《Biochemistry V》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Biochemistry V 课程代码 PHAR1113 课程性质 大类基础课程 授课对象 药学专业全英文方向 学 分 3 学 时 54 主讲教师 生物化学与分子生物学系教师 修订日期 2021/6/20 生物化学与分子生物学(第9版)查锡良,周春燕,药立波ISBN: 指定教材 978-7-117-26624-6人民卫生出版社 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: 生物化学是从分子水平研究生命活动的一门学科。经历了一个多世纪的发展,生物化学 的研究对象扩展到了细胞、生命活动的过程、个体的生长、发育和繁殖。Biochemistry V 以人体及与人类生命活动相关的生物为对象,以新陈代谢系统为中心,是药学基础理论、基 本知识和基本技能的重要奠基课程。本课程阐述了药理学和药物化学的基本概念,使学生知 其所以然,具有一定的新药研发能力,具有参与临床合理用药的能力,以及一定的科学研究 能力。全英文教学也将使学生具备一定的英语听、说、读、写能力,能够阅读本专业相关外 文资料。最终成长为优秀的有人文关怀的药学人才。 Biochemistry covers the basics and frontier of biological science.It asks the molecular basis and chemistry of the life.It seeks to understand the attributes of different macromolecules that constitute the basics of life;how signal of life is being transduced;how energy is being produced and utilized;how environment regulates the organism,how organism sense and response to the alterations and how different organs of higher eukaryotes interact and communicate with each other and etc.It is an important and indispensible course in medical education.This course is designed for students studying pharmaceutics and will introduce the basic biochemical rules and concepts. (二)课程目标: 根据药学专业的培养目标、毕业要求,本课程着重从以下几个方面强调对学生的培养。 课程目标1:知识目标 1.1掌握生物化学的基本理论如核酸、蛋白质等生物大分子的结构和功能,酶的调节机 Master fundamental biochemistry theories,such as the structures and functions of macromolecules and the regulation of enzymes
《Biochemistry V》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 英文名称 Biochemistry V 课程代码 PHAR1113 课程性质 大类基础课程 授课对象 药学专业全英文方向 学 分 3 学 时 54 主讲教师 生物化学与分子生物学系教师 修订日期 2021/6/20 指定教材 生 物 化 学 与 分 子 生 物 学 ( 第 9 版 ) 查 锡 良 , 周 春 燕 , 药 立 波 ISBN : 978-7-117-26624-6 人民卫生出版社 二、课程目标 (一)总体目标: 生物化学是从分子水平研究生命活动的一门学科。经历了一个多世纪的发展,生物化学 的研究对象扩展到了细胞、生命活动的过程、个体的生长、发育和繁殖。Biochemistry V 以人体及与人类生命活动相关的生物为对象,以新陈代谢系统为中心,是药学基础理论、基 本知识和基本技能的重要奠基课程。本课程阐述了药理学和药物化学的基本概念,使学生知 其所以然,具有一定的新药研发能力,具有参与临床合理用药的能力,以及一定的科学研究 能力。全英文教学也将使学生具备一定的英语听、说、读、写能力,能够阅读本专业相关外 文资料。最终成长为优秀的有人文关怀的药学人才。 