
Sec 1 Preparation of RX Free radical halogenation produces mixtures,not good lab synthesis ounless:all H's are equivalent,or halogenation is highly selective. Free radical allylic halogenation produces alkyl halide with double bond on the neighboring carbon
Sec 1 Preparation of RX ◼Free radical halogenation ⚫produces mixtures, not good lab synthesis ⚫unless: all H’s are equivalent, or halogenation is highly selective. ◼Free radical allylic halogenation ⚫produces alkyl halide with double bond on the neighboring carbon
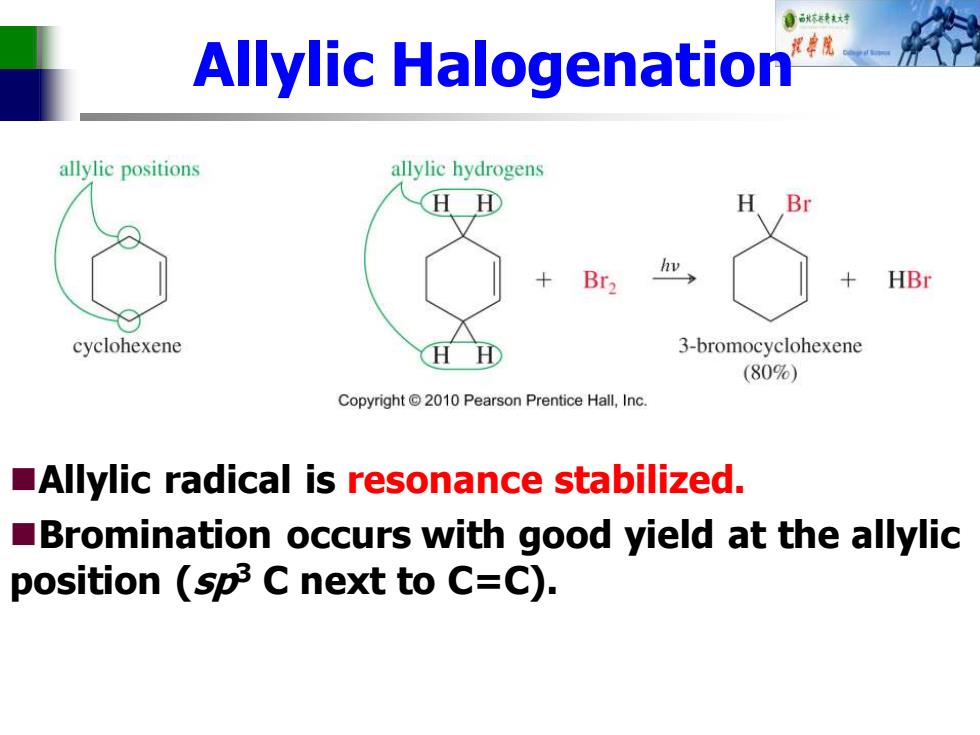
Allylic Halogenation allylic positions allylic hydrogens HH H Br2 HBr cyclohexene H 3-bromocyclohexene (80%) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Allylic radical is resonance stabilized. Bromination occurs with good yield at the allylic position (sp3 C next to C=C)
Allylic Halogenation ◼Allylic radical is resonance stabilized. ◼Bromination occurs with good yield at the allylic position (sp3 C next to C=C)
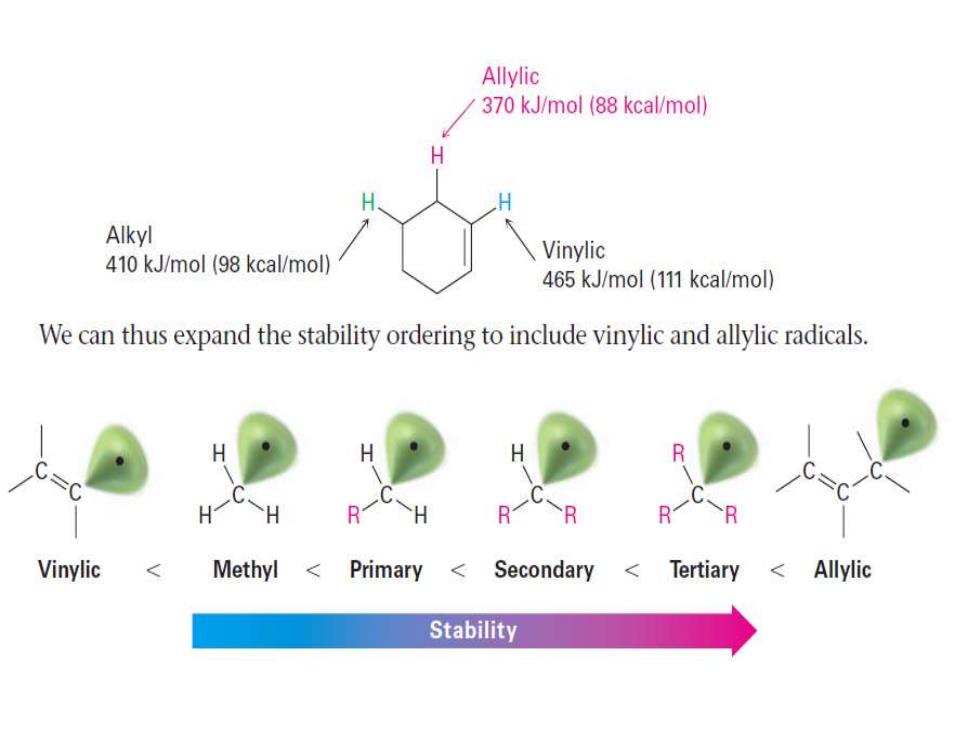
