
7Chapter2 Diseases of Digestive SystemVIMSigns,diagnosis&recoveryInflammationof themouthis a clinical sign of many diseases inlarge animals.Frothy salivation and reluctance to eat orresistance to oral examinationarethe clinical signs of acuteactive stomatitis.The animal should be sedated, and the mouthexamined carefully witha speculum.Any ulcers should becuretted刮to expose embedded foreign material,eg,grassawns,etc.Differential diagnosesincludeactinobacillosis放线杆菌病(woodentongue),foot-and-mouth disease,ma'lignant catarrhal fever牛恶性卡它热,and bovine viral diarrhea.Epidemicdiseases suchasswine vesicular disease猪传染性水泡病,andvesicularstomatitis inhorses must be differentiated from otherforms of acutenoninfectious or contagious stomatitis.16Guangdong Ocean University
16 p Signs, diagnosis & recovery Inflammation of the mouth is a clinical sign of many diseases in large animals. Frothy salivation and reluctance to eat or resistance to oral examination are the clinical signs of acute active stomatitis. The animal should be sedated, and the mouth examined carefully with a speculum. Any ulcers should be curetted刮 to expose embedded foreign material, eg, grass awns, etc. Chapter 2 Diseases of Digestive System p Differential diagnoses include actinobacillosis放线杆菌病 (wooden tongue), foot-and-mouth disease, ma‘lignant catarrhal fever牛恶 性卡它热, and bovine viral diarrhea. Epidemic diseases such as swine vesicular disease猪传染性水泡病, and vesicular stomatitis in horses must be differentiated from other forms of acute noninfectious or contagious stomatitis

7Chapter2Diseases of Digestive SystemVIMTreatment>If the etiology is ingestion of foreign material,changing thequality andquantityof thehaymayeffect recovery.【治疗原则】消除病因:摘除;锉平cynodont;原发病加强护理:柔软、营养、易消化净化口腔:1%食盐或1%硼酸,0.1%高锰酸钾收敛和消炎:1%明矾或1%酸,0.1%氯化苯甲烃铵,0.1%黄色素。10%硝酸银,洗涤后涂1%磺胺甘油VC、VB,及抗生素中兽医:清火消炎,消肿止痛一青黛散Guangdong Ocean University
17 【治疗原则】 消除病因:摘除;锉平cynodont ;原发病 加强护理:柔软、营养、易消化 净化口腔:1%食盐或1%硼酸,0.1%高锰酸钾 收敛和消炎:1%明矾或1%鞣酸,0.1%氯化苯甲烃 铵,0.1%黄色素。10%硝酸银,洗涤后涂1%磺胺 甘油;VC、VB2及抗生素 中兽医:清火消炎,消肿止痛—青黛散 ØIf the etiology is ingestion of foreign material, changing the quality and quantity of the hay may effect recovery. lTreatment Chapter 2 Diseases of Digestive System

7Chapter2Diseases of Digestive SystemVIMTREADBYYOURSELVESINYOURCHINESETEXTBOOK(《兽医内科学》)in page 10, PLEASE:普通高等教育一五”国家级观划教材1) catarrhal stomatitis;全国高等农林院校“十一五”规划教材2) vesicular stomatitis;兽医内科学3)ulcerativestomatitisSHOUYINEIKEXUE王建华主编18GuangdongOcean University
