
Isoelectric Point of Amino Acids Isoelectric point(pl)is defined as the pH at which amino acids exist as the zwitterion (neutral charge). The pl depends on structure of the side chain of the amino acid. Acidic amino acids,isoelectric pH ~3. Basic amino acids,isoelectric pH ~9. -Neutral amino acids,isoelectric pH is slightly acidic,5-6. Chapter 24 16
Chapter 24 16 Isoelectric Point of Amino Acids ▪ Isoelectric point (pI) is defined as the pH at which amino acids exist as the zwitterion (neutral charge). ▪ The pI depends on structure of the side chain of the amino acid. ▪ Acidic amino acids, isoelectric pH ~3. ▪ Basic amino acids, isoelectric pH ~9. ▪ Neutral amino acids, isoelectric pH is slightly acidic, 5–6
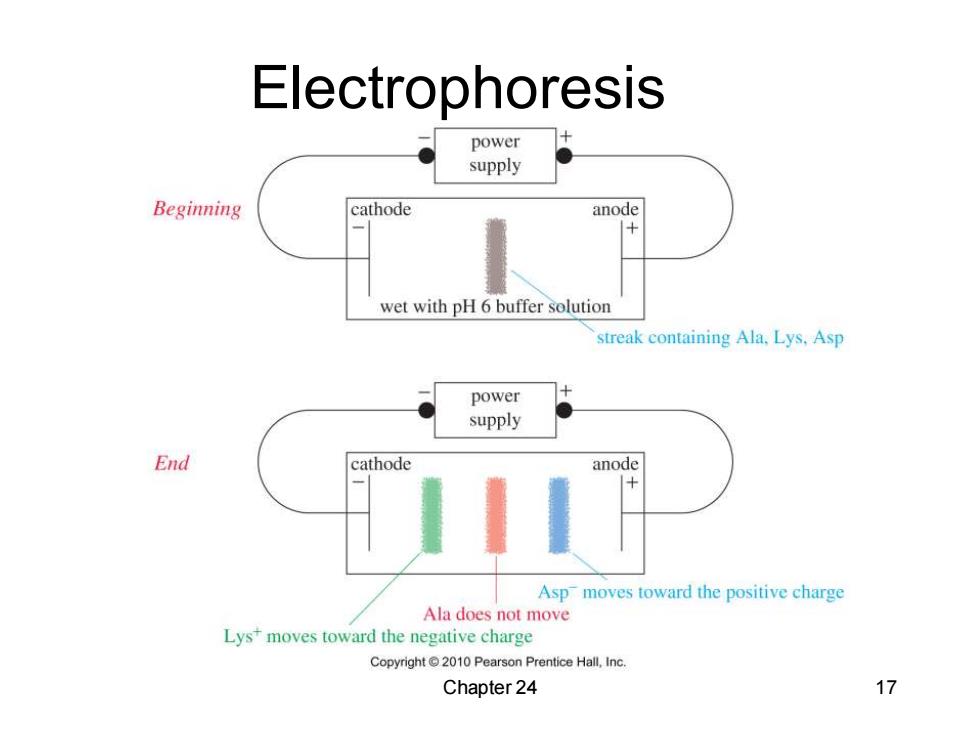
Electrophoresis power supply Beginning cathode anode wet with pH 6 buffer solution streak containing Ala,Lys.Asp power supply End cathode anode Asp moves toward the positive charge Ala does not move Lys moves toward the negative charge Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 24 17
Chapter 24 17 Electrophoresis

Reductive Amination NH NH, R-C-COOH excess NH3 R-C一COO+NH4 2 R一CH-COO Pd a-ketoacid imine a-amino acid Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. This method for synthesizing amino acids is biomimetic,mimics the biological process. React an a-ketoacid with ammonia,then reduce the imine with H2/Pd. Racemic mixture is obtained. Chapter 24 18
Chapter 24 18 Reductive Amination ▪ This method for synthesizing amino acids is biomimetic, mimics the biological process. ▪ React an -ketoacid with ammonia, then reduce the imine with H2 /Pd. ▪ Racemic mixture is obtained
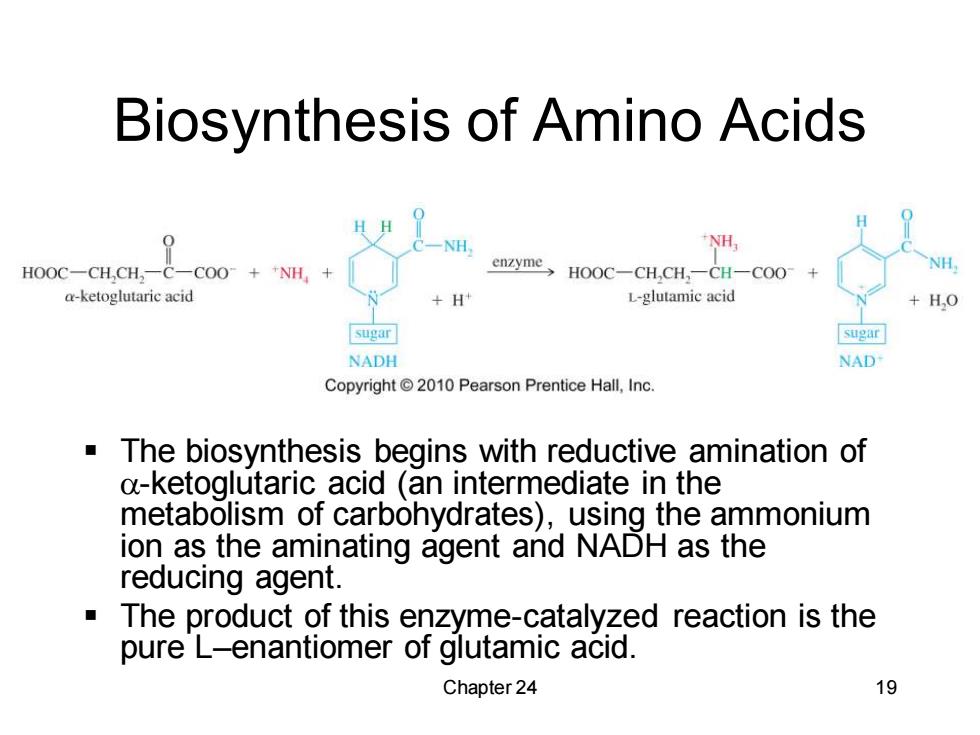
