
4.2 The application of the standard equilibrium constant 4.2.1 Determining the extent of a chemical reaction 4.2.2 Predicting the direction of a chemical reaction -4.2.3 Calculating equilibrium concentrations from K values
4.2.1 Determining the extent of a chemical reaction §4.2 The application of the standard equilibrium constant 4.2.3 Calculating equilibrium concentrations from Kθ values 4.2.2 Predicting the direction of a chemical reaction

4.2.1 Determining the extent of a chemical reaction aA(g)+bB(aq)+cC(s)-xX(g)+yY(aq)+Z(1) )(Y)cop [p(A)/peJalc(B)/c The larger the value of Ke,the greater the extent of the reaction; The smaller the value of Ke,the smaller the extent of the reaction; A reactant is partially consumed to convert the products if the value of Ko is neither very larger nor very small, i.e.,chemical equilibria exist.(for example,10-3<K<103
4.2.1 Determinin g the extent of a chemical reaction The larger the value of KΘ, the greater the extent of the reaction ; A reactant is partially consumed to convert the products if the value of KΘ is neither very larger nor very small, i.e., chemical equilibria exist. (for example, 10-3< KΘ <10 3 ) The smaller the value of KΘ , the smaller the extent of the reaction ; K [ ( ) ] [ ] ( ) [ ] ( ) [ ] ( ) b c c a p p y c c x p p A / B / X / Y / = aA(g) + bB(aq) + cC(s) xX(g) + yY(aq) + zZ(l)
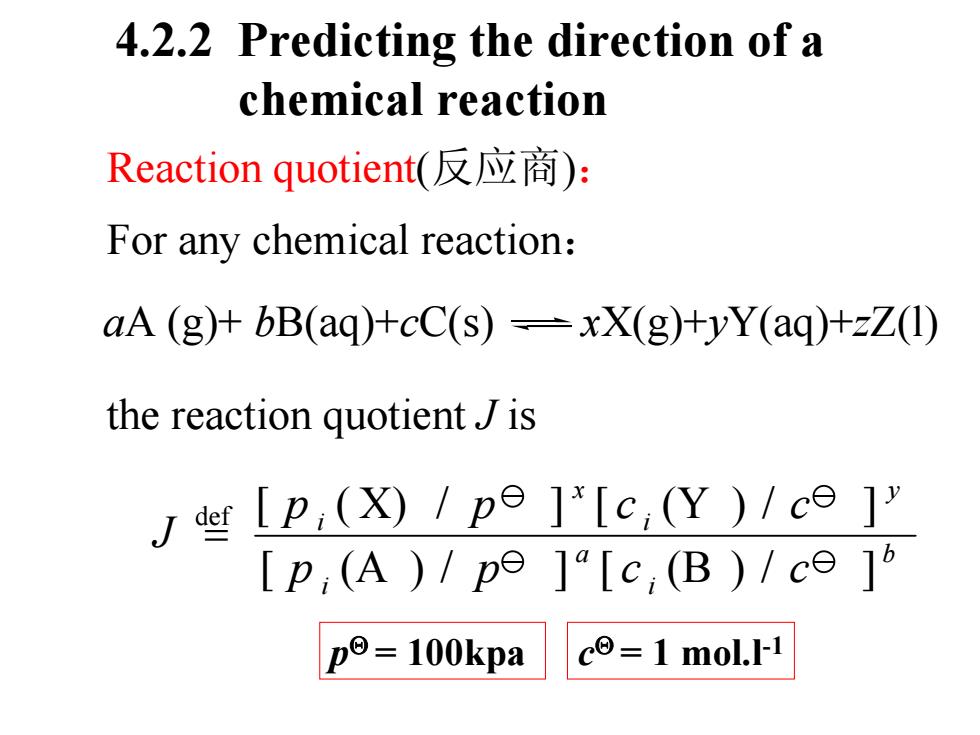
4.2.2 Predicting the direction of a chemical reaction Reaction quotiente(反应商): For any chemical reaction: aA (g)+bB(aq)+cC(s)=xX(g)+yY(aq)+zZ(1) the reaction quotientJ is J d[p(x)/pe ]"lc,(Y)/c ] [p,(A)1pe][c,(B)/ce] p=100kpa c=1 mol.I-1