Biochemistry covers the basics and frontier of biological science. It asks the molecular basis and chemistry of the life. It seeks to understand the attributes of different macromolecules that constitute the basics of life; how signal of life is being transduced; how energy is being produced and utilized; how environment regulates the organism, how organism sense and response to the alterations and how different organs of higher eukaryotes interact and communicate with each other and etc. It is an important and indispensible course in medical education. This course is designed for students studying pharmaceutics and will introduce the basic biochemical rules and concepts. (二)课程目标: 根据药学专业的培养目标、毕业要求,本课程着重从以下几个方面强调对学生的培养。 课程目标 1:知识目标 1.1 掌握生物化学的基本理论如核酸、蛋白质等生物大分子的结构和功能,酶的调节机 制等;Master fundamental biochemistry theories, such as the structures and functions of macromolecules and the regulation of enzymes
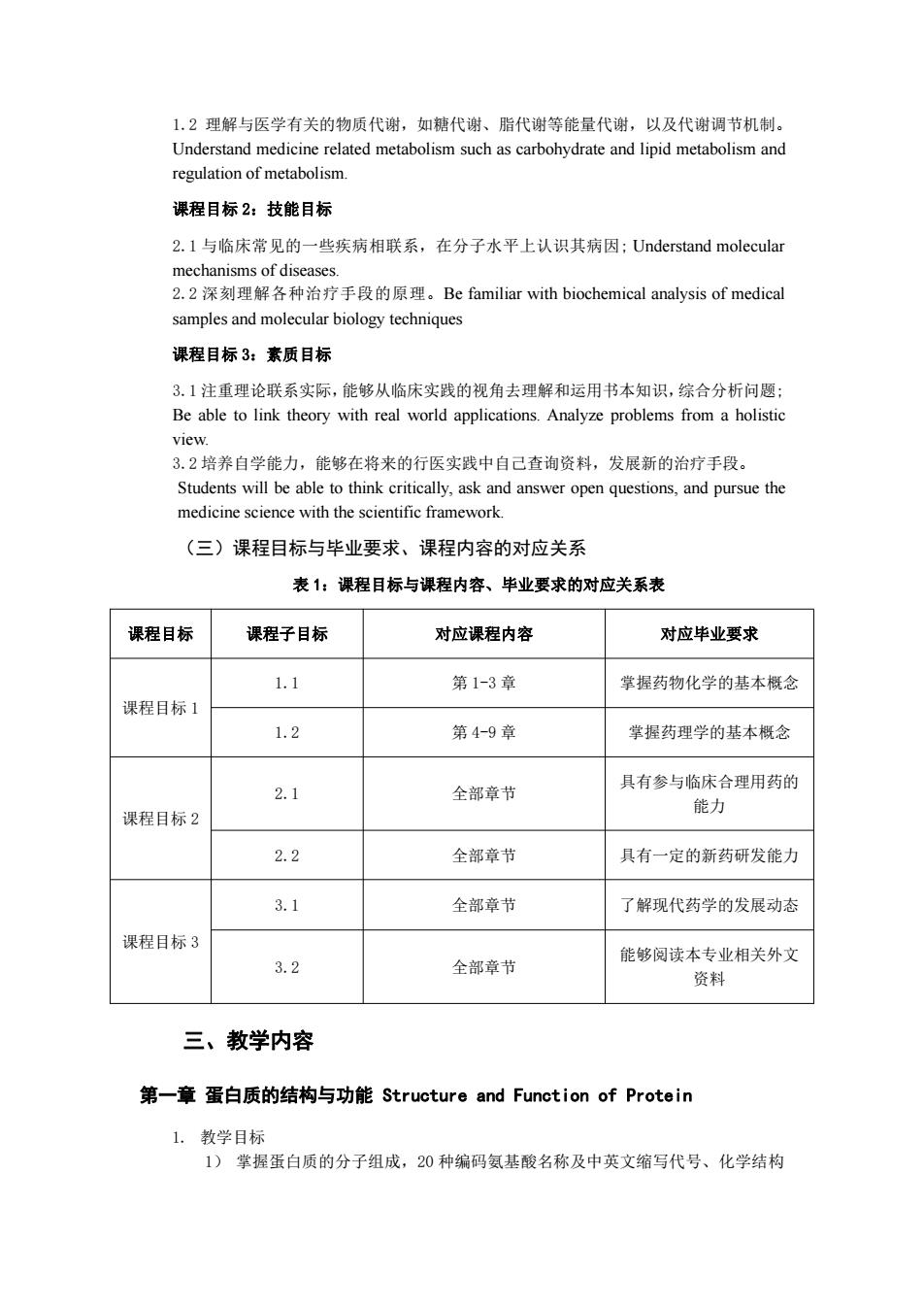
1.2理解与医学有关的物质代谢,如糖代谢、脂代谢等能量代谢,以及代谢调节机制。 Understand medicine related metabolism such as carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and regulation of metabolism. 课程目标2:技能目标 2.1与临床常见的一些疾病相联系,在分子水平上认识其病因:Understand molecular mechanisms of diseases. 2.2深刻理解各种治疗手段的原理。Be familiar with biochemical analysis of medical samples and molecular biology techniques 课程目标3:素质目标 3.1注重理论联系实际,能够从临床实践的视角去理解和运用书本知识,综合分析问题: Be able to link theory with real world applications.Analyze problems from a holistic view. 3.2培养自学能力,能够在将来的行医实践中自己查询资料,发展新的治疗手段。 Students will be able to think critically,ask and answer open questions,and pursue the medicine science with the scientific framework. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系 表1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 课程目标 课程子目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 1.1 第1-3章 掌握药物化学的基本概念 课程目标1 1.2 第4-9章 掌握药理学的基本概念 2.1 全部章节 具有参与临床合理用药的 能力 课程目标2 2.2 全部章节 具有一定的新药研发能力 3.1 全部章节 了解现代药学的发展动态 课程目标3 能够阅读本专业相关外文 3.2 全部章节 资料 三、教学内容 第一章蛋白质的结构与功能Structure and Function of Protein 1.教学目标 1)掌握蛋白质的分子组成,20种编码氨基酸名称及中英文缩写代号、化学结构
1.2 理解与医学有关的物质代谢,如糖代谢、脂代谢等能量代谢,以及代谢调节机制。 Understand medicine related metabolism such as carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and regulation of metabolism. 课程目标 2:技能目标 2.1 与临床常见的一些疾病相联系,在分子水平上认识其病因; Understand molecular mechanisms of diseases. 2.2 深刻理解各种治疗手段的原理。