
CHAPTER THREE National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw macro College of Management, HUST CHAPTER THREE National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes

Learning objectives what determines the economy's total output/income how the prices of the factors of production are determined how total income is distributed what determines the demand for goods and services how equilibrium in the goods market is achieved CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 1
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 1 Learning objectives ▪ what determines the economy’s total output/income ▪ how the prices of the factors of production are determined ▪ how total income is distributed ▪ what determines the demand for goods and services ▪ how equilibrium in the goods market is achieved

Content 1.Factors determine the total output/income 2.Distribution of national income 3.Goods market equilibrium 4.Loanable funds market equilibrium 5.General equilibrium and changing of S,I 6.Chapter summary CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 2
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 2 Content 1. Factors determine the total output/income 2. Distribution of national income 3. Goods market equilibrium 4. Loanable funds market equilibrium 5. General equilibrium and changing of S, I 6. Chapter summary
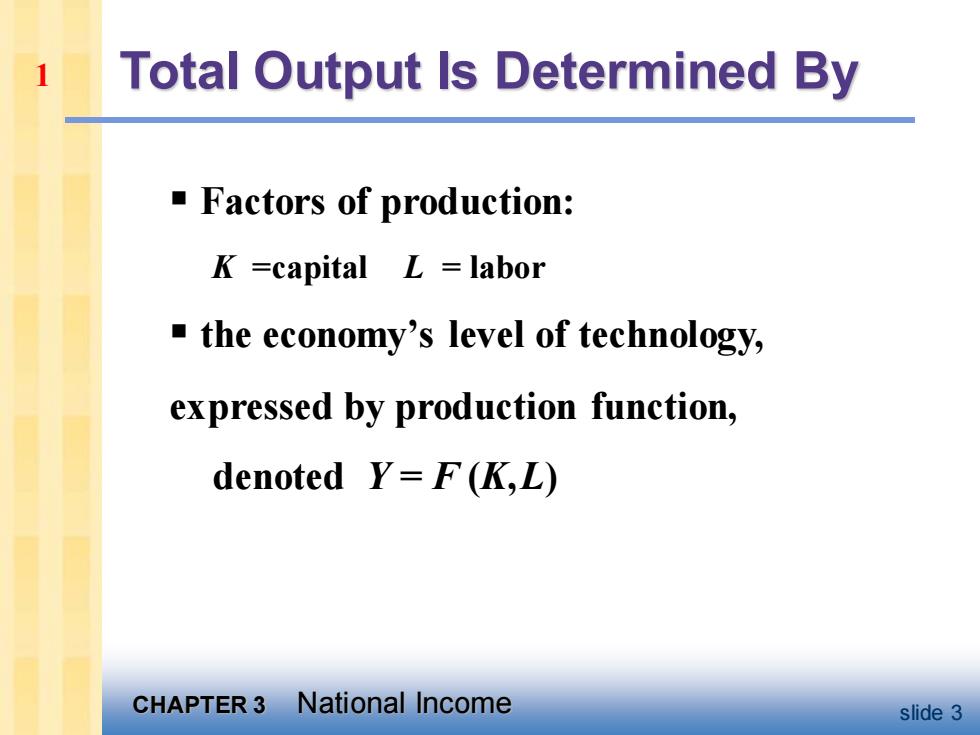
Total Output Is Determined By Factors of production: K =capital L =labor the economy's level of technology, expressed by production function, denoted Y=F(K,L) CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 3
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 3 Total Output Is Determined By ▪ Factors of production: K =capital L = labor ▪ the economy’s level of technology, expressed by production function, denoted Y = F (K,L) 1
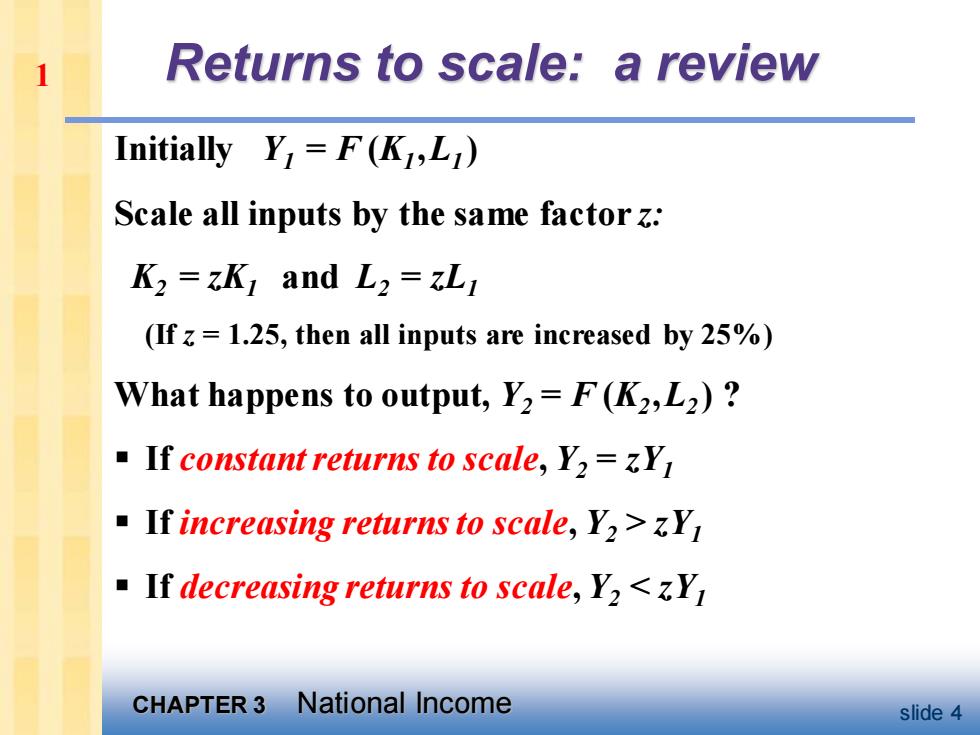
Returns to scale:a review Initially Y=F(K,L) Scale all inputs by the same factor z: K2=zK and L2=L (If 1.25,then all inputs are increased by 25%) What happens to output,Y2=F(K2,L2)? If constant returns to scale,Y2=Y If increasing returns to scale,Y2>Y If decreasing returns to scale,Y2<Y CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 4
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 4 Returns to scale: a review Initially Y1 = F (K1 ,L1 ) Scale all inputs by the same factor z: K2 = zK1 and L2 = zL1 (If z = 1.25, then all inputs are increased by 25%) What happens to output, Y2 = F (K2 ,L2 ) ? ▪ If constant returns to scale, Y2 = zY1 ▪ If increasing returns to scale, Y2 > zY1 ▪ If decreasing returns to scale, Y2 < zY1 1