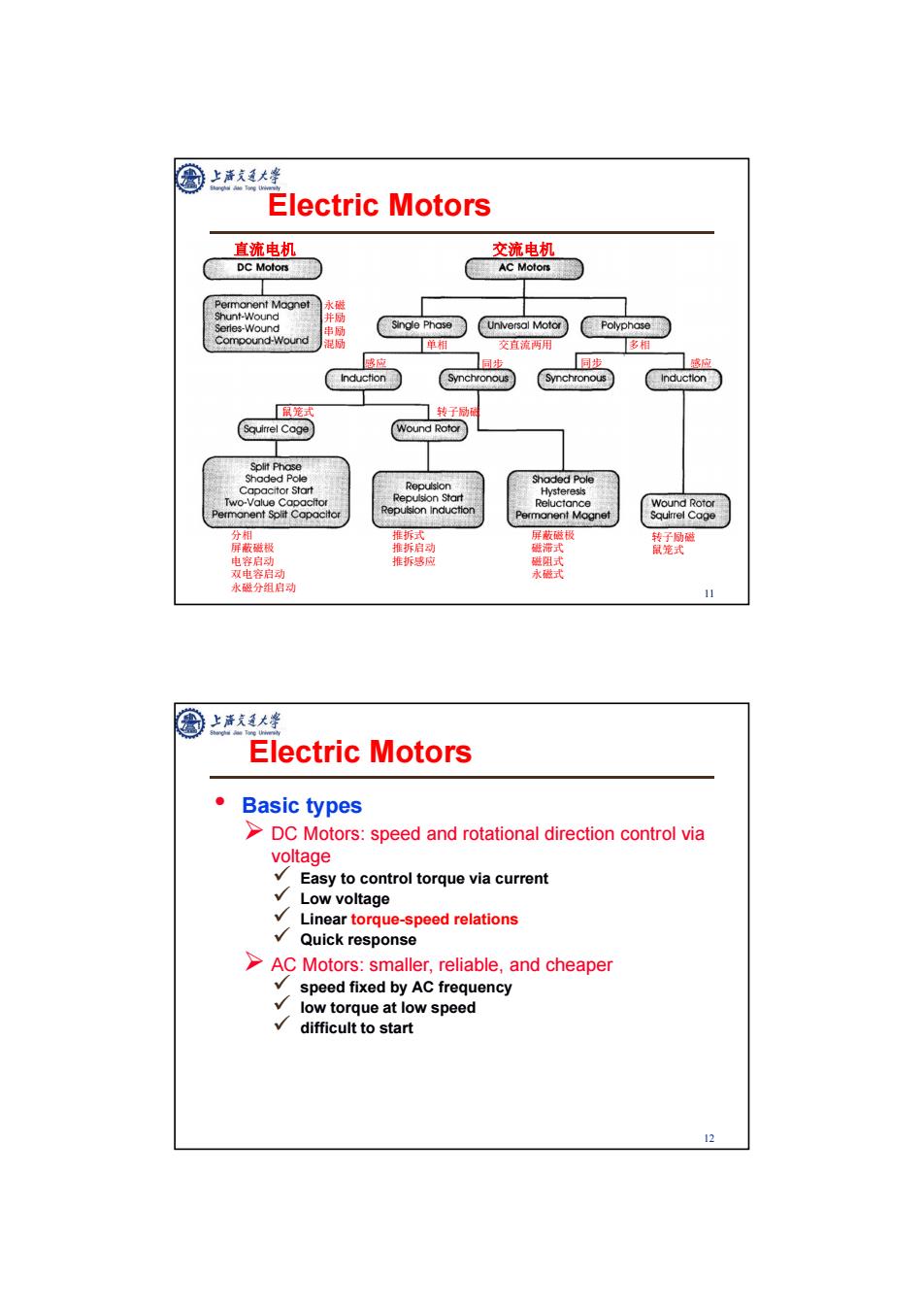
上帝克道大学 Electric Motors 直流电机 交流电机 DC Motors AC Motors黑 水磁 Shunt-Wound 并励 Serles-Wound 串励 Single Phase Universal Motor Polyphase Compound-Wound 混计 单相 交直流两用 多相 感应 同步 同步 感应 Induction Synchronous Synchronous 鼠笼式 转子励硫 Squirrel Cage Wound Rotor Split Phase shoded Pole Repulsion Shaded Pole Capacitor Start Two-Value Capacitor Repulsion Start Hysteresis Reluctance Wound Rotor Permanent Split Copacitor Permanent Mognet Squirrel Cage 分相 推拆式 屏蔽磁极 转子励磁 屏蔽磁极 碰滞式 鼠笼式 电容启动 推拆感应 磁阻式 双电容启动 永碳式 永磁分组启动 11 上清通大学 Electric Motors Basic types >DC Motors:speed and rotational direction control via voltage Easy to control torque via current √ Low voltage Linear torque-speed relations Quick response >AC Motors:smaller,reliable,and cheaper √ speed fixed by AC frequency low torque at low speed difficult to start 12