Be familiar with biochemical analysis of medical samples and molecular biology techniques 课程目标 3:素质目标 3.1 注重理论联系实际,能够从临床实践的视角去理解和运用书本知识,综合分析问题; Be able to link theory with real world applications. Analyze problems from a holistic view. 3.2 培养自学能力,能够在将来的行医实践中自己查询资料,发展新的治疗手段。 Students will be able to think critically, ask and answer open questions, and pursue the medicine science with the scientific framework. (三)课程目标与毕业要求、课程内容的对应关系 表 1:课程目标与课程内容、毕业要求的对应关系表 课程目标 课程子目标 对应课程内容 对应毕业要求 课程目标 1 1.1 第 1-3 章 掌握药物化学的基本概念 1.2 第 4-9 章 掌握药理学的基本概念 课程目标 2 2.1 全部章节 具有参与临床合理用药的 能力 2.2 全部章节 具有一定的新药研发能力 课程目标 3 3.1 全部章节 了解现代药学的发展动态 3.2 全部章节 能够阅读本专业相关外文 资料 三、教学内容 第一章 蛋白质的结构与功能 Structure and Function of Protein 1. 教学目标 1) 掌握蛋白质的分子组成,20 种编码氨基酸名称及中英文缩写代号、化学结构

及分类法。在蛋白质结构中连接氨基酸的共价键和非共价键。蛋白质的一级结 构和空间结构(构象)。蛋白质的理化性质。The molecular component of proteins;abbreviation,chemical constitution and taxonomy of 20 common amino acids;covalent bond and noncovalent bond linkage of amino acids in proteins;the primary structure of proteins;physical and chemical properties of amino acids. 2)熟悉蛋白质一级结构、空间结构与功能的关系,一级结构是空间构象的基础, 一 级结构的个体差异与分子病。The primary structure of proteins; structure-function relationships of proteins;primary structure is the basis of the conformation of proteins; 3)了解蛋白质分离纯化方法的基本原理:多肽链中氨基酸序列分析及空间结构测 定方法。Fundamental principles of separation and purification of proteins;amino acid sequence analysis of polypeptide;methods of spatial structure determination. 2.教学重难点 1)氨基酸结构和理化性质 2)蛋白质结构与功能 3)血红蛋白携氧曲线 3.教学内容 1)蛋白质的分子组成:元素组成。组成单位一一氨基酸,氨基酸的理化性质。氨 基酸的等电点。氨基酸的紫外吸收性质。茚三酮反应。肽、N-末端和C-末端。 The structure and classification of amino acids;physical and chemical properties of amino acids;peptide;N-terminus and C-terminus. 2)蛋白质的分子结构:一级结构(Primary structure),二级结构(secondary structure),模体(motif),空间结构(spatial structure)一一构象 (conformation):主链构象、侧链构象(main chain and side chain),三级 结构(tertiary structure of proteins),结构域(structural domain)和分 子伴侣(molecular chaperones)。四级结构(quaternary structure)。 3)蛋白质的分类:辅基,纤维状蛋白,球状蛋白,蛋白质家族和同源蛋白质 (homologous protein). 4)蛋白质结构与功能的关系(Structure-function relationship of proteins): 一级结构是空间构象的基础,一级结构的个体差异(individual difference) 与分子病(molecular disease)。构象与功能的关系:肌红蛋白(myoglobin)和 血红蛋白结构(hemoglobin),血红蛋白的构象变化与结合氧,蛋白质构象改变 与疾病。 5)蛋白质的理化性质及其分离纯化(physical-chemical property, disassociation and purification of proteins):蛋白质的两性解离 (amphoteric dissociation of proteins)和等电点(isoelectric point),胶 体性质(colloidal properties).,蛋白质的变性(denaturation)、沉淀 (precipitation)和凝固(coagulation),紫外吸收(ultraviolet absorption) 和几种重要呈色反应(colormetric reaction)。蛋白质的分离和纯化:透析、 超滤、盐析、丙酮沉淀、免疫沉淀、电泳(electrophoresis),凝胶过滤(gel filtration),离子交换层析,超速离心法。多肽链中氨基酸序列分析。蛋白 质空间结构测定(spatial structure determination)
