1 The Keynesian Cross A simple closed economy model in which income is determined by expenditure.(due to J.M.Keynes) ▣Notation: I planned investment E=C+I+G planned expenditure Y=real GDP=actual expenditure Difference between actual planned expenditure: unplanned inventory investment CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 5
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 5 The Keynesian Cross ▪ A simple closed economy model in which income is determined by expenditure. (due to J.M. Keynes) ▪ Notation: I = planned investment E = C + I + G = planned expenditure Y = real GDP = actual expenditure ▪ Difference between actual & planned expenditure: unplanned inventory investment 1
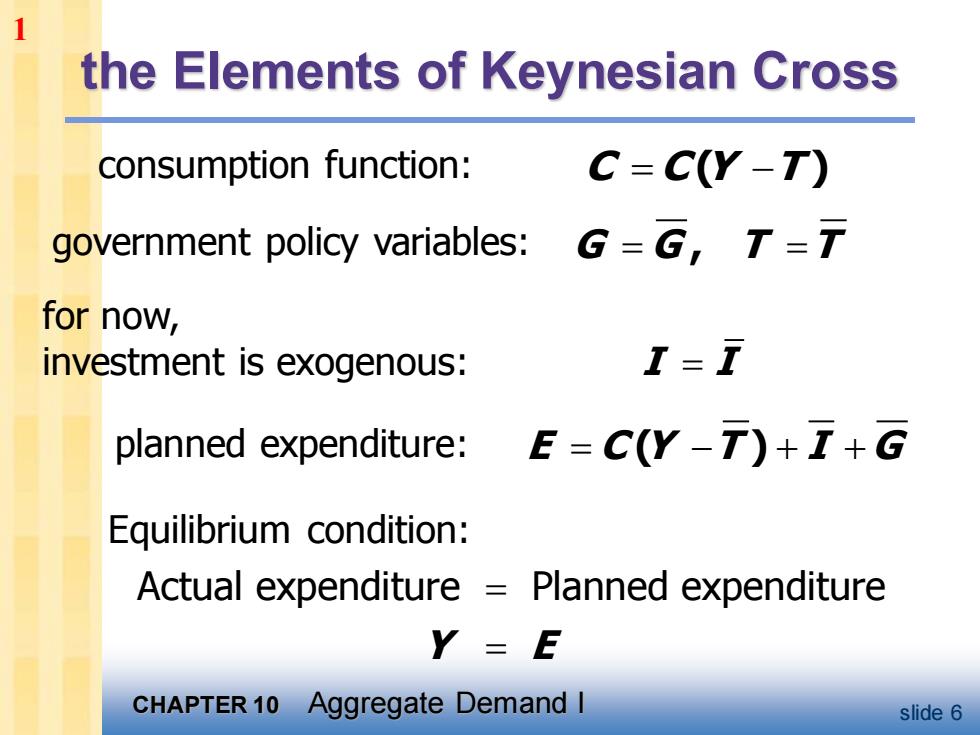
1 the Elements of Keynesian Cross consumption function: C=C(Y-T) government policy variables:G=G,T= for now, investment is exogenous: T-T planned expenditure:E=C(Y-T)++G Equilibrium condition: Actual expenditure =Planned expenditure Y=E CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 6