For any chemical reaction : 4.2.2 Predicting the direction of a chemical reaction the reaction quotient J is aA (g)+ bB(aq)+ cC(s) xX(g)+yY(aq)+zZ(l) b i a i y i x i p p c c p p c c J [ (A ) / ] [ (B ) / ] [ ( X) / ] [ (Y ) / ] = def Reaction quotient (反应商 ) : p Θ = 100kpa c Θ = 1 mol.l-1
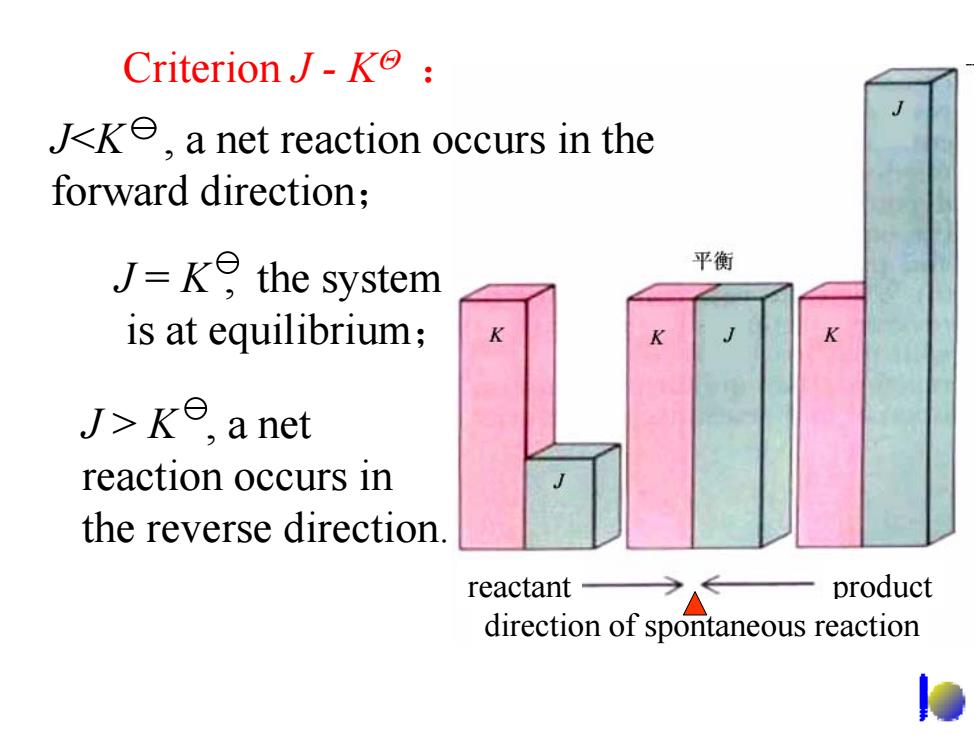
CriterionJ-K J<ke,a net reaction occurs in the forward direction; J=ke the system 平衡 is at equilibrium; J>ke,a net reaction occurs in the reverse direction reactant product direction of spontaneous reaction
Criterion J - KΘ : J = K , the system is at equilibrium; J > K , a net reaction occurs in the reverse direction. reactant product direction of spontaneous reaction J<K , a net reaction occurs in the forward direction;

4.2.3 Calculating equilibrium concentrations from ke values Example:For the synthesis of COCl2(g)in a constant volume container at 373K C0(g+Cl2(g)=C0C2(g)Ke=1.5×108。 Suppose the initial concentration of CO and Cl2 are 0.0350mol-L-1 and 0.0270mol-L,respectively Calculate the equilibrium quantities of all the components and a(CO)
4.2.3 Calculating equilibrium concentrations from K values Suppose the initial concentration of CO and Cl2 are 0.0350mol·L-1 and 0.0270mol·L-1, respectively. Calculate the equilibrium quantities of all the components and α (CO). Example :For the synthesis of COCl 2(g) in a constant volume container at 373K CO(g)+Cl 2(g) COCl 2(g) K =1.5 ×10 8