11 Electric Motors 直流电机 交流电机 永磁 并励 串励 混励 单相 交直流两用 多相 感应 同步 同步 感应 鼠笼式 转子励磁 分相 屏蔽磁极 电容启动 双电容启动 永磁分组启动 推拆式 推拆启动 推拆感应 屏蔽磁极 磁滞式 磁阻式 永磁式 转子励磁 鼠笼式 12 • Basic types DC Motors: speed and rotational direction control via voltage Easy to control torque via current Low voltage Linear torque-speed relations Quick response AC Motors: smaller, reliable, and cheaper speed fixed by AC frequency low torque at low speed difficult to start Electric Motors

圈上话衣大峰 OUTLINE Actuators introduction DC Motor:Principles of operation DC Motor:Torque-speed curves DC Motor:Performance parameters 13 圈上大学 DC Motors:Principles of Operation .A wire carrying current experiences a force in a magnetic field. F= iU×B) Magnetic Flux Density(磁通量) (Tesla) Induced force Current Length of wire in the (amp) direction of i(m) I×B I×B=|Bsin9 B 14
13 OUTLINE Actuators introduction DC Motor: Principles of operation DC Motor: Torque-speed curves DC Motor: Performance parameters 14 DC Motors: Principles of Operation • A wire carrying current experiences a force in a magnetic field. Magnetic Flux Density (磁通量) (Tesla) F i(l B) Induced force Current (amp) Length of wire in the direction of i (m) I B I B IB I B sin
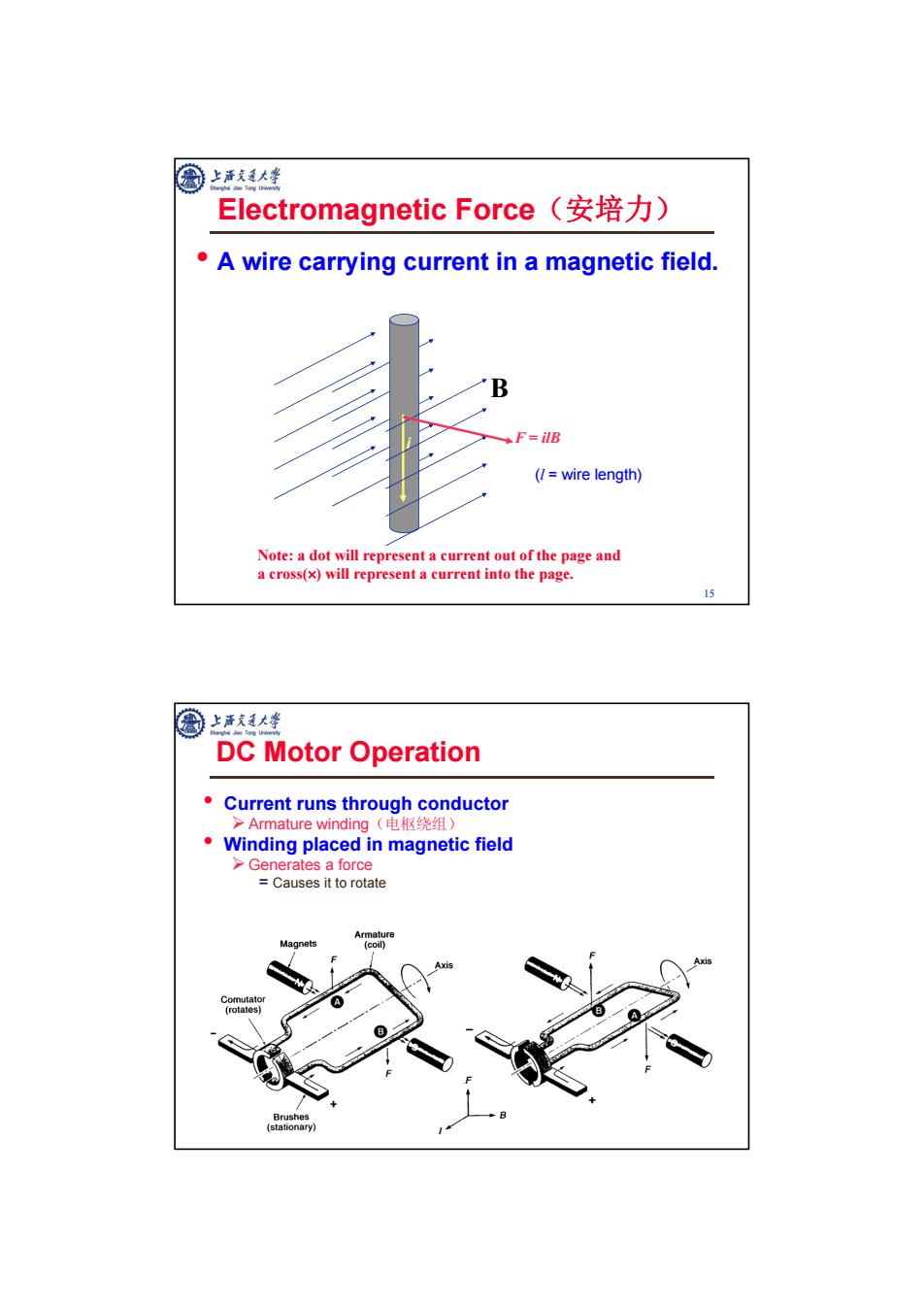
国上大峰 Electromagnetic Force(安培力) A wire carrying current in a magnetic field. B F=ilB (7=wire length) Note:a dot will represent a current out of the page and a cross(x)will represent a current into the page. 15 上海我通大学 DC Motor Operation Current runs through conductor >Armature winding(电枢绕组) Winding placed in magnetic field >Generates a force Causes it to rotate Armatt Magnets coil)
