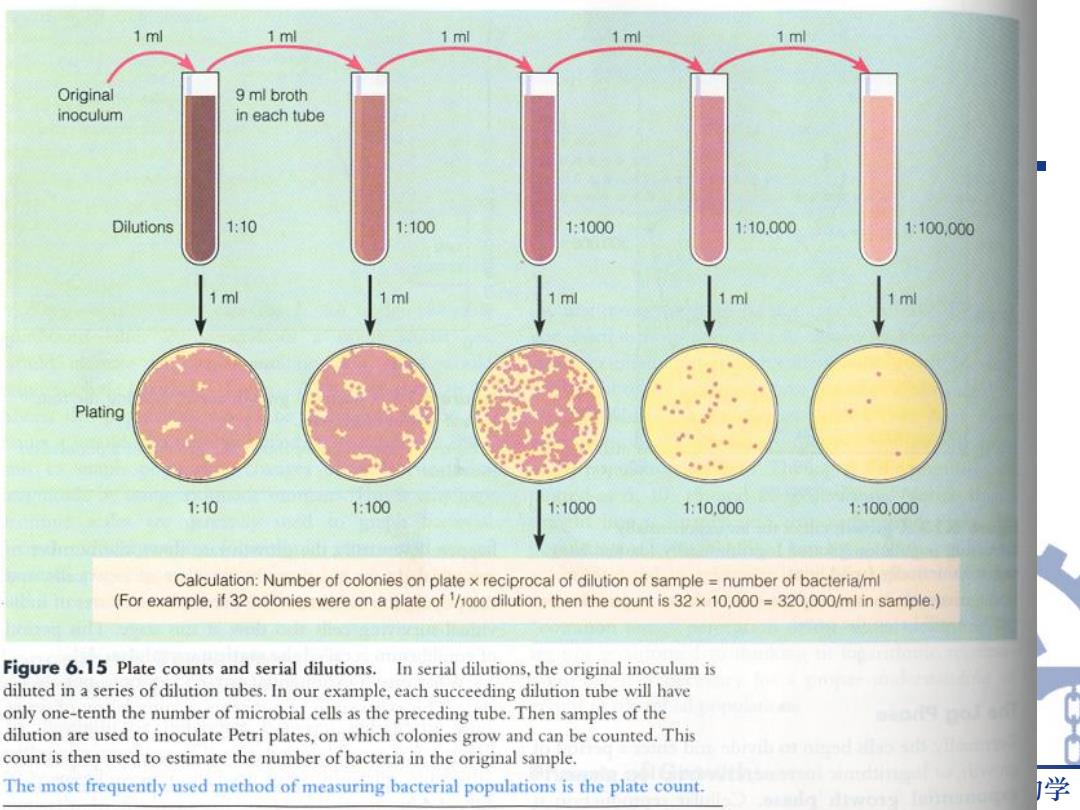
1 ml 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml Original 9 ml broth inoculum in each tube Dilutions 1:10 1:100 1:10.000 1100.000 ml 1 ml m 1 ml Plating 1:10 1:100 1:1000 1:10.000 1:100.000 Calculation:Number of colonies on plate x reciprocal of dilution of sample number of bacteria/ml (For example,if 32 colonies were on a plate of /1000 dilution,then the count is 32 x 10.000 320.000/ml in sample Figure 6.15 Plate counts and serial dilutions.In serial dilutions,the original inoculum is diluted in a series of dilution tubes.In our example,each succeeding dilution tube will have only one-tenth the number of microbial cells as the preceding tube.Then samples of the dilution are used to inoculate Petri plates,on which colonies grow and can be counted.This count is then used to estimate the number of bacteria in the original sample. The most frequently used method of measuring bacterial populations is the plate count. 学
Shanghai Jiao Tong University 陈峰,上海交通大学生命学院微生物学
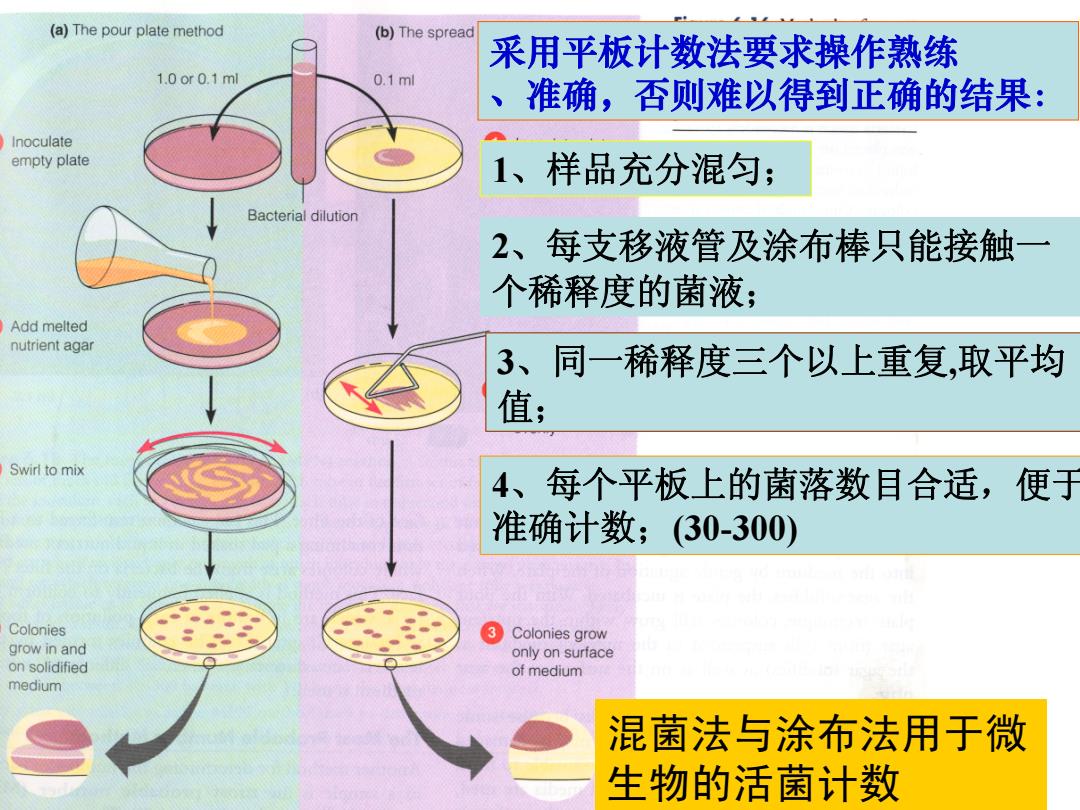
(a)The pour plate method (b)The spread 采用平板计数法要求操作熟练 1.0or0.1ml 0.1ml 、准确,否则难以得到正确的结果: Inoculate empty plate 1、样品充分混匀; Bacterial dilution 2、每支移液管及涂布棒只能接触 个稀释度的菌液; Add melted nutrient agar 3、同一稀释度三个以上重复,取平均 值; Swirl to mix 4、每个平板上的菌落数目合适,便于 准确计数;(30-300) Colonies 3 Colonies grow grow in and only on surface on solidified of medium medium 混菌法与涂布法用于微 生物的活菌计数
采用平板计数法要求操作熟练 、准确,否则难以得到正确的结果: 1、样品充分混匀; 2、每支移液管及涂布棒只能接触一 个稀释度的菌液; 3、同一稀释度三个以上重复,取平均 值; 4、每个平板上的菌落数目合适,便 于 准确计数;(30-300) 混菌法与涂布法用于微 生物的活菌计数

