
Economies of Scale to Exploit Fixed Costs How do you decide whether to go shopping at a convenience store or at Sam's Club? We are going to talk about the following subjects: Lot sizing for a single product(EOQ) Aggregating multiple products in a single order Lot sizing with multiple products or customers Lots are ordered and delivered independently for each product Lots are ordered and delivered jointly for all products Lots are ordered and delivered jointly for a subset of products SEIEE AU406 10-11
+ - SEIEE AU406 Economies of Scale to Exploit Fixed Costs How do you decide whether to go shopping at a convenience store or at Sam’s Club? We are going to talk about the following subjects: Lot sizing for a single product (EOQ) Aggregating multiple products in a single order Lot sizing with multiple products or customers Lots are ordered and delivered independently for each product Lots are ordered and delivered jointly for all products Lots are ordered and delivered jointly for a subset of products 10-11
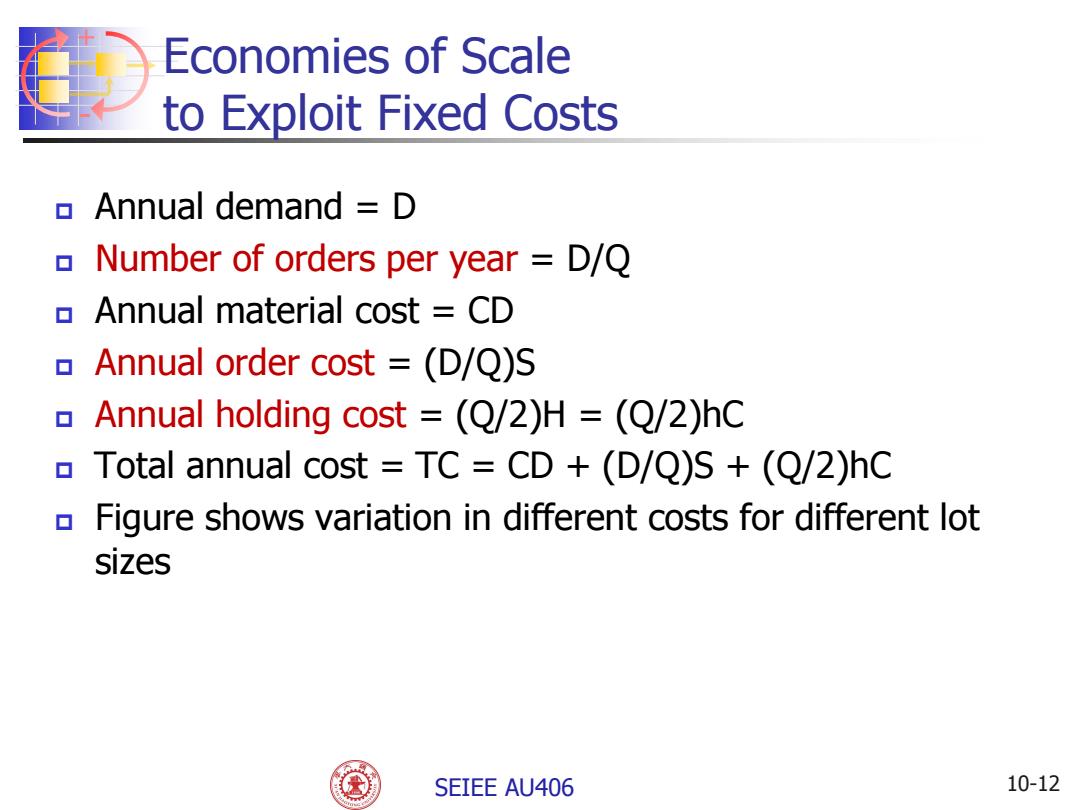
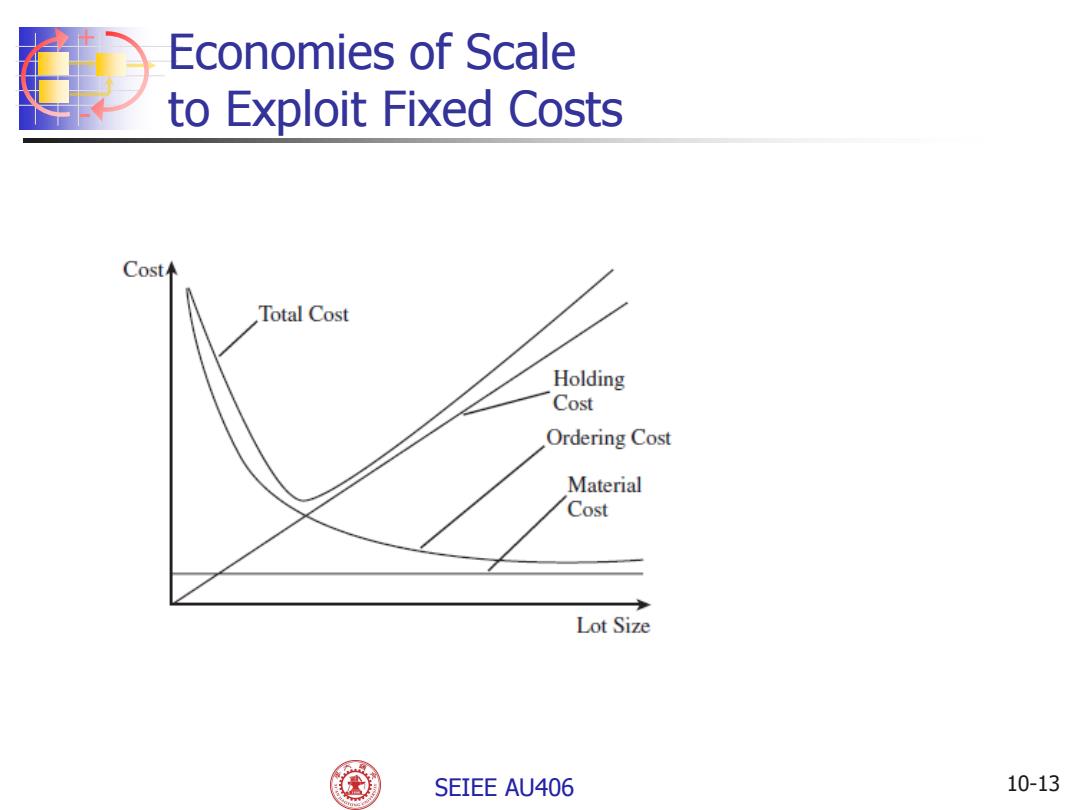
