苏州大学医学部药学院 教 案 课程名 称: Physical Chemistry 授课对 象: 2019级药学全英文班
苏州大学医学部药学院 教 案 课程名 称: Physical Chemistry 授课对 象: 2019 级药学全英文班

授课学 时: 54 教材版 《MARTIN'S PHYSICAL PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES》第6 本: 版 主讲教 邓益斌韩亮/刘密丁大伟 师: 苏州大学医学部药学院制 2020年8月20日 苏州大学医学部药学院授课教案 授课教师:邓益斌授课日期:2020.9.8 课程名 所属学 Physical Chemistry 药学 称 科
授课学 时: 54 教材版 本: 《MARTIN’S PHYSICAL PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES》第 6 版 主讲教 师: 邓益斌/韩亮/刘密/丁大伟 苏州大学医学部药学院制 2020 年 8 月 20 日 苏州大学医学部药学院授课教案 授课教师:邓益斌授课日期:2020.9.8 课程名 称 Physical Chemistry 所属学 科 药学
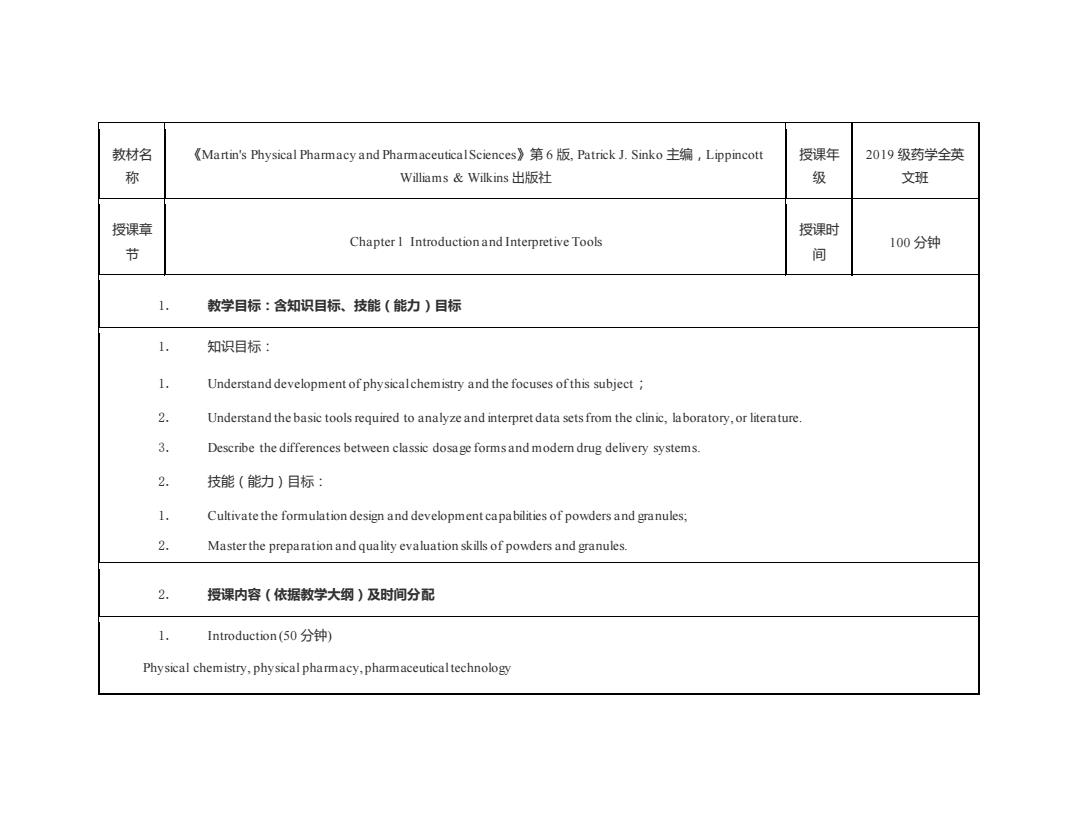
教材名 《Martin's Physical Pharmacy and PharmaceuticalSciences》第6版,Patrick J.Sinko主编,Lippincott 授课年 2019级药学全英 称 Williams&Wilkins出版社 级 文班 授课章 授课时 Chapter I Introductionand Interpretive Tools 节 100分钟 间 1. 教学目标:含知识目标、技能(能力)目标 1. 知识目标: 1. Understand development of physicalchemistry and the focuses ofthis subject 2. Understand the basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets from the clinic,laboratory,or literature. 3. Describe the differences between classic dosage forms and modem drug delivery systems. 2. 技能(能力)目标: 1. Cultivate the formulation design and development capabilities of powders and granules; 2. Master the preparation and quality evaluation skills of powders and granules. 2. 授课内容(依据教学大纲)及时间分配 1. Introduction(50分钟) Physical chemistry,physical pharmacy,pharmaceuticaltechnology
教材名 称 《Martin's Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences》第 6 版, Patrick J. Sinko 主编,Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 出版社 授课年 级 2019 级药学全英 文班 授课章 节 Chapter 1 Introduction and Interpretive Tools 授课时 间 100 分钟 1. 教学目标:含知识目标、技能(能力)目标 1. 知识目标: 1. Understand development of physical chemistry and the focuses of this subject; 2. Understand the basic tools required to analyze and interpret data sets from the clinic, laboratory, or literature. 3. Describe the differences between classic dosage forms and modern drug delivery systems. 2. 技能(能力)目标: 1. Cultivate the formulation design and development capabilities of powders and granules; 2. Master the preparation and quality evaluation skills of powders and granules. 2. 授课内容(依据教学大纲)及时间分配 1. Introduction (50 分钟) Physical chemistry, physical pharmacy, pharmaceutical technology