15 Electromagnetic Force(安培力) • A wire carrying current in a magnetic field. B i F = ilB (l = wire length) Note: a dot will represent a current out of the page and a cross() will represent a current into the page. 16 DC Motor Operation • Current runs through conductor Armature winding(电枢绕组) • Winding placed in magnetic field Generates a force = Causes it to rotate
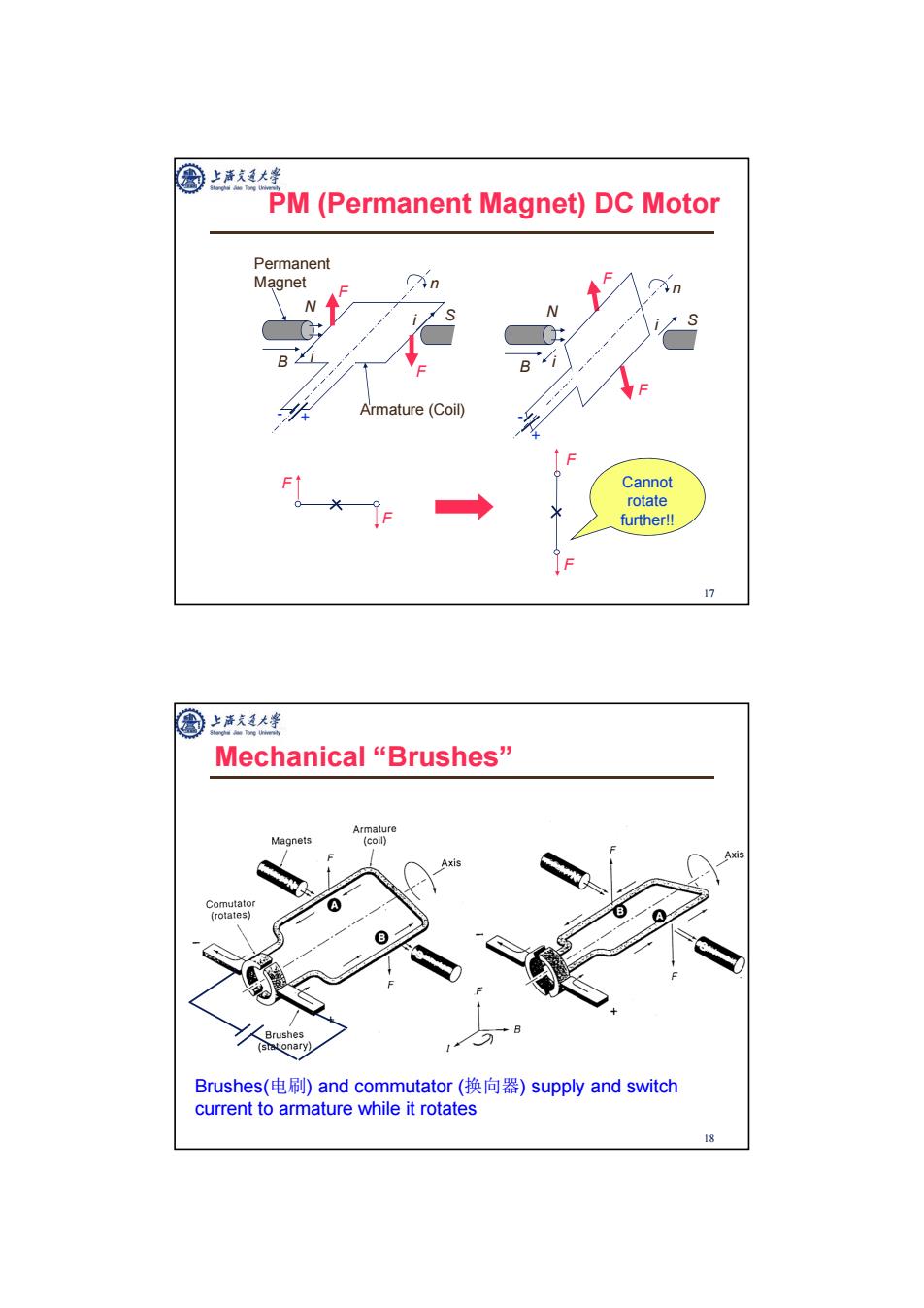
上帝克道大学 PM(Permanent Magnet)DC Motor Permanent Magnet n Armature (Coil) Cannot rotate further!! 1 国上大峰 Mechanical“Brushes” Armature Magnets (coil) Comutato (rotates) Brushes (⑤tationary) Brushes(电刷)and commutator(换向器)supply and switch current to armature while it rotates 18
