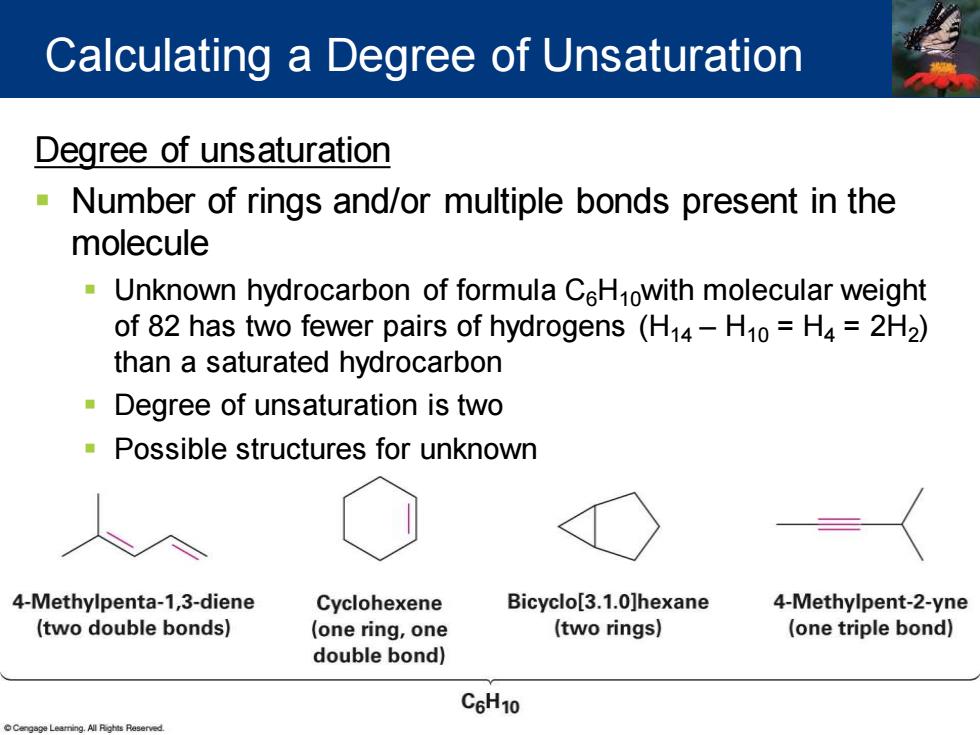
Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation Degree of unsaturation Number of rings and/or multiple bonds present in the molecule Unknown hydrocarbon of formula CeHnowith molecular weight of 82 has two fewer pairs of hydrogens(H14-H10=H4=2H2) than a saturated hydrocarbon Degree of unsaturation is two Possible structures for unknown 4-Methylpenta-1,3-diene Cyclohexene Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane 4-Methylpent-2-yne (two double bonds) (one ring,one (two rings) (one triple bond) double bond) C6H10
Degree of unsaturation ▪ Number of rings and/or multiple bonds present in the molecule ▪ Unknown hydrocarbon of formula C6H10with molecular weight of 82 has two fewer pairs of hydrogens (H14 – H10 = H4 = 2H2 ) than a saturated hydrocarbon ▪ Degree of unsaturation is two ▪ Possible structures for unknown Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation
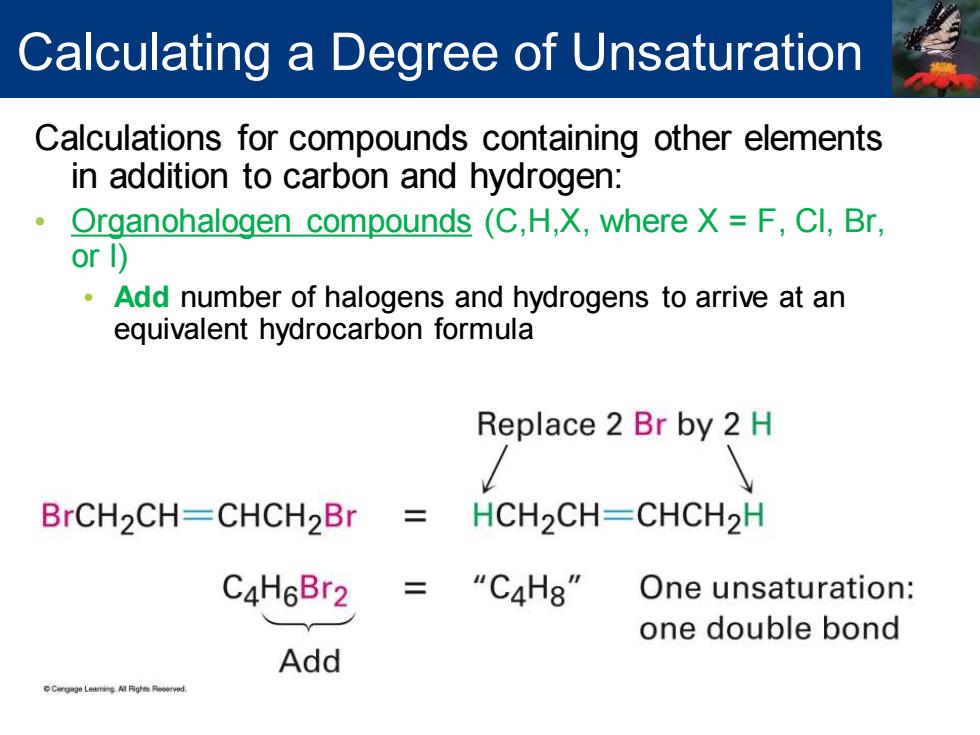
Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation Calculations for compounds containing other elements in addition to carbon and hydrogen: Organohalogen compounds (C,H,X,where X F,Cl,Br, or 1) Add number of halogens and hydrogens to arrive at an equivalent hydrocarbon formula Replace 2 Br by 2 H BrCH2CH-CHCH2Br HCH2CH-CHCH2H C4H6Br2 “C4H8" One unsaturation: one double bond Add LeamingAl Pigh Reer时
