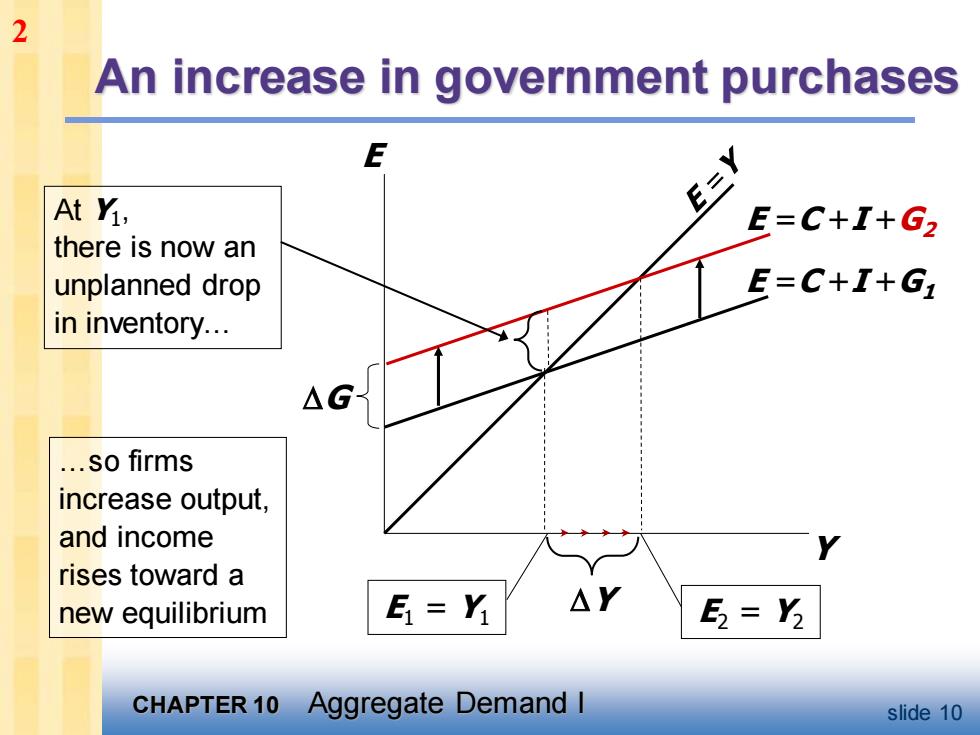
2 An increase in government purchases At Yi, E=Y E=C+I+G, there is now an unplanned drop E=C+I+G in inventory. △G .so firms increase output, and income rises toward a new equilibrium E=Y △Y E2=Y3 CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 10
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 10 An increase in government purchases Y E E =C +I +G1 E1 = Y1 E =C +I +G2 E2 = Y2 Y At Y1 , there is now an unplanned drop in inventory. .so firms increase output, and income rises toward a new equilibrium G 2
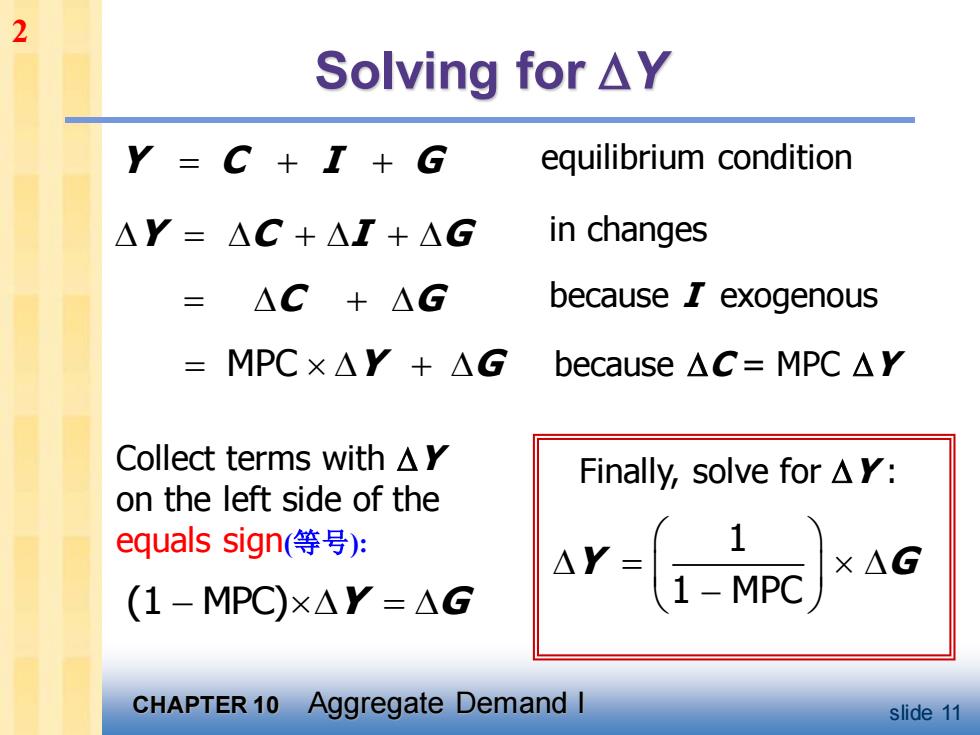
2 Solving for△Y Y=C+I+G equilibrium condition △Y=△C+△I+△G in changes △C+△G because I exogenous =MPC×△Y+△G because△C=MPC△Y Collect terms with△Y Finally,solve for△Y: on the left side of the equals sign(等号): ×△G (1-MPC)xAY=△G CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 11
