Chapter3DiseasesofRespiratorySystem$Chapter Main ContentsConspectusSection 1 Pulmonary emphysema →Section 2 Pneumonia →Section 3 Aspiration pneumonia Section 4 Laryngitis Section 5 Tracheobronchitis→Guangdong Ocean University
1 Chapter 3 Diseases of Respiratory System Chapter Main Contents • Conspectus • Section 1 Pulmonary emphysema • Section 2 Pneumonia • Section 3 Aspiration pneumonia • Section 4 Laryngitis • Section 5 Tracheobronchitis
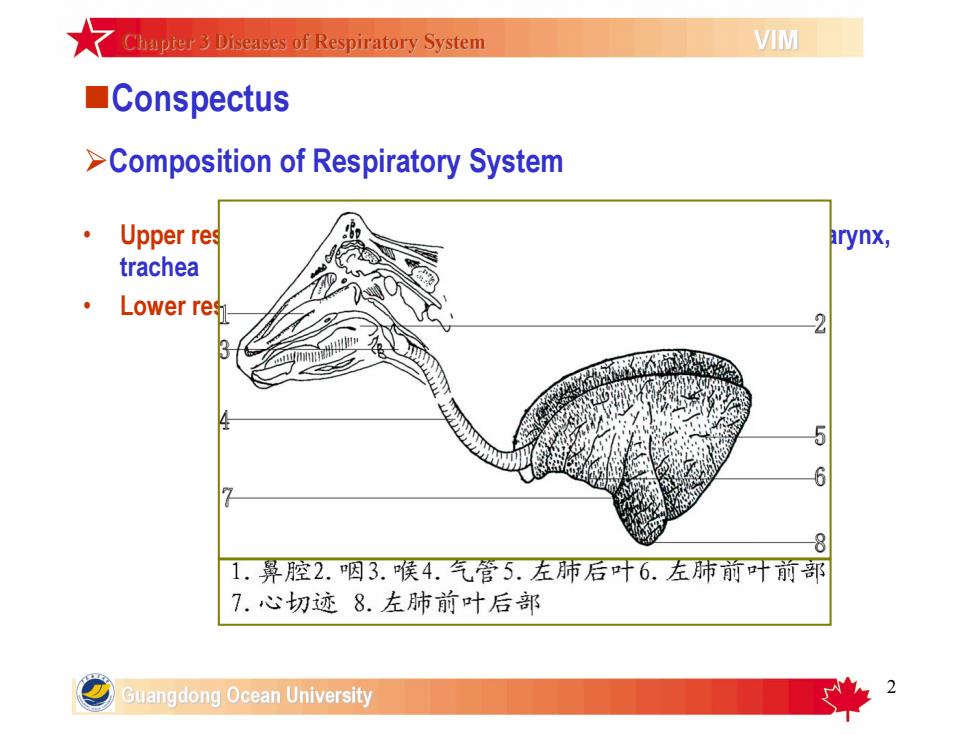
★ Chapter3Diseases of Respiratory SystemVIMConspectus>Composition of Respiratory SystemUpperresarynx,tracheaLowerrese1.鼻腔2.咽3.喉4.气管5.左肺后叶6.左肺前叶前部7.心切迹8.左肺前叶后部Guangdong Ocean University
2 nConspectus • Upper respiratory tract: Nasal cavity, sinuses paranasales(副鼻窦), larynx, trachea • Lower respiratory tract: bronchus, lung ØComposition of Respiratory System

Chaprer3Diseases of Respiratory SystemVIM$FunctionsMostimportantly,itdeliversoxygentothe cardiovascular systemfordistribution to the body and itremovescarbondioxide.Gastransferoccurs in the alveoli of the lungs,where the air-blood barrier is a thin,permeable membrane.To be continuedGuangdong Ocean University
3 Functions lMost importantly, it delivers oxygen to the cardiovascular system for distribution to the body and it removes carbon dioxide. Gas transfer occurs in the alveoli of the lungs, where the air-blood barrier is a thin, permeable membrane. To be continued

KChapter3Diseases of Respiratory SystemVIMFunctionsInadditiontogasexchange,therespiratorysystemperforms numerousother functions, includingmaintaining acid-base balance, acting as a bloodreservoir,filteringandprobablydestroyingemboli栓子metabolizingsomebioactivesubstances(eg,prostaglandins前列腺素,corticosteroids皮质类固醇),and activating somesubstances (eg,angiotensin血管紧张素). The respiratory system alsoprotects its own delicate airways by warming and humidifyinginhaled air and by filtering out large particulate material orcoughing as well as phagocytizing吞噬 minute particles and microbesby macrophages.Guangdong Ocean University
4 lFunctions l In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system performs numerous , including maintaining acid-base balance, acting as a blood reservoir, filtering and probably destroying emboli栓子, metabolizing some bioactive substances (eg, prostaglandins 前列腺素, corticosteroids皮质类固醇), and activating some substances (eg, angiotensin血管紧张素). The respiratory system also protects its own delicate airways by warming and humidifying inhaled air and by filtering out large particulate material or coughing as well as phagocytizing吞噬 minute particles and microbes by macrophages
★Chapter3Diseasesof Respiratory SystemVIMClinical Signsof Respiratory Malfunction>Nasaldischargemaybeserous浆液性的,purulent脓的(withdiedneutrophils), or hemorrhagic, depending on the degree of mucosaldamage.>He'moptysis (thecoughingupofblood)occursafterruptureofpulmonary aneurysms动脉瘤in the lungs of cattle withchronic lungabscesses脓肿.Bleedingmayalsoresultfromtrauma,andbrackenfern蕨类orsweetclover草木犀toxicity.Hyperp'nea(喘息,an increaseinrateand depthof pulmonaryventilation)becomes dys'pnea呼吸困难when the breathing appears to belabored andcausingdistress.Other responsesinclude coughing,and shallowbreathing withgrunting, often associated with the pain of pleuritis胸膜炎.Guangdong Ocean University
5 nClinical Signs of Respiratory Malfunction Ø Nasal discharge may be serous浆液性的, purulent脓的 (with died neutrophils), or hemorrhagic, depending on the degree of mucosal damage. Ø He’moptysis (the coughing up of blood) occurs after rupture of pulmonary aneurysms动脉瘤 in the lungs of cattle with chronic lung abscesses脓肿. Bleeding may also result from trauma, and bracken fern蕨类 or sweet clover草木犀 toxicity. Ø Hyperp’nea (喘息,an increase in rate and depth of pulmonary ventilation) becomes dys’pnea呼吸困难 when the breathing appears to be labored and causing distress. Ø Other responses include coughing, and shallow breathing with grunting, often associated with the pain of pleuritis胸膜炎