Calculations for compounds containing other elements in addition to carbon and hydrogen: • Organohalogen compounds (C,H,X, where X = F, Cl, Br, or I) • Add number of halogens and hydrogens to arrive at an equivalent hydrocarbon formula Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation
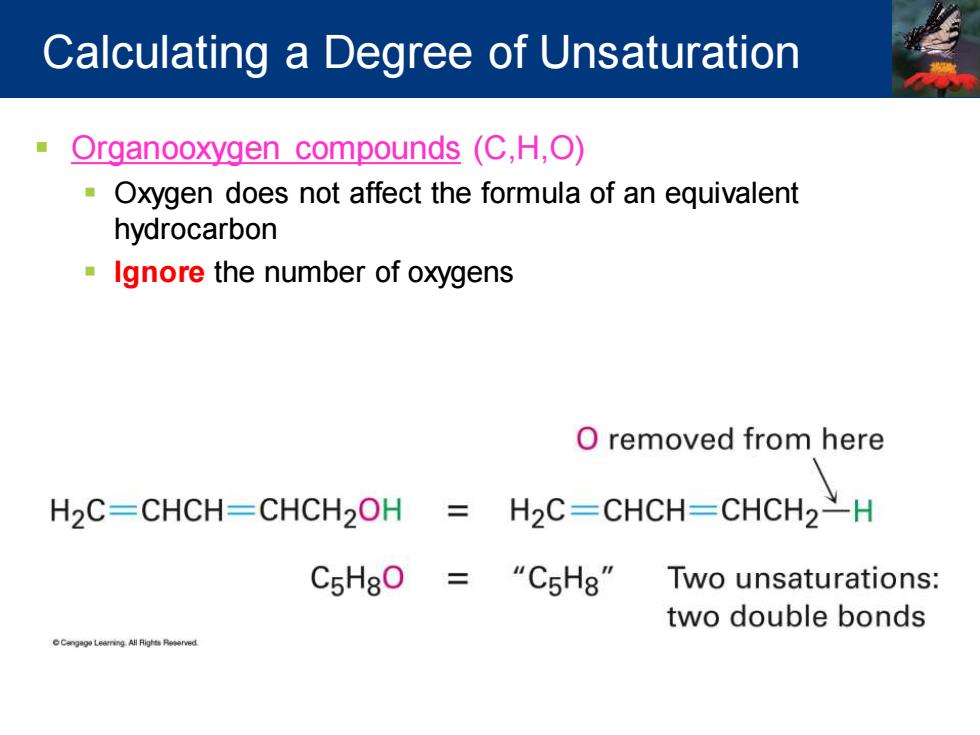
Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation Organooxygen compounds(C,H,O) Oxygen does not affect the formula of an equivalent hydrocarbon Ignore the number of oxygens O removed from here H2C=CHCH-CHCH2OH 三 H2C=CHCH-CHCH2H C5HgO=“CsHg”Two unsaturations:: two double bonds
▪ Organooxygen compounds (C,H,O) ▪ Oxygen does not affect the formula of an equivalent hydrocarbon ▪ Ignore the number of oxygens Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation

Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation Organonitrogen compounds (C,H,N) Has one more hydrogen than a related hydrocarbon Subtract the number of nitrogens from the number of hydrogens for equivalent hydrocarbon formula H CH2 H H CH2 H CH2 N-H H CH2 H N Removed H C5HgN=“CsHg" Two unsaturations:one ring and one double bond Cngg Learing Al Rig Raserved