Allylic 370 kJ/mol (88 kcal/mol) H Alkyl 410 kJ/mol (98 kcal/mol) Vinylic 465 kJ/mol (111 kcal/mol) We can thus expand the stability ordering to include vinylic and allylic radicals. H H R R H R1 B Vinylic Methyl Primary < Secondary Tertiary <Allylic Stability
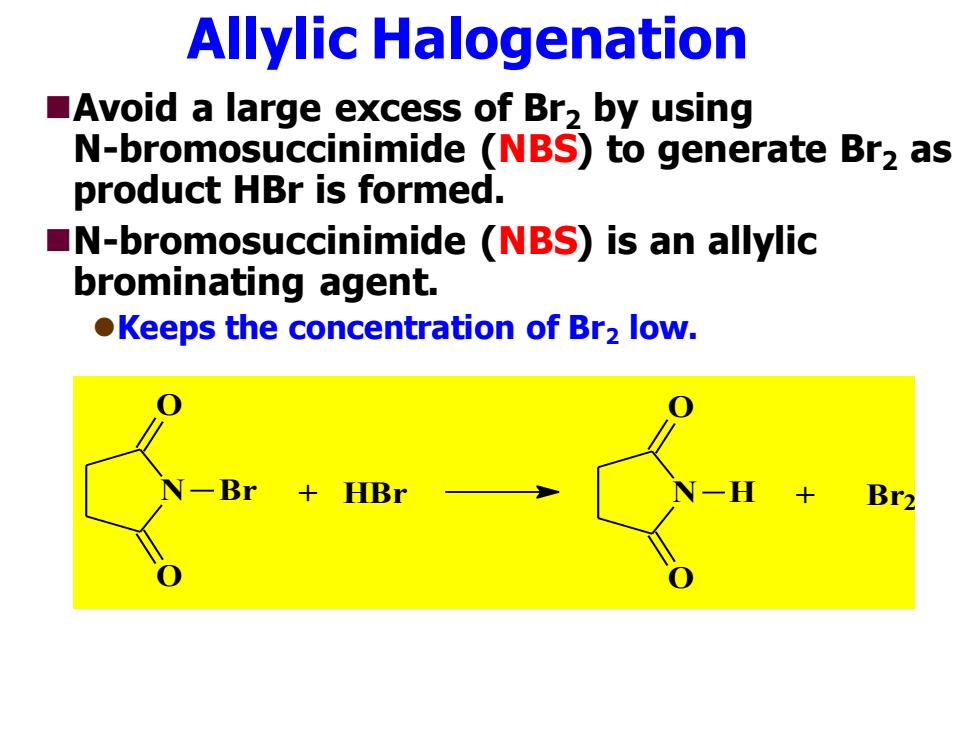
Allylic Halogenation Avoid a large excess of Br2 by using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS)to generate Br2 as product HBr is formed. N-bromosuccinimide (NBS)is an allylic brominating agent. Keeps the concentration of Br2 low. Br2
Allylic Halogenation ◼Avoid a large excess of Br2 by using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) to generate Br2 as product HBr is formed. ◼N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is an allylic brominating agent. ⚫Keeps the concentration of Br2 low. N O O Br + HBr N O O H + Br2

自秋特大材 Reaction Mechanism allylic shift Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The mechanism involves an allylic radical stabilized by resonance. Both allylic radicals can react with bromine. Resonance hybrid
Reaction Mechanism ◼The mechanism involves an allylic radical stabilized by resonance. ◼Both allylic radicals can react with bromine