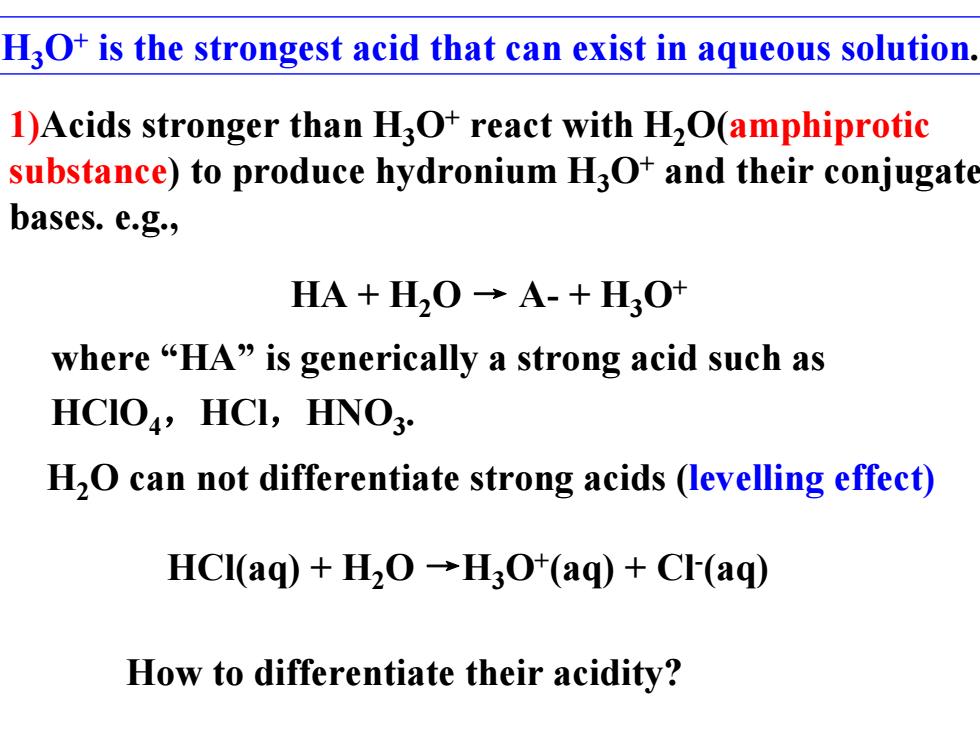
H3O+is the strongest acid that can exist in aqueous solution. 1)Acids stronger than H3O+react with H2O(amphiprotic substance)to produce hydronium H3O+and their conjugate bases.e.g., HA+H20→A-+H30+ where“HA”is generically a strong acid such as HCIO,HCI,HNO3. H2O can not differentiate strong acids (levelling effect) HCI(aq)+H2O-H3O*(aq)+CF(aq) How to differentiate their acidity?
H3O+ is the strongest acid that can exist in aqueous solution. HCl(aq) + H2O →H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) H2O can not differentiate strong acids (levelling effect) HA + H2O → A- + H3O+ where “HA” is generically a strong acid such as HClO4,HCl,HNO3. How to differentiate their acidity? 1)Acids stronger than H3O+ react with H2O(amphiprotic substance) to produce hydronium H3O+ and their conjugate bases. e.g

a less basic(弱碱性)solvent(versus water))can differentiate the relative acidic strength of the acids, e.g.,HAC,where the strong acids do not ionize completely. Order of the strength of the following acids: HI>HCIO>HCI>HSO>HNO3 2)Acids weaker than H3O+react with H2O to a much smaller extent,producing H3O+and their conjugate bases (differentiating effect).e.g., HF(aq)+H2O=H3O+(aq)+F(aq)
a less basic(弱碱性) solvent (versus water) can differentiate the relative acidic strength of the acids, e.g., HAC, where the strong acids do not ionize completely. HI>HClO4>HCl>H2SO4>HNO3 2)Acids weaker than H3O+ react with H2O to a much smaller extent, producing H3O+ and their conjugate bases (differentiating effect). e.g., HF(aq) + H2O → H3O+(aq) + F-(aq) Order of the strength of the following acids:

OH-is the strongest base that can exist in aqueous solution 1)Bases like O2-H,NH2,CH3,which are stronger than OH,react with H2O to produce OH-and their conjugate acids (levelling effect).e.g., O2-(aq)+H2O-OH-(aq)+OH-(aq) H,O can not differentiate strong bases. How to differentiate the strength of bases? A solvent(弱酸性)whose strength of acid is a weaker than that of H,O can do it (differentiating effect),e.g.,NH3
OH- is the strongest base that can exist in aqueous solution O2-(aq) + H2O → OH-(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O can not differentiate strong bases. 1) Bases like O2-、H-, NH2-, CH3-, which are stronger than OH-, react with H2O to produce OH- and their conjugate acids (levelling effect). e.g., How to differentiate the strength of bases? A solvent (弱酸性) whose strength of acid is a weaker than that of H2O can do it (differentiating effect), e.g., NH3

For a conjugate acid-base pair: The stronger the acid,the weaker its conjugate base; The stronger the base,the weaker its conjugate acid. Strength of acid酸性:HClO,>H2SO4>H3PO4> HAC>H2CO3>NH>H2O Strength of base碱性:ClO,<HSO4<H,PO4< Ac<HCO;<NH3 <OH concepts 酸浓度(concentration of acid):以溶质酸的量计算得到的 浓度(mol.);酸度(acidity):溶液中H离子浓度或pH值; 酸强度(strength of acid):酸的强弱 K或pK
The stronger the acid ,the weaker its conjugate base ; The stronger the base ,the weaker its conjugate acid. HAc H CO NH H O HClO H SO H PO 2 3 4 2 4 2 4 3 4 > > > > > > + 酸性: − − − − − − < < < < < < Ac HCO NH OH ClO HSO H PO 3 3 碱性: 4 4 2 4 Strength of acid Strength of base For a conjugate acid-base pair: 酸浓度(concentration of acid):以溶质酸的量计算得到的 浓度(mol.l-1); 酸度(acidity):溶液中H +离子浓度或pH值; 酸强度(strength of acid ):酸的强弱 θ a θ Ka 或 p K concepts

5.2 Ionization equilibrium of water and the pH scale 5.2.1 Ionization equilibrium of water 5.2.2 The pH scale
§ 5.2 Ionization equilibrium of water and the pH scale 5.2.2 The pH scale 5.2.1 Ionization equilibrium of water