
CHAPTER NINE Introduction to AS/AD Model ooeu macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER NINE Introduction to AS/AD Model m a c r o College of Management, HUST

Chapter objectives Difference between short run long run Introduction to aggregate demand Aggregate supply in the short run long run See how model of aggregate supply and demand can be used to analyze short-run and long-run effects of "shocks" CHAPTER 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 1
slide 1 § Difference between short run & long run § Introduction to aggregate demand § Aggregate supply in the short run & long run § See how model of aggregate supply and demand can be used to analyze short-run and long-run effects of “shocks

Content 1.Difference between short run long run 2.Aggregate demand 3.Aggregate supply in the short long run 4.Shocks to AD and AS 5.Stabilization policy(稳定政策) 6.Chapter summary CHAPTER 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 2
slide 2 1. Difference between short run & long run 2. Aggregate demand 3. Aggregate supply in the short & long run 4. Shocks to AD and AS 5. Stabilization policy(稳定政策) 6. Chapter summary
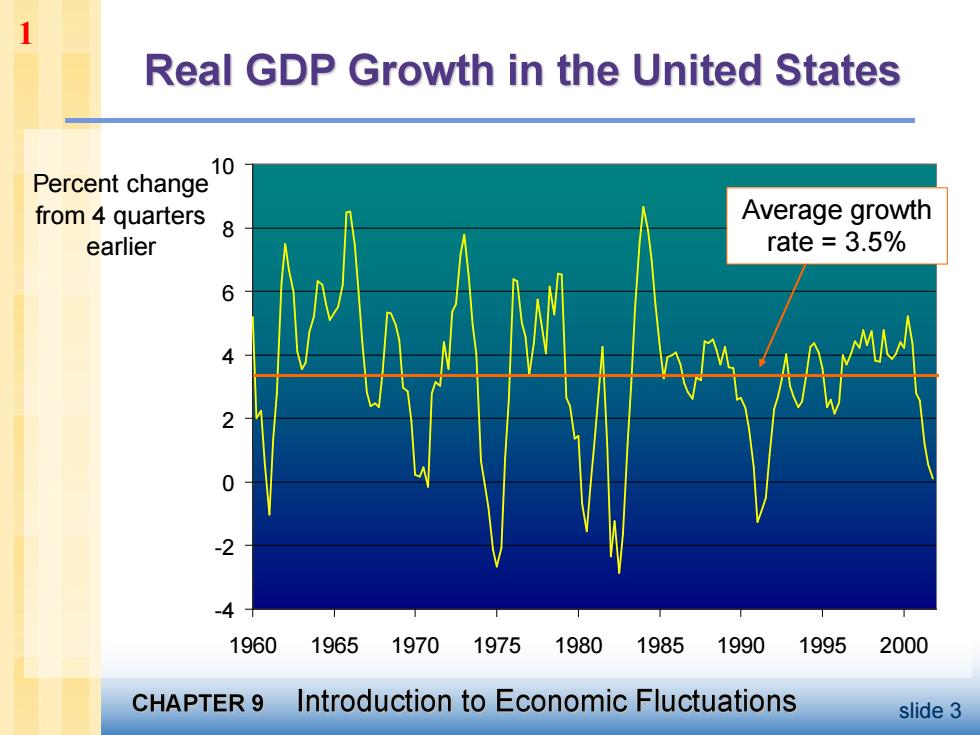
1 Real GDP Growth in the United States 10 Percent change from 4 quarters Average growth earlier rate 3.5% 6 -4 1960 1965 1970197519801985 19901995 2000 CHAPTER 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 3
slide 3 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Percent change from 4 quarters earlier Average growth rate = 3.5% 1

1 Time horizons ■Long run: Prices are flexible,respond to changes in supply or demand ■Short run: many prices are"sticky"at some predetermined level The economy behaves much differently when prices are sticky. CHAPTER 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 4
slide 4 § Long run: Prices are flexible, respond to changes in supply or demand § Short run: many prices are “sticky” at some predetermined level The economy behaves much differently when prices are sticky. 1