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 11 Solving for Y Y C I G = + + = + + Y C I G = + MPC Y G = + C G (1 MPC) − = Y G 1 1 MPC Y G = − equilibrium condition in changes because I exogenous because C = MPC Y Collect terms with Y on the left side of the equals sign(等号): Finally, solve for Y : 2
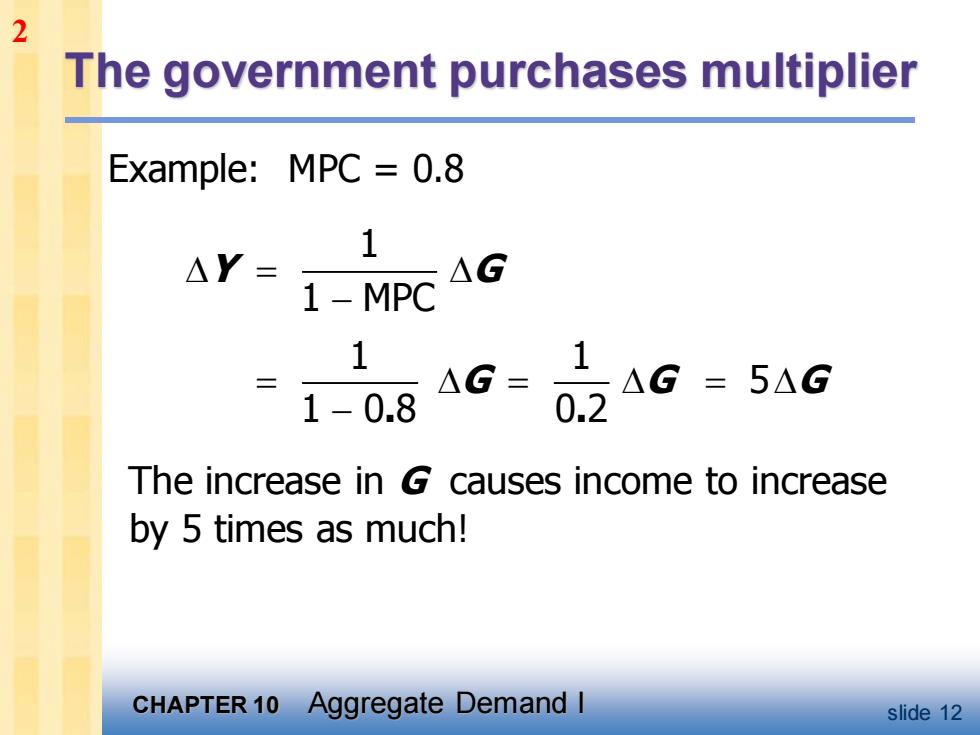
2 The government purchases multiplier Example:MPC 0.8 1 △Y= 1-MPC AG 1 1 三 △G= △G =5△G 1-0.8 0.2 The increase in G causes income to increase by 5 times as much! CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 12
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 12 The government purchases multiplier Example: MPC = 0.8 1 1 MPC 1 1 5 1 0 8 0 2 . . Y G G G G = − = = = − The increase in G causes income to increase by 5 times as much! 2
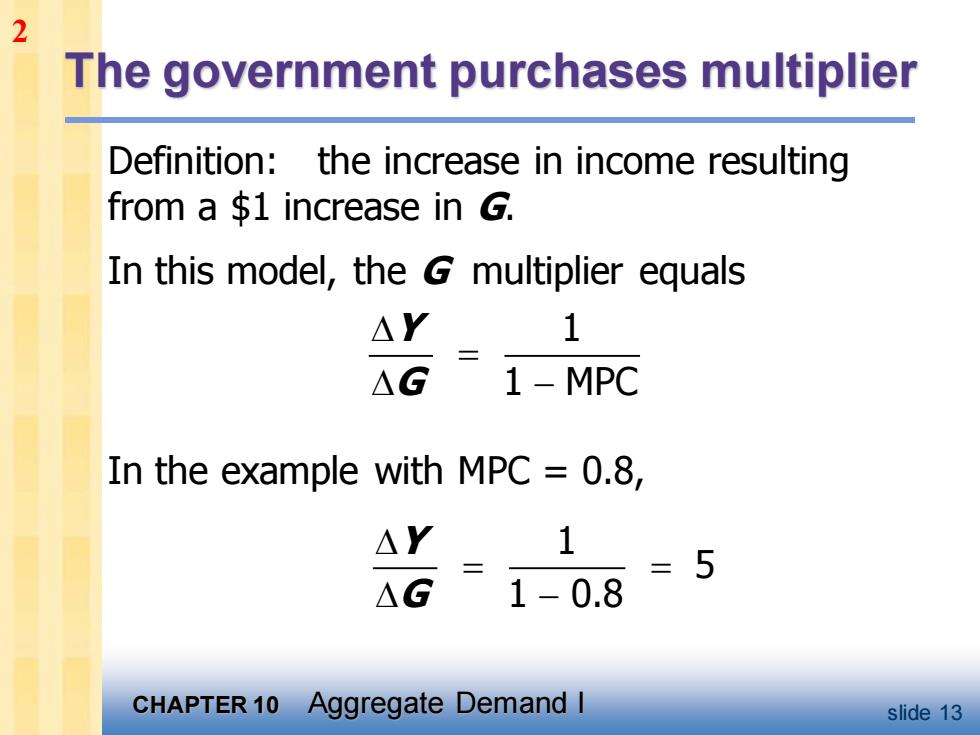