及分类法。在蛋白质结构中连接氨基酸的共价键和非共价键。蛋白质的一级结 构和空间结构(构象)。蛋白质的理化性质。The molecular component of proteins; abbreviation, chemical constitution and taxonomy of 20 common amino acids; covalent bond and noncovalent bond linkage of amino acids in proteins; the primary structure of proteins; physical and chemical properties of amino acids. 2) 熟悉蛋白质一级结构、空间结构与功能的关系,一级结构是空间构象的基础, 一级结构的个体差异与分子病。The primary structure of proteins; structure-function relationships of proteins; primary structure is the basis of the conformation of proteins; 3) 了解蛋白质分离纯化方法的基本原理;多肽链中氨基酸序列分析及空间结构测 定 方 法 。Fundamental principles of separation and purification of proteins; amino acid sequence analysis of polypeptide; methods of spatial structure determination. 2. 教学重难点 1) 氨基酸结构和理化性质 2) 蛋白质结构与功能 3) 血红蛋白携氧曲线 3. 教学内容 1) 蛋白质的分子组成:元素组成。组成单位——氨基酸,氨基酸的理化性质。氨 基酸的等电点。 氨基酸的紫外吸收性质。茚三酮反应。肽、N-末端和 C-末端。 The structure and classification of amino acids; physical and chemical properties of amino acids; peptide; N-terminus and C-terminus. 2) 蛋白质的分子结构:一级结构(Primary structure),二级结构(secondary structure),模体(motif),空间结构(spatial structure)——构象 (conformation):主链构象、侧链构象(main chain and side chain),三级 结构(tertiary structure of proteins),结构域(structural domain)和分 子伴侣(molecular chaperones)。四级结构(quaternary structure)。 3) 蛋白质的分类:辅基,纤维状蛋白,球状蛋白,蛋白质家族和同源蛋白质 (homologous protein). 4) 蛋白质结构与功能的关系(Structure-function relationship of proteins): 一级结构是空间构象的基础,一级结构的个体差异(individual difference) 与分子病(molecular disease)。构象与功能的关系:肌红蛋白(myoglobin)和 血红蛋白结构(hemoglobin),血红蛋白的构象变化与结合氧,蛋白质构象改变 与疾病。 5) 蛋白质的理化性质及其分离纯化(physical-chemical property , disassociation and purification of proteins):蛋白质的两性解离 (amphoteric dissociation of proteins)和等电点(isoelectric point),胶 体性质(colloidal properties),蛋白质的变性(denaturation)、沉淀 (precipitation)和凝固(coagulation),紫外吸收(ultraviolet absorption) 和几种重要呈色反应(colormetric reaction)。蛋白质的分离和纯化: 透析、 超滤、盐析、丙酮沉淀、免疫沉淀、电泳(electrophoresis),凝胶过滤(gel filtration),离子交换层析,超速离心法。多肽链中氨基酸序列分析。蛋白 质空间结构测定(spatial structure determination)