上游充通大睾 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 命66原 ARTEK COUNTER 2y0 CC (a) (b) Figure 6.5 Equipment for Counting Bacterial Colonies.(a)The Quebec colony counter.The counter illuminates the petri plate uniformly from the side,and the plate is magnified for easier counting of small colonies.In this sophisticated model an electric probe is touched to each colony to record the count.(b)An automated counter.The camera forms an enlarged image of the plate:all objects of the desired size range in any part of the image are counted by the instrument.The counter may be connected to a separate computer. 陈峰,上海交通大学生命学院微生物学
Shanghai Jiao Tong University 陈峰,上海交通大学生命学院微生物学

上浒充通大睾 Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1、间接计数法(活菌计数法) 如何对菌数低的样品,如水,中的细菌数量进行统计? 2)膜过滤培养法 菌数低的样品→膜过滤→培养→ 菌落计数 陈峰,上海交通大学生命学院微生物学
Shanghai Jiao Tong University 陈峰,上海交通大学生命学院微生物学 2)膜过滤培养法 菌数低的样品→ 膜过滤 → 培养 → 菌落计数 如何对菌数低的样品,如水,中的细菌数量进行统计? 1、间接计数法(活菌计数法)

上游充通大¥ Shanghai Jiao Tong University Figure 6.17 Counting bacteria by filtration.(a)The bacteria in 100 ml of water were sieved out onto the surface of a membrane filter.(b)Such a filter,with the bacteria much more widely spaced, was placed on a pad saturated with liquid nutrient medium,and the individual bacteria grew into visible colonies.One hundred twenty four colonies are visible,so we would record 124 bacteria per 100 ml of water sample. Bacteria can be counted by filtra- tion when their quantity is very small. (b) (a) SEM 2um 1 陈峰,上海交通大学生命学院微生物学
Shanghai Jiao Tong University 陈峰,上海交通大学生命学院微生物学