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 6 the Elements of Keynesian Cross C C Y T = − ( ) I I = G G T T = = , E C Y T I G = − + + ( ) Actual expenditure Planned expenditure Y E = = consumption function: for now, investment is exogenous: planned expenditure: Equilibrium condition: government policy variables: 1
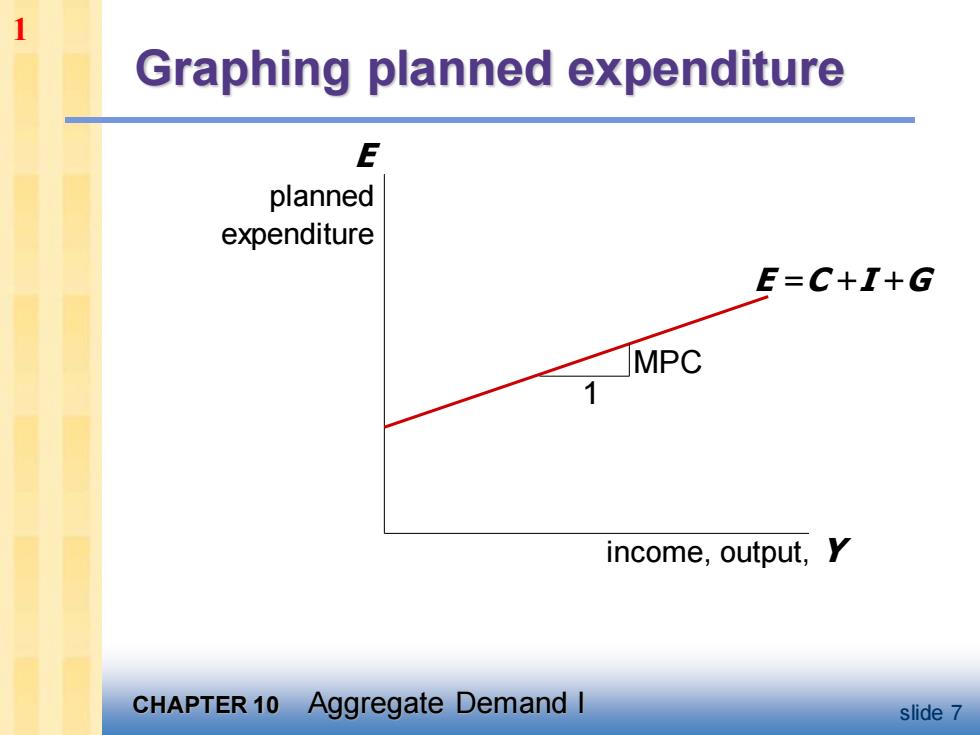
1 Graphing planned expenditure E planned expenditure E=C+I+G MPC income,output,Y CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 7
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 7 Graphing planned expenditure income, output, Y E planned expenditure E =C +I +G MPC 1 1
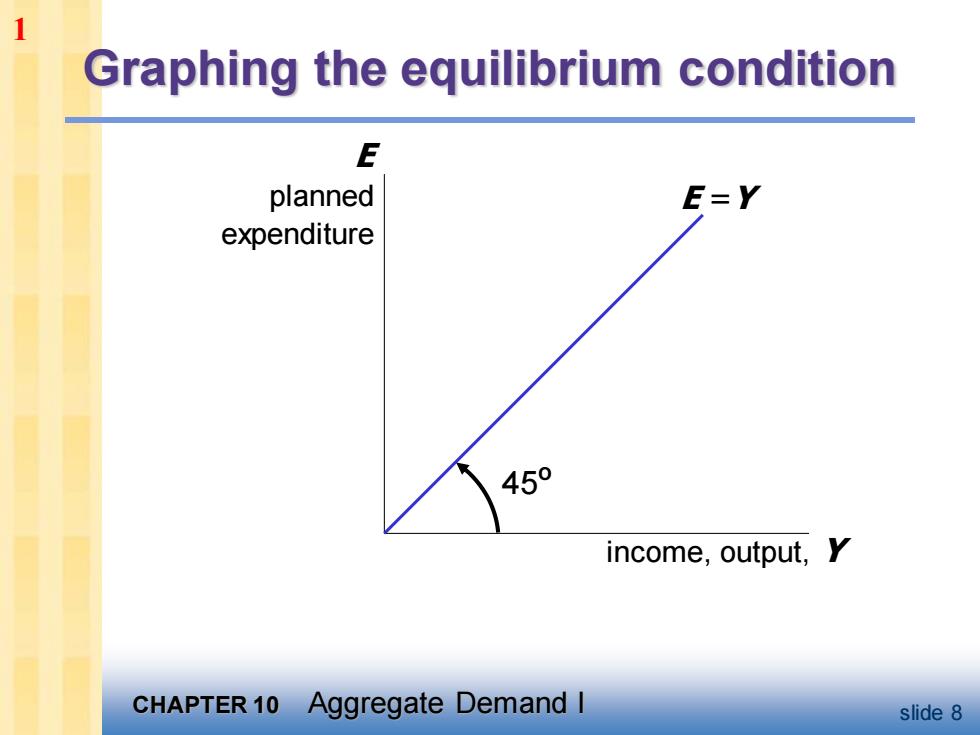
1 Graphing the equilibrium condition E planned E=Y expenditure 450 income,output,Y CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 8
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 8 Graphing the equilibrium condition income, output, Y E planned expenditure E =Y 45º 1
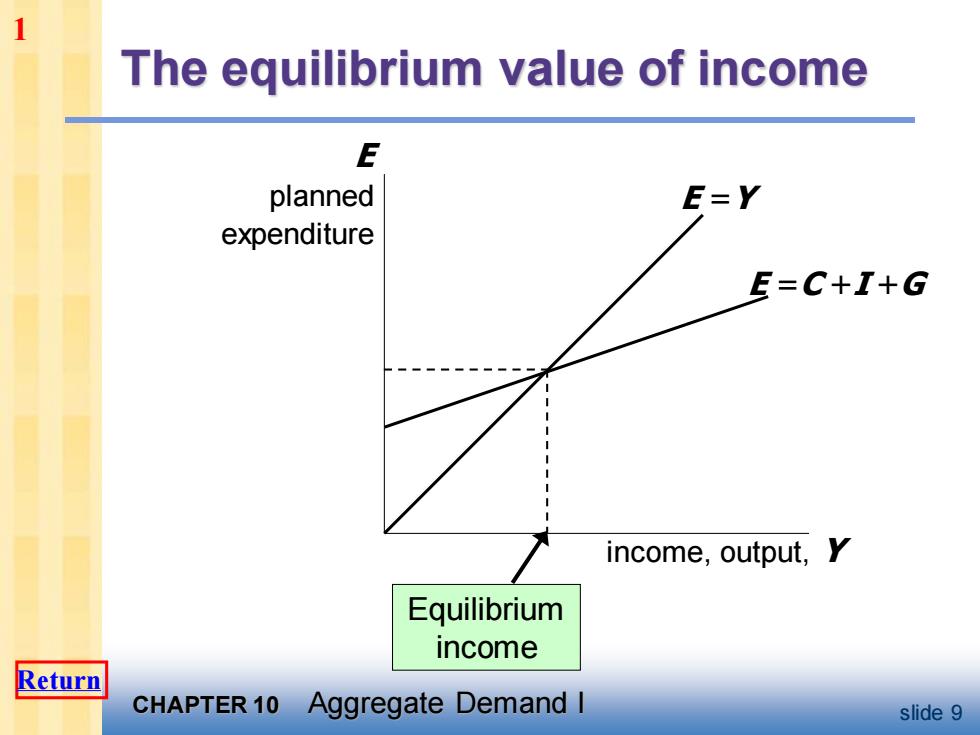
1 The equilibrium value of income E planned E=Y expenditure E=C+I+G income,output,Y Equilibrium income Return CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 9
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 9 The equilibrium value of income income, output, Y E planned expenditure E =Y E =C +I +G Equilibrium income 1 Return