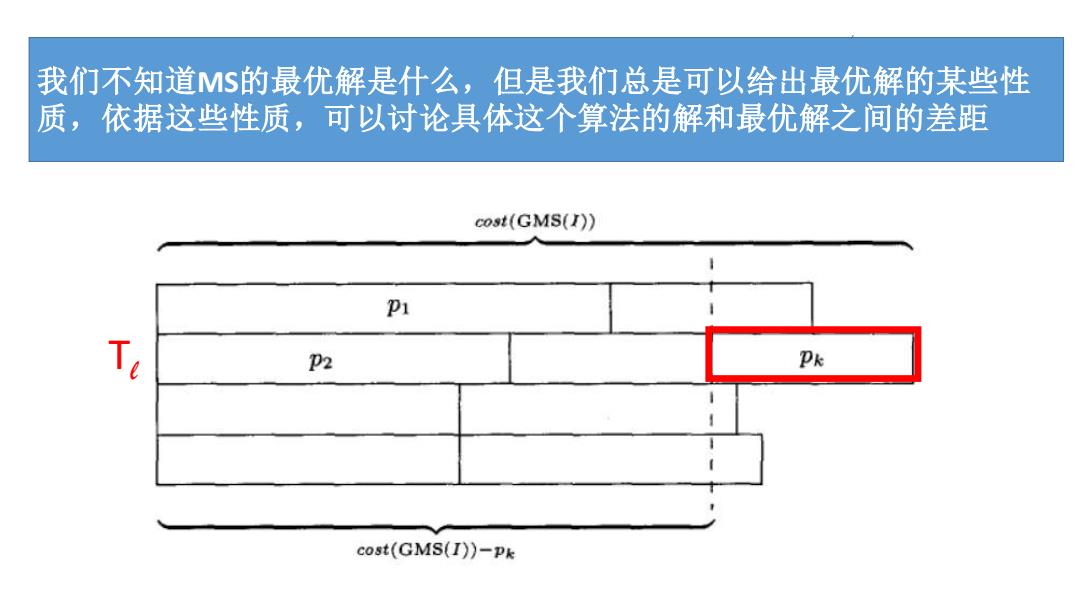
我们不知道MS的最优解是什么,但是我们总是可以给出最优解的某些性 质,依据这些性质,可以讨论具体这个算法的解和最优解之间的差距 cost(GMS(I)) P1 T P2 Pk cost(GMS(I))-Pk
我们不知道MS的最优解是什么,但是我们总是可以给出最优解的某些性 质,依据这些性质,可以讨论具体这个算法的解和最优解之间的差距 Tl