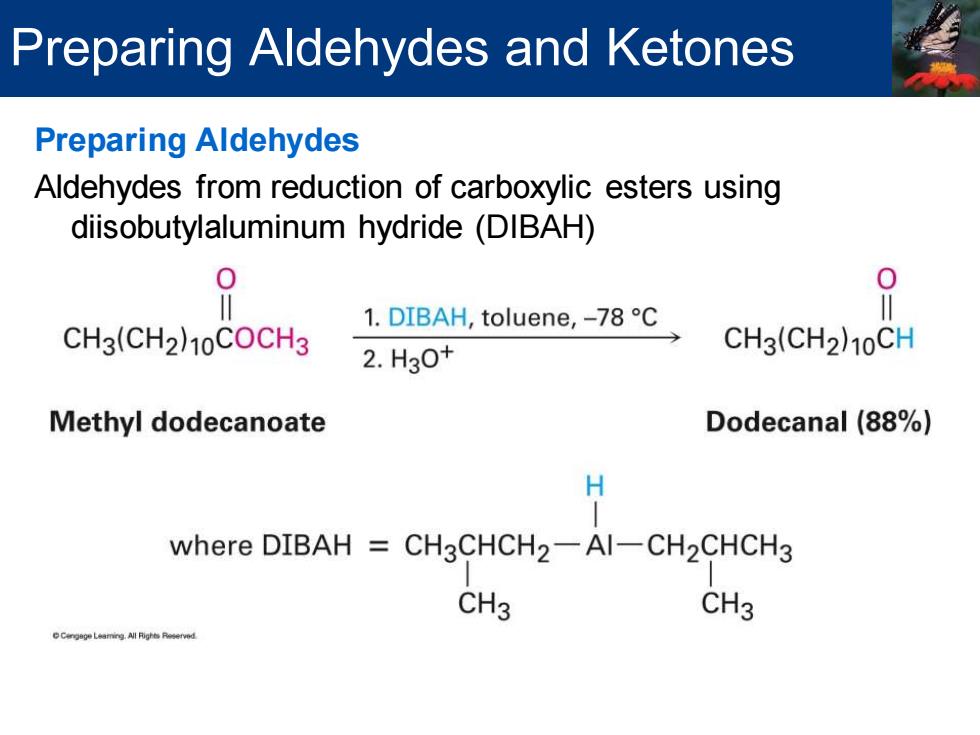
Preparing Aldehydes and Ketones Preparing Aldehydes Aldehydes from reduction of carboxylic esters using diisobutylaluminum hydride(DIBAH) 9 CH3(CH2)10COCH3 1.DIBAH,toluene,-78C O= 2.H30t CH3(CH2)10CH Methyl dodecanoate Dodecanal (88%) H where DIBAH CH3CHCH2-Al-CH2CHCH3 CH3 CH3
Preparing Aldehydes Aldehydes from reduction of carboxylic esters using diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBAH) Preparing Aldehydes and Ketones
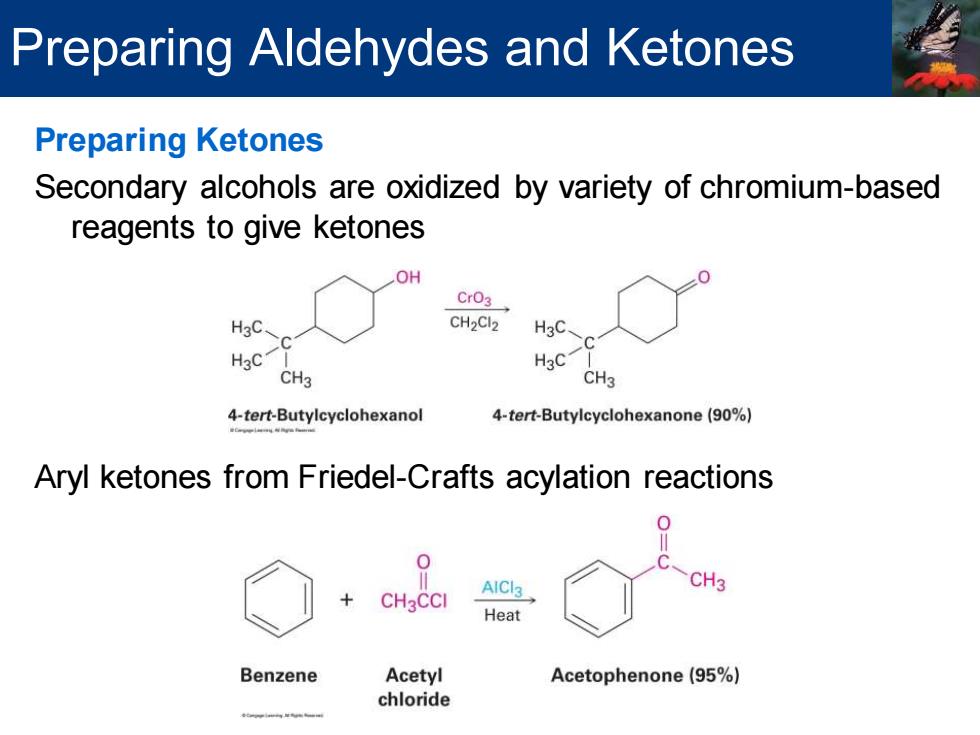
Preparing Aldehydes and Ketones Preparing Ketones Secondary alcohols are oxidized by variety of chromium-based reagents to give ketones OH CrO3 H3C CH2Cl2 H3C、 H3C H3C CH3 CH3 4-tert-Butylcyclohexanol 4-tert-Butylcyclohexanone(90%) Aryl ketones from Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions AICl3 CH3 Heat Benzene Acetyl Acetophenone(95%) chloride
