
Complete Proteins Provide all the essential amino acids. Examples:Those found in meat,fish, milk,and eggs. Plant proteins are generally incomplete. -Vegetarians should eat many different kinds of plants,or supplement their diets with milk and/or eggs. Chapter 24 11
Chapter 24 11 Complete Proteins ▪ Provide all the essential amino acids. ▪ Examples: Those found in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. ▪ Plant proteins are generally incomplete. ▪ Vegetarians should eat many different kinds of plants, or supplement their diets with milk and/or eggs

Rare Amino Acids -4-Hydroxyproline and 5-hydroxylysine is found in collagen. D-Glutamic acid is found in cell walls of bacteria. D-Serine is found in earthworms. y-Aminobutyric acid is a neurotransmitter. -B-Alanine is a constituent of the vitamin pantothenic acid. Chapter 24 12
Chapter 24 12 Rare Amino Acids ▪ 4-Hydroxyproline and 5-hydroxylysine is found in collagen. ▪ D-Glutamic acid is found in cell walls of bacteria. ▪ D-Serine is found in earthworms. ▪ -Aminobutyric acid is a neurotransmitter. ▪ -Alanine is a constituent of the vitamin pantothenic acid

Properties of Amino Acids High melting points,over 200C More soluble in water than in ether. Larger dipole moments than simple acids or simple amines. Less acidic than most carboxylic acids;less basic than most amines. pK2=10 H3N-CH-C-O pK,=12 R Chapter 24 13
Chapter 24 13 Properties of Amino Acids ▪ High melting points, over 200C. ▪ More soluble in water than in ether. ▪ Larger dipole moments than simple acids or simple amines. ▪ Less acidic than most carboxylic acids; less basic than most amines. H3 N CH R C O O + _ pKa = 10 pKb = 12

Zwitterion Formation H,N-CH一C-OH H.N-CH-C-O R R uncharged structure dipolar ion,or zwitterion (minor component) (major component) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Amino acid exists as a dipolar ion. -COOH loses H+,-NH2 gains H+. -Actual structure depends on pH. Chapter 24 14
Chapter 24 14 Zwitterion Formation ▪ Amino acid exists as a dipolar ion. ▪ —COOH loses H+ , —NH2 gains H+ . ▪ Actual structure depends on pH
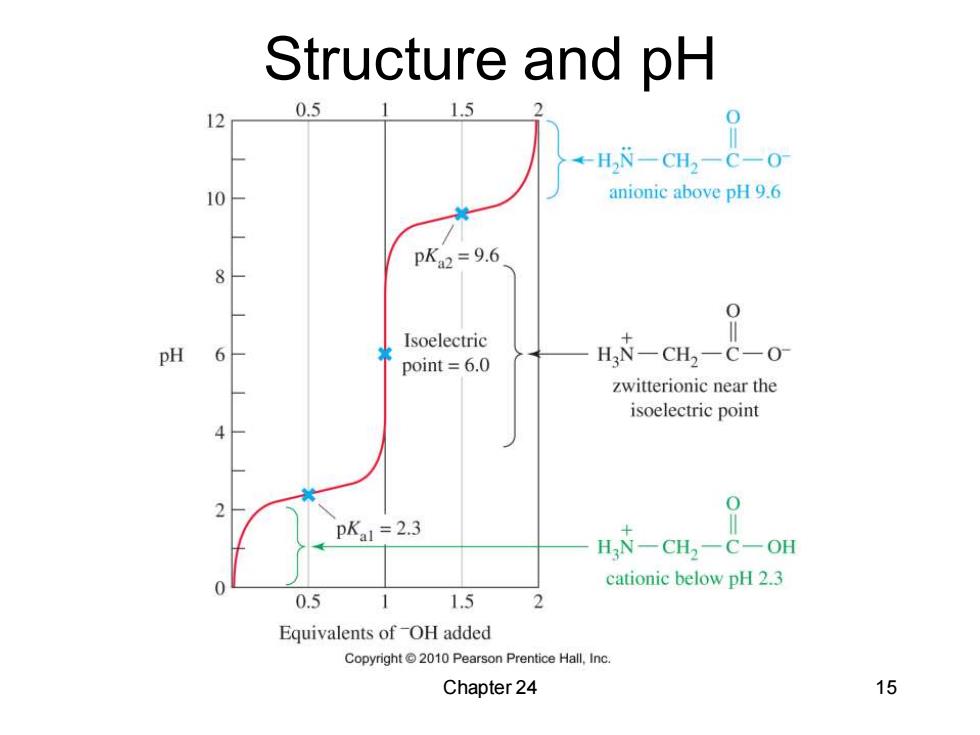
Structure and pH 15 12 0.5 ←H,N-CH2-C-0 anionic above pH 9.6 pKa2=9.6 0 Isoelectric point=6.0 H N-CH2-C-0- zwitterionic near the isoelectric point 0 pKal =2.3 H N-CH2-C-OH cationic below pH 2.3 0.5 1.5 Equivalents of OH added Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 24 15
Chapter 24 15 Structure and pH