Economies of Scale to Exploit Fixed Costs Annual demand D Number of orders per year D/Q Annual material cost CD Annual order cost =(D/Q)S Annual holding cost =(Q/2)H =(Q/2)hC Total annual cost TC CD +(D/Q)S +(Q/2)hC Figure shows variation in different costs for different lot sizes SEIEE AU406 10-12
+ - SEIEE AU406 Economies of Scale to Exploit Fixed Costs Annual demand = D Number of orders per year = D/Q Annual material cost = CD Annual order cost = (D/Q)S Annual holding cost = (Q/2)H = (Q/2)hC Total annual cost = TC = CD + (D/Q)S + (Q/2)hC Figure shows variation in different costs for different lot sizes 10-12
Economies of Scale to Exploit Fixed Costs Cost◆ Total Cost Holding Cost Ordering Cost Material Cost Lot Size SEIEE AU406 10-13
+ - SEIEE AU406 Economies of Scale to Exploit Fixed Costs 10-13
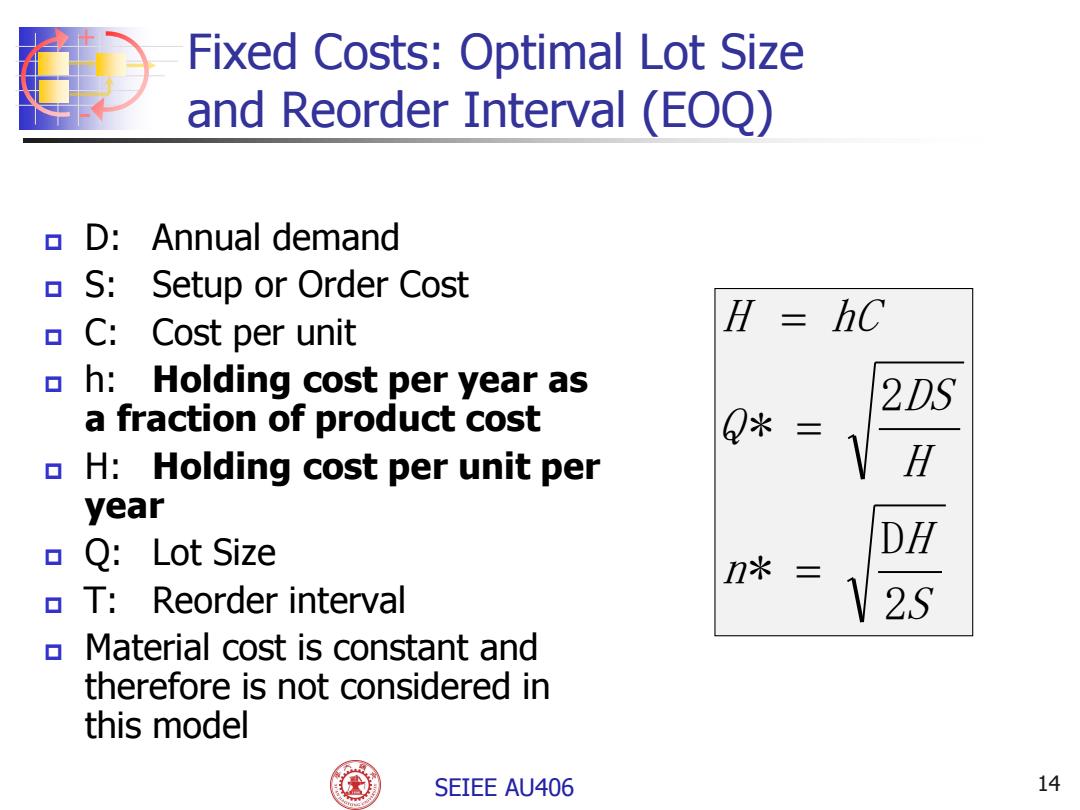
Fixed Costs:Optimal Lot Size and Reorder Interval (EOQ) D:Annual demand S:Setup or Order Cost C:Cost per unit H=hC h:Holding cost per year as 2DS a fraction of product cost Q* = H:Holding cost per unit per H year Q:Lot Size DH n* T:Reorder interval 2S Material cost is constant and therefore is not considered in this model SEIEE AU406 14