Preparing Ketones Secondary alcohols are oxidized by variety of chromium-based reagents to give ketones Aryl ketones from Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions Preparing Aldehydes and Ketones
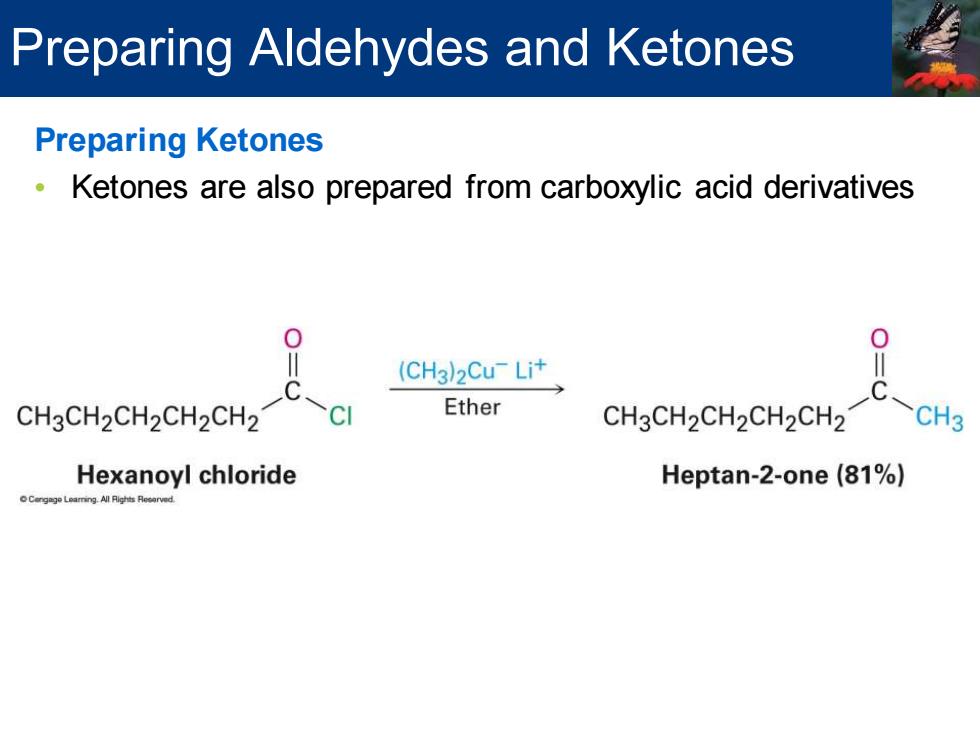
Preparing Aldehydes and Ketones Preparing Ketones Ketones are also prepared from carboxylic acid derivatives 0 0 (CH3)2Cu-Lit CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2 Ether CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2 CH3 Hexanoyl chloride Heptan-2-one(81%)
Preparing Ketones • Ketones are also prepared from carboxylic acid derivatives Preparing Aldehydes and Ketones
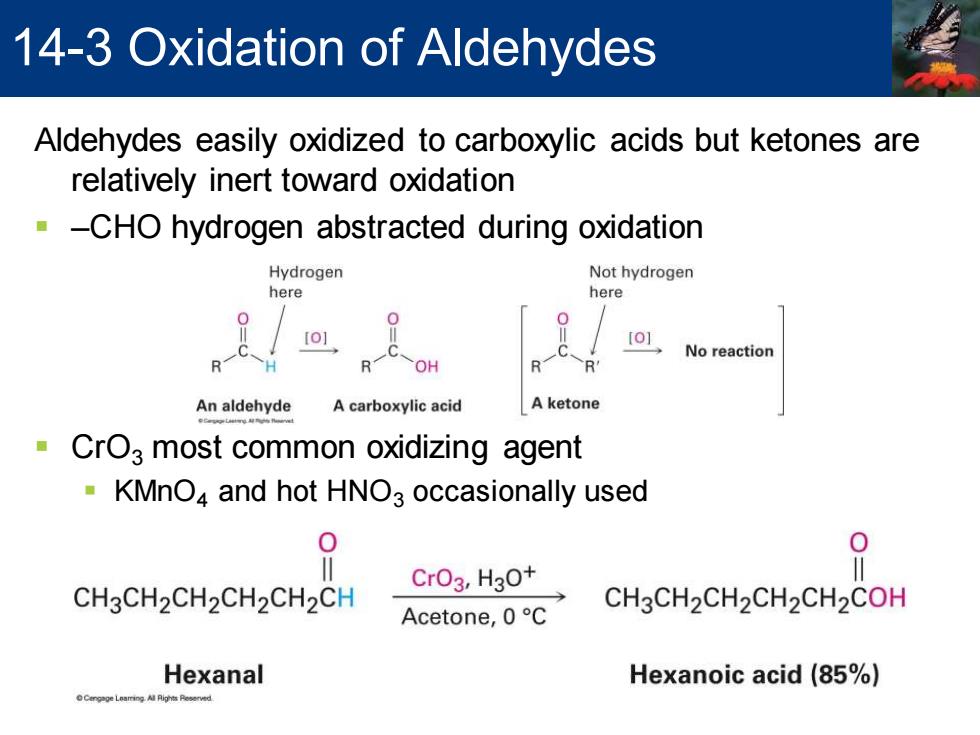
14-3 Oxidation of Aldehydes Aldehydes easily oxidized to carboxylic acids but ketones are relatively inert toward oxidation -CHO hydrogen abstracted during oxidation Hydrogen Not hydrogen here here [O] No reaction R OH R An aldehyde A carboxylic acid Aketone CrO3 most common oxidizing agent KMnO4 and hot HNO3 