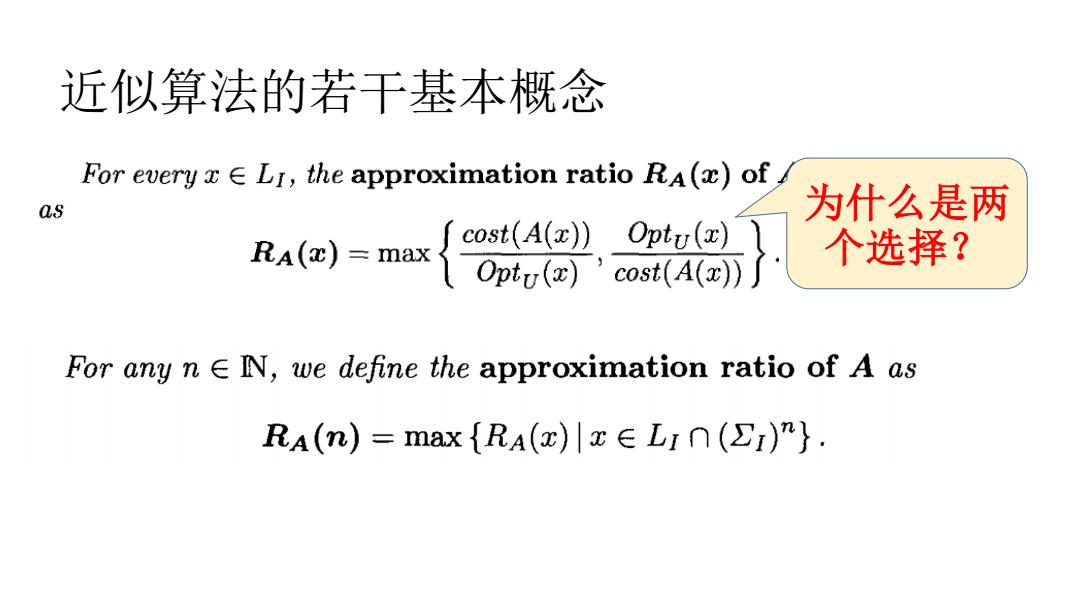
近似算法的若干基本概念 For every x E LI,the approximation ratio Ra(x)of as 为什么是两 Scost(A(x))Optu() RA()=max Optu(co(A 个选择? For any nE N,we define the approximation ratio of A as RA(n)=max{RA()ELI(I)m}
近似算法的若干基本概念 为什么是两 个选择?

我们希望能够得到某个近似算法的如下结论: For any positive real 6 1,we say that A is a 6-approximation algo- rithm for U if RA(x)≤δfor every x∈LI. 如果不能,我们要努力得到某个近似算法的这个结论: For every function f:NN-R,we say that A is an f(n)-approximation algorithm for U if RA(n)≤f(n)for every n∈N
我们希望能够得到某个近似算法的如下结论: 如果不能,我们要努力得到某个近似算法的这个结论:

如何评价一个近似算法的“好坏” 1,针对某个特定的问题输入,A的解和最优解的误差 在不知道最优解的情况下,如何评估? 2,针对某个规模的各种问题输入,A的最大误差; 3,针对问题的所有可能输入,A的误差变化趋势: 将所有输入可能,建模为n的增长 4,给出一个误差的界限,证明A近似算法的误差的界限 绝对的某个值,或者某个函数