4.教学方法 教师教授为主,适当的PBL教学和翻转课堂.Lecturing supplemented with PBL and flipped classroom. 5.教学评价 闭卷考试结合形成性评价.Close book exams:midterm and final exams..Formats:MCQ, Term definitions,Essay questions.Procedural evaluations:Presentations and homework 第二章核酸的结构与功能Structure and Function of Nucleic Acid 1.教学目标 l)掌握核酸的化学组成chemical composition of nucleic acid,核苷酸的碱基 (base)及磷酸戊糖(phosphate pentose)。核酸的一级结构。DNA的二级结构, DNA双螺旋、超螺旋和核小体结构特点与其生理意义。RNA种类,RNA的二级结 构,tRNA的三级结构与功能。 2)熟悉核酸的重要理化性质及意义physico-chemical property and significance of nucleic acid.。核酸酶的概念nucleinase.。 3)了解DNA结构多样性:真核生物染色体的结构及其它小分子RNA的种类与功能。 structural versatility of DNA,structure of chromosome of eukaryote, types and function of RNA. 2.教学重难点 1)核苷酸的结构 2)双螺旋模型要点 3)三种主要RNA的功能与特点 4)核酸变性复性与杂交 3.教学内容 1)核酸的化学组成及一级结构(primary structure):核苷(nucleoside)、核苷酸 (nucleotide)的组成及结构。核酸的一级结构。 2)DNA的空间结构与功能(spatial structure and function of DNA):DNA双螺 旋结构模型要点(main points of DNA double helix model),双螺旋结构的 多样性。超螺旋结构(superhelix)、核小体(nucleosome).及DNA在真核细胞内 的组装(package of DNA in eucaryotic cell)。 3)RNA的结构与功能(structure and function of RNA):RNA类型及功能(types and function of RNA)。tRNA的三级结构(tertiary structure)。rRNA为组分的核 糖体。其他小分子RNA及RNA组学简介。 4)核酸的理化性质(physico--chemical property of nucleic acid),:核酸分子的 紫外吸收。DNA的变性(denaturation)、复性(renaturation)与分子杂交 (molecular hybridization),,增色效应(hyperchromicity)。 4.教学方法 教师教授为主,适当的PBL教学和翻转课堂。Lecturing supplemented with PBL and flipped classroom. 5.教学评价 闭卷考试结合形成性评价.Close book exams:midterm and final exams..Formats:MCQ, Term definitions,Essay questions.Procedural evaluations:Presentations and
4. 教学方法 教师教授为主,适当的 PBL 教学和翻转课堂。Lecturing supplemented with PBL and flipped classroom. 5.教学评价 闭卷考试结合形成性评价。Close book exams: midterm and final exams. Formats: MCQ, Term definitions, Essay questions. Procedural evaluations: Presentations and homework 第二章 核酸的结构与功能 Structure and Function of Nucleic Acid 1. 教学目标 1) 掌握核酸的化学组成 chemical composition of nucleic acid,核苷酸的碱基 (base)及磷酸戊糖(phosphate pentose)。核酸的一级结构。DNA 的二级结构, DNA 双螺旋、超螺旋和核小体结构特点与其生理意义。RNA 种类,RNA 的二级结 构,tRNA 的三级结构与功能。 2) 熟 悉 核 酸 的 重 要 理 化 性 质 及 意 义 physico-chemical property and significance of nucleic acid。核酸酶的概念 nucleinase。 3) 了解 DNA 结构多样性;真核生物染色体的结构及其它小分子 RNA 的种类与功能。 