18 n READ BY YOURSELVES IN YOUR CHINESE TEXTBOOK(《兽医内科学》) in page 10, PLEASE: 1) catarrhal stomatitis; 2) vesicular stomatitis; 3) ulcerative stomatitis Chapter 2 Diseases of Digestive System
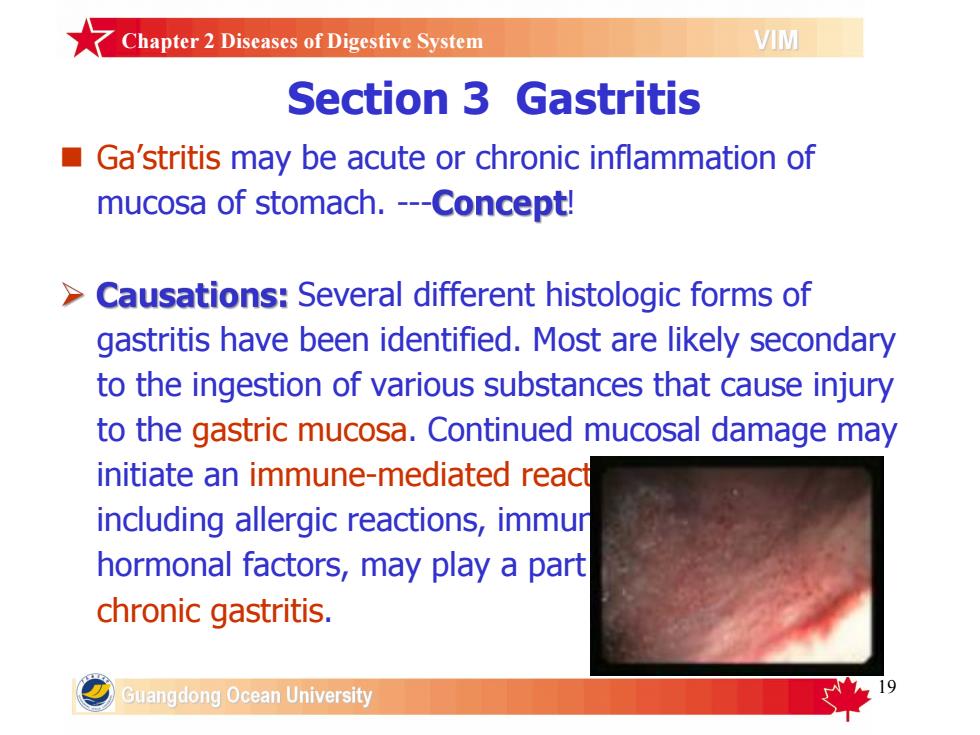
ZChapter2Diseases of Digestive SystemVIMSection 3 GastritisGa'stritismaybeacuteorchronicinflammationofmucosa of stomach. ---Concept!>Causations:Several differenthistologicforms ofgastritis have been identified. Most are likely secondaryto the ingestion of various substances that cause injuryto the gastric mucosa. Continued mucosal damage mayinitiateanimmune-mediatedreactincludingallergicreactions,immurhormonal factors,mayplayapartchronic gastritis.Guangdong Ocean University
19 Section 3 Gastritis n Ga’stritis may be acute or chronic inflammation of mucosa of stomach. - ! Several different histologic forms of gastritis have been identified. Most are likely secondary to the ingestion of various substances that cause injury to the gastric mucosa. Continued mucosal damage may initiate an immune-mediated reaction. Other factors, including allergic reactions, immune mechanisms, and hormonal factors, may play a part in the etiology of chronic gastritis. Chapter 2 Diseases of Digestive System
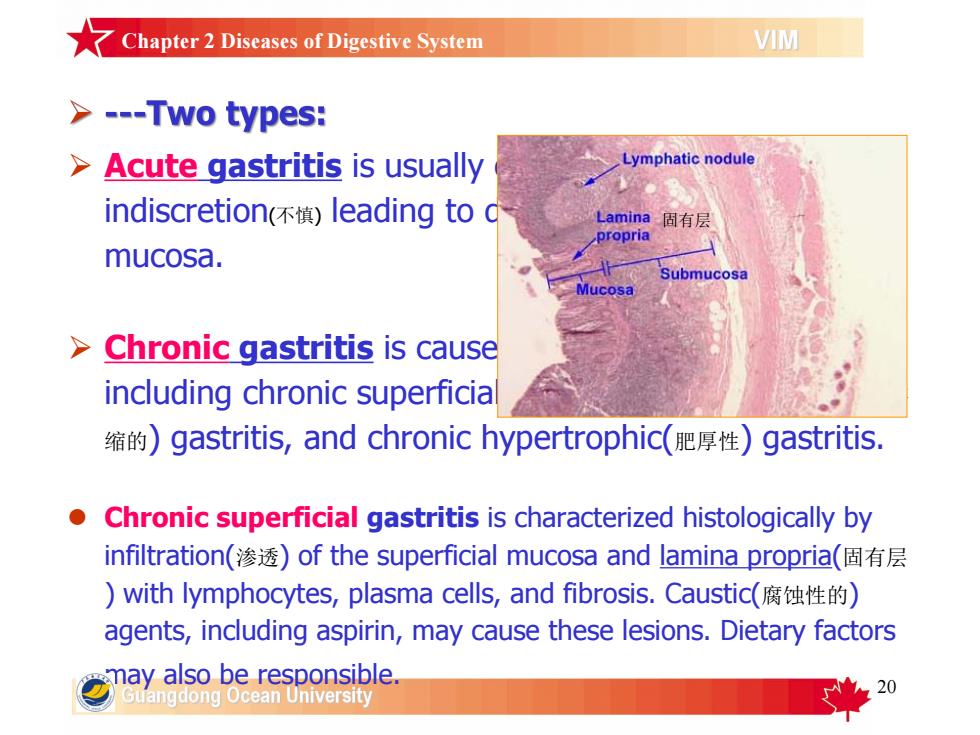
Chapter2Diseases of DigestiveSystemVIM> ---Two types:LymphaticnoduleAcute gastritis is usuallyindiscretion(不慎)leading to (Lamina固有层propriamucosa.SubmucosaMuCosaChronicgastritisiscauseincluding chronic superficia缩的)gastritis,and chronic hypertrophic(肥厚性)gastritis.Chronic superficial gastritis is characterized histologically byinfiltration(渗透)ofthesuperficialmucosaandlaminapropria(固有层)with lymphocytes,plasma cells,andfibrosis.Caustic(腐蚀性的)agents, including aspirin, may cause these lesions. Dietary factorsmayalsoberesponsible20ancdongocea
20 Ø Acute gastritis is usually caused by dietary indiscretion(不慎) leading to damage of the gastric mucosa. Ø Chronic gastritis is caused by a variety of diseases, including chronic superficial gastritis, chronic atrophic(萎 缩的) gastritis, and chronic hypertrophic(肥厚性) gastritis. l Chronic superficial gastritis is characterized histologically by infiltration(渗透) of the superficial mucosa and lamina propria(固有层 ) with lymphocytes, plasma cells, and fibrosis. Caustic(腐蚀性的) agents, including aspirin, may cause these lesions. Dietary factors may also be responsible. 固有层 Chapter 2 Diseases of Digestive System