occasionally used 0 CrO3,H30+ CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH Acetone,0C CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2COH Hexanal Hexanoic acid (85%) pge Lamingl ighs Reserved
Aldehydes easily oxidized to carboxylic acids but ketones are relatively inert toward oxidation ▪ –CHO hydrogen abstracted during oxidation ▪ CrO3 most common oxidizing agent ▪ KMnO4 and hot HNO3 occasionally used 14-3 Oxidation of Aldehydes
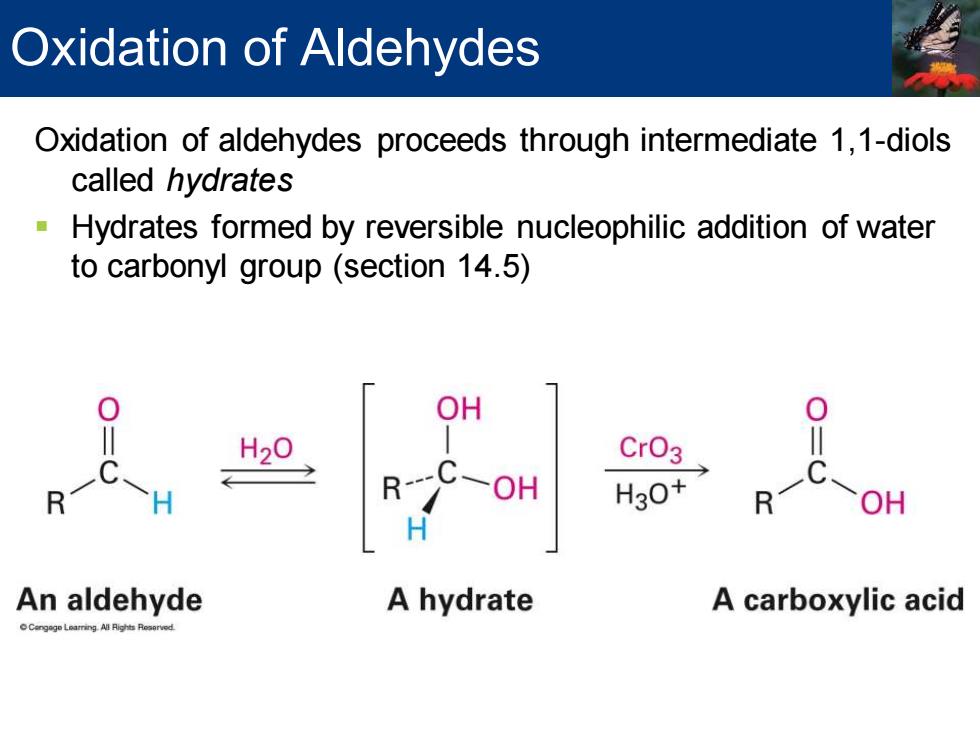
Oxidation of Aldehydes Oxidation of aldehydes proceeds through intermediate 1,1-diols called hydrates Hydrates formed by reversible nucleophilic addition of water to carbonyl group (section 14.5) OH H20 R-OH HO R OH An aldehyde A hydrate A carboxylic acid
Oxidation of aldehydes proceeds through intermediate 1,1-diols called hydrates ▪ Hydrates formed by reversible nucleophilic addition of water to carbonyl group (section 14.5) Oxidation of Aldehydes