Biosynthesis of Amino Acids H 0 NH. NH HOOC-CH,CH,-C-COO+NH, enzyme HOOC-CH,CH:-CH-COO a-ketoglutaric acid +H L-glutamic acid +H,O sugar sugar NADH NAD Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The biosynthesis begins with reductive amination of a-ketoglutaric acid (an intermediate in the metabolism of carbohydrates),using the ammonium ion as the aminating agent and NADH as the reducing agent. The product of this enzyme-catalyzed reaction is the pure L-enantiomer of glutamic acid. Chapter 24 19
Chapter 24 19 Biosynthesis of Amino Acids ▪ The biosynthesis begins with reductive amination of -ketoglutaric acid (an intermediate in the metabolism of carbohydrates), using the ammonium ion as the aminating agent and NADH as the reducing agent. ▪ The product of this enzyme-catalyzed reaction is the pure L–enantiomer of glutamic acid
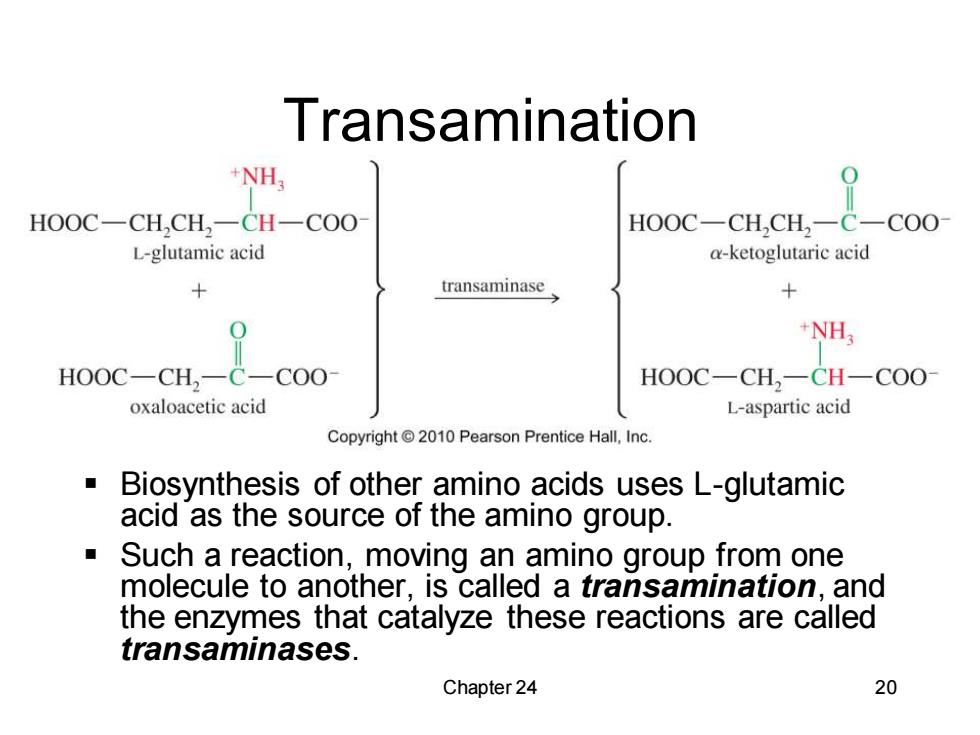
Transamination NH, HOOC-CH,CH,-CH-COO HOOC-CH,CH,-C-COO L-glutamic acid a-ketoglutaric acid transaminase + +NH: HOOC-CH,-C-COO- HOOC-CH,-CH-COO oxaloacetic acid L-aspartic acid Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Biosynthesis of other amino acids uses L-glutamic acid as the source of the amino group. Such a reaction,moving an amino group from one molecule to another,is called a transamination,and the enzymes that catalyze these reactions are called transaminases. Chapter 24 20
Chapter 24 20 Transamination ▪ Biosynthesis of other amino acids uses L-glutamic acid as the source of the amino group. ▪ Such a reaction, moving an amino group from one molecule to another, is called a transamination, and the enzymes that catalyze these reactions are called transaminases