如何评价一个近似算法的“好坏” 1,针对某个特定的问题输入,A的解和最优解的误差 在不知道最优解的情况下,如何评估? 2,针对某个规模的各种问题输入,A的最大误差; 3,针对问题的所有可能输入,A的误差变化趋势: 将所有输入可能,建模为n的增长 4,给出一个误差的界限,证明A近似算法的误差的界限 绝对的某个值,或者某个函数
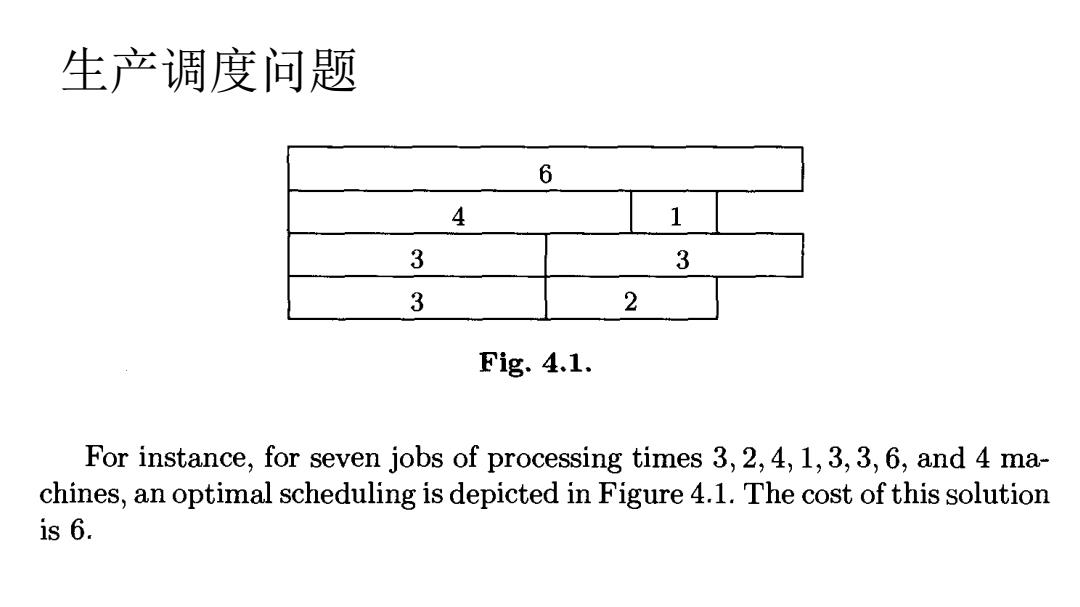
生产调度问题 6 4 1 3 3 3 2 Fig.4.1. For instance,for seven jobs of processing times 3,2,4,1,3,3,6,and 4 ma- chines,an optimal scheduling is depicted in Figure 4.1.The cost of this solution s6
生产调度问题
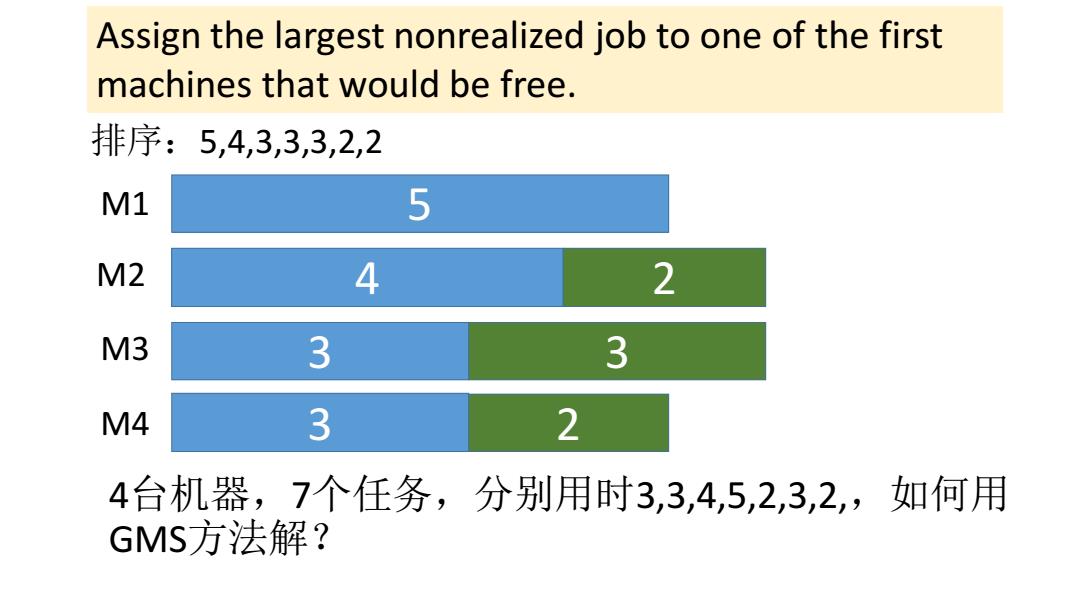
Assign the largest nonrealized job to one of the first machines that would be free. 排序:5,4,3,3,3,2,2 M1 5 M2 4 2 M3 3 3 M4 3 2 4台机器,7个任务,分别用时3,3,4,5,2,3,2,如何用 GMS方法解?
4台机器,7个任务,分别用时3,3,4,5,2,3,2,,如何用 GMS方法解? M1 M2 M3 M4 5 4 3 3 3 2 2 Assign the largest nonrealized job to one of the first machines that would be free. 排序:5,4,3,3,3,2,2