structural versatility of DNA, structure of chromosome of eukaryote, types and function of RNA. 2. 教学重难点 1) 核苷酸的结构 2) 双螺旋模型要点 3) 三种主要 RNA 的功能与特点 4) 核酸变性复性与杂交 3. 教学内容 1) 核酸的化学组成及一级结构(primary structure):核苷(nucleoside)、核苷酸 (nucleotide)的组成及结构。核酸的一级结构。 2) DNA 的空间结构与功能(spatial structure and function of DNA):DNA 双螺 旋结构模型要点(main points of DNA double helix model) ,双螺旋结构的 多样性。超螺旋结构(superhelix)、核小体(nucleosome)及 DNA 在真核细胞内 的组装(package of DNA in eucaryotic cell)。 3) RNA 的结构与功能(structure and function of RNA):RNA 类型及功能(types and function of RNA)。tRNA 的三级结构(tertiary structure)。rRNA 为组分的核 糖体。其他小分子 RNA 及 RNA 组学简介。 4) 核酸的理化性质(physico-chemical property of nucleic acid):核酸分子的 紫外吸收。DNA 的变性(denaturation)、复性(renaturation)与分子杂交 (molecular hybridization),增色效应(hyperchromicity)。 4. 教学方法 教师教授为主,适当的 PBL 教学和翻转课堂。Lecturing supplemented with PBL and flipped classroom. 5.教学评价 闭卷考试结合形成性评价。Close book exams: midterm and final exams. Formats: MCQ, Term definitions, Essay questions. Procedural evaluations: Presentations and

homework 第三章酶Enzyme 1.教学目标 1)掌握酶的概念和分子组成,酶蛋白、辅助因子(辅酶或辅基)、全酶。酶的必需 基团和活性中心。同工酶概念。酶促反应特点。酶促反应动力学概念,米氏方 程及K的意义。酶的激活与抑制、原理及特点。酶原、酶原激活概念。作为辅 酶或辅基成分的B族维生素及其作用:微量元素的主要功能。concept and molecular organization of enzyme,apoenzyme,cofactor(coenzyme or prothetic group),holoenzyme,essential group and active center of enzyme,concept of isoenzyme.features of enzymatic reaction,concept of enzyme kinetics,Michealis equation and significance of Km, activation,inhibition and principle and features of enzyme,concept of proenzyme,proenzyme activation.Coenzyme and prothetic group part of B-family vitamin;Major function of minor element. 2)熟悉酶的作用机制。影响酶作用的温度及pH因素。变构酶概念、作用特点及意 义。维生素概念及分类。微量元素的概念和种类.Mechanism of action of enzyme, effect of temperature and pH on enzyme action,concept,functional features of allosteric enzyme.Concept and classification of vitamin; concept and species of minor element; 3)了解酶的命名与分类。酶含量的调节。酶与医学的关系。脂溶性维生素的化学 结构与功用,微量元素与临床疾病的关系。Denomination and classification of enzyme,regulation of enzyme,relationship between enzyme and medicine.Chemicial constitution and function of fat soluble vitamins: relationship between minor element and clinical disease. 2.教学重难点 1)酶的作用机制 2)酶反应动力学 3)酶的调节机制 4)维生素 3.教学内容 l)酶的概念和分子结构:酶的概念,酶的组成一一单纯酶(simple enzyme)和结合 酶(conjugated enzymes).,全酶(holoenzyme)包括酶蛋白(apoenzyme)和辅酶 (coenzyme)或辅基(prothetic group)。