17 PM (Permanent Magnet) DC Motor B N S Permanent Magnet i i + - n F F Armature (Coil) B N i S i + - n F F F F F F Cannot rotate further!! 18 Mechanical “Brushes” Brushes(电刷) and commutator (换向器) supply and switch current to armature while it rotates
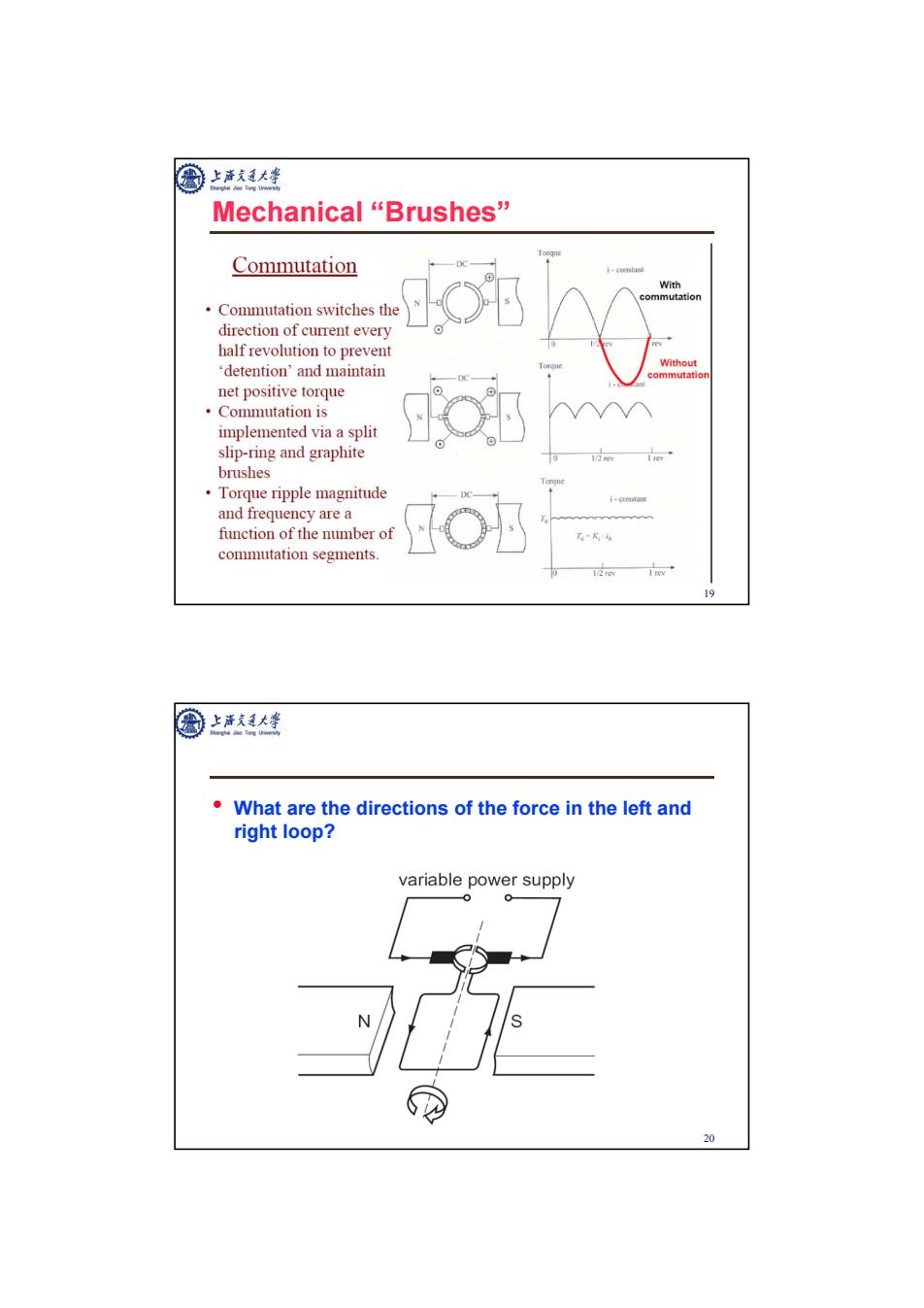
Mechanical“Brushes” Commutation With nmutation Commutation switches the direction of current every half revolution to prevent 'detention'and maintain Without commutatio net positive torque ·Commutation is implemented via a split o幼 slip-ring and graphite brushes Torque ripple magnitude and frequency are a function of the number of Hob commutation segments. 12a 19 What are the directions of the force in the left and right loop? variable power supply 0 0 20
19 Mechanical “Brushes” 20 • What are the directions of the force in the left and right loop?