SEIEE AU406 + - Fixed Costs: Optimal Lot Size and Reorder Interval (EOQ) D: Annual demand S: Setup or Order Cost C: Cost per unit h: Holding cost per year as a fraction of product cost H: Holding cost per unit per year Q: Lot Size T: Reorder interval Material cost is constant and therefore is not considered in this model S H n H DS Q H hC 2 D * 2 * 14

Example 1:EOQ o Demand,D=12,000 computers per year d 1000 computers/month Unit cost,C=$500 Holding cost fraction,h =0.2 Fixed cost,S $4,000/order oQ*=Sqt[(2)(12000)(4000)/(0.2)(500)]=980 computers Cycle inventory Q/2 490 Flow time Q/2d 980/(2)(1000)=0.49 month Reorder interval,T =0.98 month SEIEE AU406 15
+ - SEIEE AU406 Example 1: EOQ Demand, D = 12,000 computers per year d = 1000 computers/month Unit cost, C = $500 Holding cost fraction, h = 0.2 Fixed cost, S = $4,000/order Q* = Sqrt[(2)(12000)(4000)/(0.2)(500)] = 980 computers Cycle inventory = Q/2 = 490 Flow time = Q/2d = 980/(2)(1000) = 0.49 month Reorder interval, T = 0.98 month 15