酶活性中心(enzyme active center). 的概念与作用。同工酶(isoenzyme)的概念。 2)酶促反应的特点与机制:高催化效率、高特异性及可调节性。酶-底物复合物 (enzyme-substrate compound)的形成、诱导契合假说(induced-fit hypothesis). 简介。 3)酶促反应动力学(enzyme kinetics):酶促反应动力学概念。底物浓度 (concentration of substrate)和酶浓度对反应速度的影响,米氏方程 (Michealis equation)简介、Km值的意义、Vmax及Km值的测定法。温度、pH、 激活剂(reactivator)及抑制剂(inhibitor)对反应速度的影响。 4)酶的调节:酶活性(enzyme activity)的调节,酶原(proenzyme)与酶原激活
homework 第三章 酶 Enzyme 1. 教学目标 1) 掌握酶的概念和分子组成,酶蛋白、辅助因子(辅酶或辅基)、全酶。酶的必需 基团和活性中心。同工酶概念。酶促反应特点。酶促反应动力学概念,米氏方 程及 Km 的意义。酶的激活与抑制、原理及特点。酶原、酶原激活概念。作为辅 酶或辅基成分的 B 族维生素及其作用;微量元素的主要功能。concept and molecular organization of enzyme, apoenzyme, cofactor(coenzyme or prothetic group), holoenzyme, essential group and active center of enzyme, concept of isoenzyme. features of enzymatic reaction, concept of enzyme kinetics, Michealis equation and significance of Km, activation, inhibition and principle and features of enzyme, concept of proenzyme, proenzyme activation.Coenzyme and prothetic group part of B-family vitamin; Major function of minor element. 2) 熟悉酶的作用机制。影响酶作用的温度及 pH 因素。变构酶概念、作用特点及意 义。维生素概念及分类。微量元素的概念和种类。Mechanism of action of enzyme, effect of temperature and pH on enzyme action, concept, functional features of allosteric enzyme.Concept and classification of vitamin; concept and species of minor element; 3) 了解酶的命名与分类。酶含量的调节。酶与医学的关系。脂溶性维生素的化学 结构与功用,微量元素与临床疾病的关系。 Denomination and classification of enzyme, regulation of enzyme, relationship between enzyme and medicine. Chemicial constitution and function of fat soluble vitamins; relationship between minor element and clinical disease. 2. 教学重难点 1) 酶的作用机制 2) 酶反应动力学 3) 酶的调节机制 4) 维生素 3. 教学内容 1) 酶的概念和分子结构:酶的概念,酶的组成——单纯酶(simple enzyme)和结合 酶(conjugated enzymes),全酶(holoenzyme)包括酶蛋白(apoenzyme)和辅酶 (coenzyme)或辅基(prothetic group)。酶活性中心(enzyme active center) 的概念与作用。同工酶(isoenzyme)的概念。 2) 酶促反应的特点与机制:高催化效率、高特异性及可调节性。酶-底物复合物 (enzyme-substrate compound)的形成、诱导契合假说(induced-fit hypothesis) 简介。 3) 酶促 反应动力 学(enzyme kinetics):酶 促反应动 力学概念 。底物浓 度 (concentration of substrate)和 酶 浓 度对 反 应 速 度 的 影 响, 米 氏 方 程 (Michealis equation)简介、Km 值的意义、Vmax 及 Km 值的测定法。温度、pH、 激活剂(reactivator)及抑制剂(inhibitor)对反应速度的影响。 4) 酶的调节:酶活性(enzyme activity) 的调节,酶原(proenzyme)与酶原激活