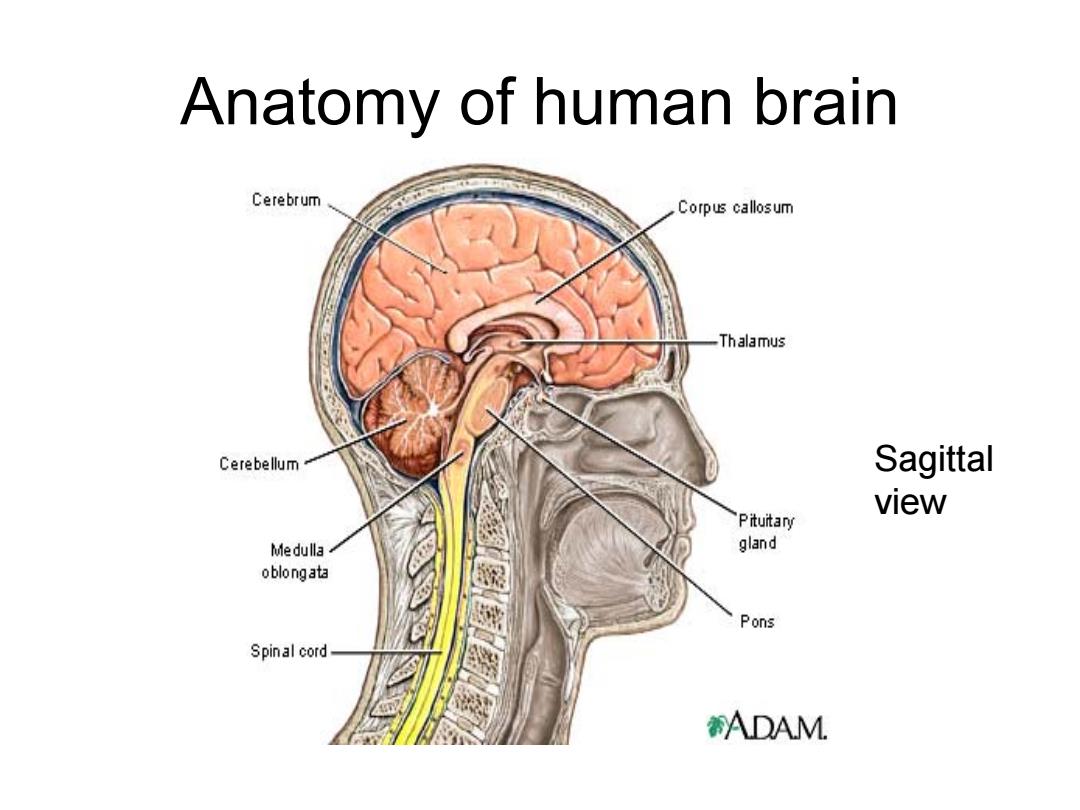
Anatomy of human brain Cerebrum Corpus callosum Thalamus Cerebellum Sagittal view Pituitary Me dulla gland oblongata Pons Spinal cord ADAM
Anatomy of human brain Sagittal view

Cerebral cortex Evolutionally formed last Receiving and processing information Control of sight,listening, movement,memory,wake, autonomic function
• Evolutionally formed last • Receiving and processing information • Control of sight, listening, movement, memory, wake, autonomic function… Cerebral cortex
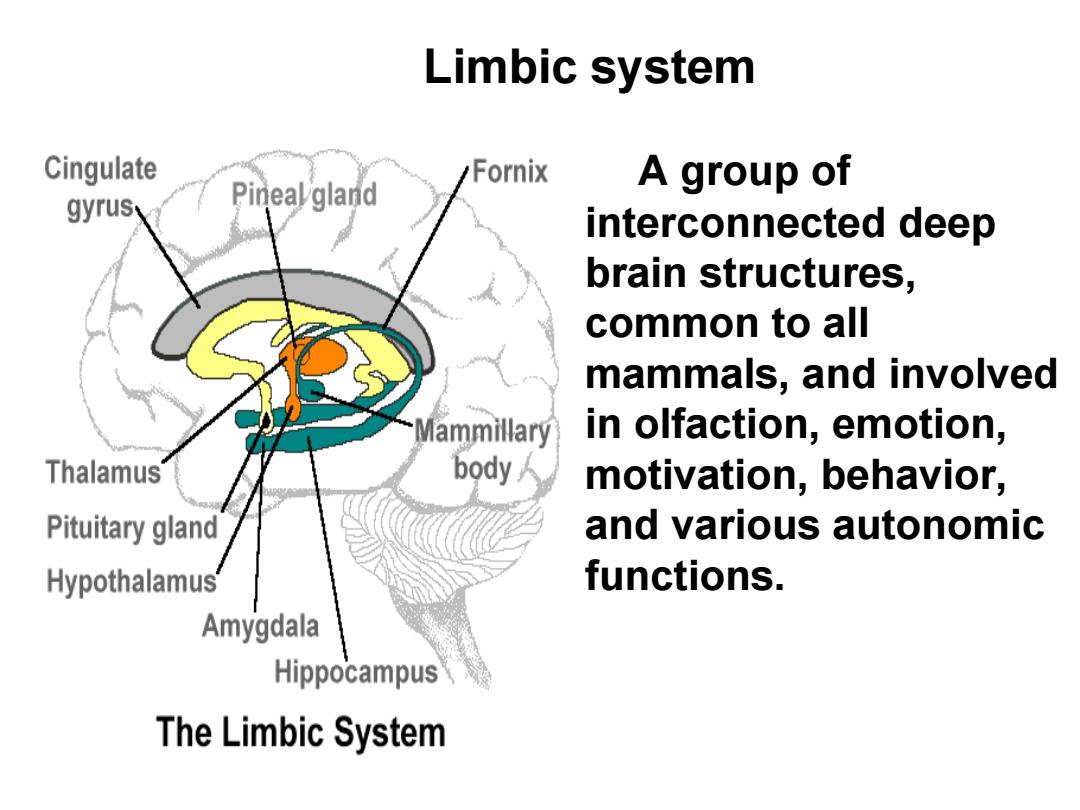
Limbic system Cingulate /Fornix A group of gyrusy Pinealgland interconnected deep brain structures, common to all mammals,and involved Mammillary in olfaction,emotion, Thalamus body人 motivation,behavior, Pituitary gland and various autonomic Hypothalamus functions. Amygdala Hippocampus The Limbic System
A group of interconnected deep brain structures, common to all mammals, and involved in olfaction, emotion, motivation, behavior, and various autonomic functions. Limbic system

Cerebellum Responsible for the regulation and coordination of complex voluntary muscular movement as well as the maintenance of posture and balance. More study indicating its involvement in psychiatric conditions
Responsible for the regulation and coordination of complex voluntary muscular movement as well as the maintenance of posture and balance. Cerebellum More study indicating its involvement in psychiatric conditions

Diencephalon >major divisions:thalamus and hypothalamus functioning: as a relay system between sensory input neurons and other parts of the brain as an interactive site for the central nervous and endocrine systems >working in tandem with the limbic system
major divisions: thalamus and hypothalamus functioning: • as a relay system between sensory input neurons and other parts of the brain • as an interactive site for the central nervous and endocrine systems working in tandem with the limbic system Diencephalon