2. Measurements,data,propagation ofuncertainty (10) Data analysis tools,dimensionalanalysis,significant figures,data types 3. Error and describing variability(10分钟) Determinate errors,indeterminateerrors,precision and accuracy 4. Descriptive statistics(10分钟) Central tendency:mean,median,modes,variability:measures of dispersion 5. Visualizing results:graphic,methods,lines (20) Linear regression analysis 3. 教学重点与难点 1. 教学重点 (1 )The concept of physicalchemistry and its research focus; (2 )The method to leam physical chemistry; (3 )Data analysisand graphic presentation ofresults. 2. 教学难点 (1 )Understand the intrinsic characteristicsof physicalchemistry; (2 )How to demonstrate results through data analysisand graphic
2. Measurements, data, propagation of uncertainty (10 分钟) Data analysis tools, dimensional analysis, significant figures, data types 3. Error and describing variability (10 分钟) Determinate errors, indeterminate errors, precision and accuracy 4. Descriptive statistics (10 分钟) Central tendency: mean, median, modes, variability: measures of dispersion 5. Visualizing results: graphic, methods, lines (20 分钟) Linear regression analysis 3. 教学重点与难点 1. 教学重点 (1)The concept of physical chemistry and its research focus; (2)The method to learn physical chemistry; (3)Data analysis and graphic presentation of results. 2. 教学难点 (1)Understand the intrinsic characteristics of physical chemistry; (2)How to demonstrate results through data analysis and graphic

4. 教学方法选择 理论课堂教学 A.多媒体教学:(简要列出本章节多媒体教学设计特点及优势) 采用示意图、图片等介绍课程内容,尤其通过举例说明对难以理解的概念进行类比阐述。 B.互动教学:(根据实际情况列出案例/实例讨论、分析讨论、分组讨论、翻转课堂等互动教学内容标题) 课堂讲解、学生提问与课后习题相结合 5. 更新或补充内容提要 无 6. 复习思考题 1.After preparing a prescription calling for six capsules each containingthree grains ofaspirin,you remove the contents completely and weigh each.The weights are 2.85,2.80,3.02,3.05,2.95,and 3.15 grains.Compute the average weight of the contentsof the capsules,the average deviation,and the standard deviation.One gram is equalto 15.432 grains (gr.). 2.The dosage ofsome drugs is expressed in "units."Units are a measure of potency rather than quantity.For example,it has been found that each microgram ofpenicillinV is equivalent to 1.6 potency units.How many unitsare equivalent to 250 mg of penicillin V? 3.A milligram of d-alpha tocopherol is equivalent to 1.49 I.U.of vitamin E.A formula for vitamin E calls for 20 I.U.per capsule.How many kilograms of d-alpha tocopherolare required to make 200,000 capsules?
4. 教学方法选择 1. 理论课堂教学 A. 多媒体教学:(简要列出本章节多媒体教学设计特点及优势) 采用示意图、图片等介绍课程内容,尤其通过举例说明对难以理解的概念进行类比阐述。 B. 互动教学:(根据实际情况列出案例/实例讨论、分析讨论、分组讨论、翻转课堂等互动教学内容标题) 课堂讲解、学生提问与课后习题相结合 5. 更新或补充内容提要 无 6. 复习思考题 1. After preparing a prescription calling for six capsules each containing three grains of aspirin, you remove the contents c ompletely and weigh each. The weights are 2.85, 2.80, 3.02, 3.05, 2.95, and 3.15 grains. Compute the average weight of the contents of the capsules, the average deviation, and the standard deviation. One gram is equal to 15.432 grains (gr.). 2. The dosage of some drugs is expressed in “units.” Units are a mea sure of potency rather than quantity. For example, it has been found that each microgram of penicillinV is equivalent to 1.6 potency units. How many units are equivalent to 250 mg of penicillin V? 3. A milligram of d-alpha tocopherol is equivalent to 1.49 I.U. of vitamin E. A formula for vitamin E calls for 20 I.U. per capsule. How many kilograms of d-alpha tocopherol are required to make 200,000 capsules?