▪ Organonitrogen compounds (C,H,N) ▪ Has one more hydrogen than a related hydrocarbon ▪ Subtract the number of nitrogens from the number of hydrogens for equivalent hydrocarbon formula Calculating a Degree of Unsaturation
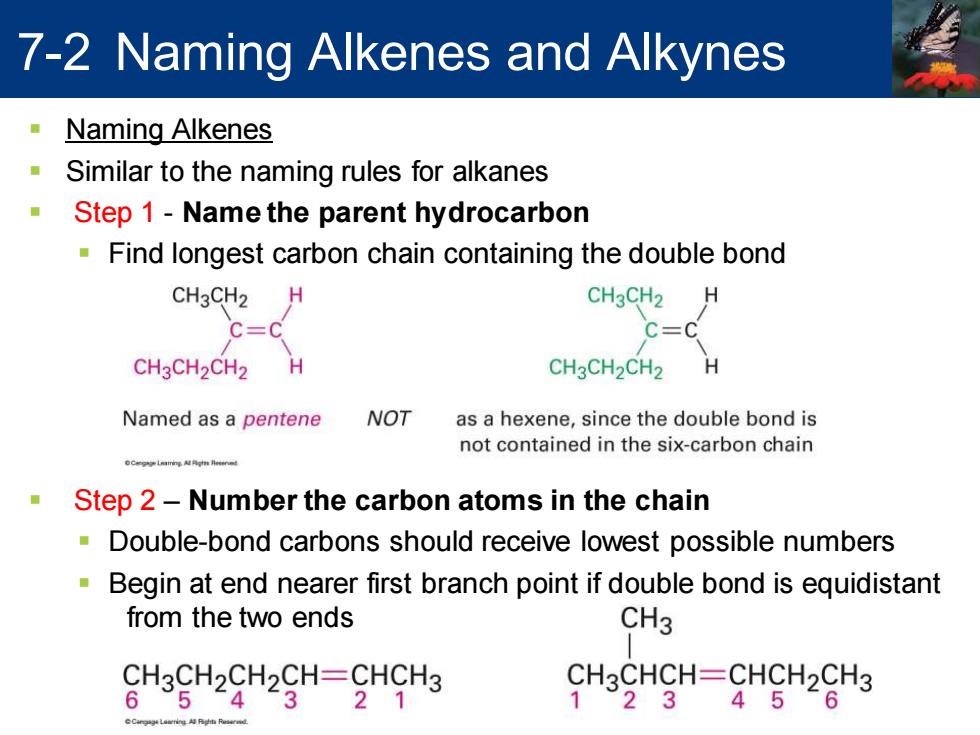
7-2 Naming Alkenes and Alkynes Naming Alkenes Similar to the naming rules for alkanes Step 1-Name the parent hydrocarbon Find longest carbon chain containing the double bond CH3CH2 H CH3CH2 C=C C=C CH3CH2CH2 H CH3CH2CH2 H Named as a pentene NOT as a hexene,since the double bond is not contained in the six-carbon chain OCgLai eat Step 2-Number the carbon atoms in the chain Double-bond carbons should receive lowest possible numbers Begin at end nearer first branch point if double bond is equidistant from the two ends CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH=CHCH3 CH3CHCH=CHCH2CH3 654321 123456
7-2 Naming Alkenes and Alkynes ▪ Naming Alkenes ▪ Similar to the naming rules for alkanes ▪ Step 1 - Name the parent hydrocarbon ▪ Find longest carbon chain containing the double bond ▪ Step 2 – Number the carbon atoms in the chain ▪ Double-bond carbons should receive lowest possible numbers ▪ Begin at end nearer first branch point if double bond is equidistant from the two ends