2 The government purchases multiplier Definition:the increase in income resulting from a $1 increase in G. In this model,the G multiplier equals △Y 1 二 △G 1-MPC In the example with MPC =0.8, △Y 1 =5 △G 1-0.8 CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 13
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 13 The government purchases multiplier In the example with MPC = 0.8, Definition: the increase in income resulting from a $1 increase in G. In this model, the G multiplier equals 1 1 MPC Y G = − 1 5 1 0.8 Y G = = − 2
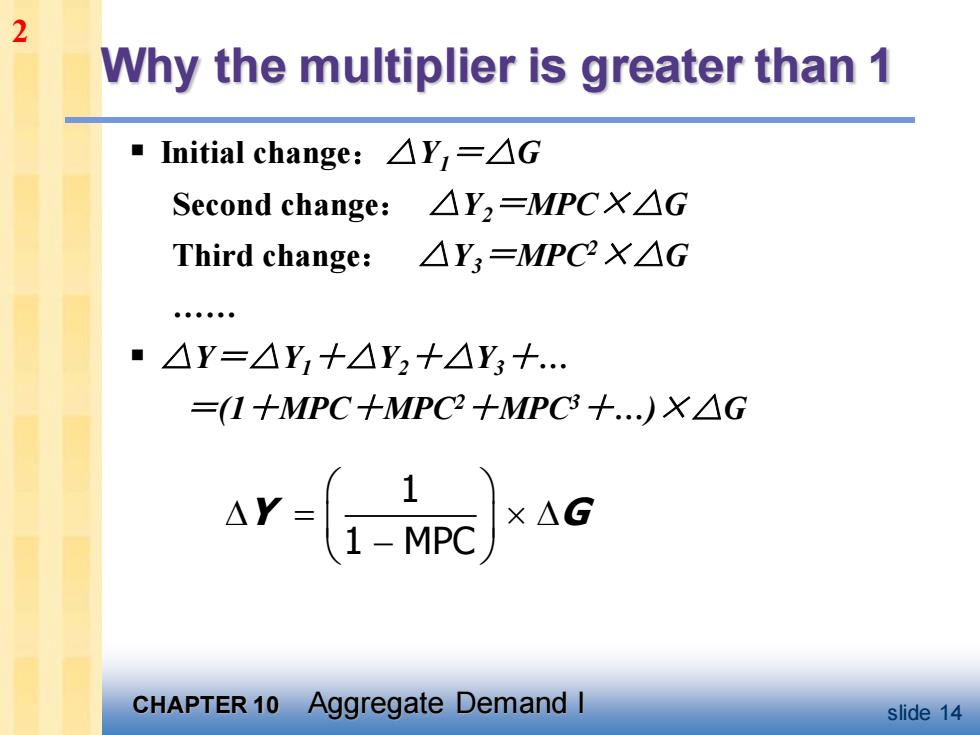
2 Why the multiplier is greater than 1 "Initial change:△Y,=△G Second change:△Y,=MPCX△G Third change:△Y,=MPC2X△G ■△Y=△Y,+△Y,+△Y3+. -(1+MPC +MPC2+MPC3 +.XAG AY 1-MPCG CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 14
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 14 Why the multiplier is greater than 1 ▪ Initial change:△Y1=△G Second change: △Y2=MPC×△G Third change: △Y3=MPC2×△G . ▪ △Y=△Y1+△Y2+△Y3+. =(1+MPC+MPC2+MPC3+.)×△G 2 1 1 MPC Y G = −