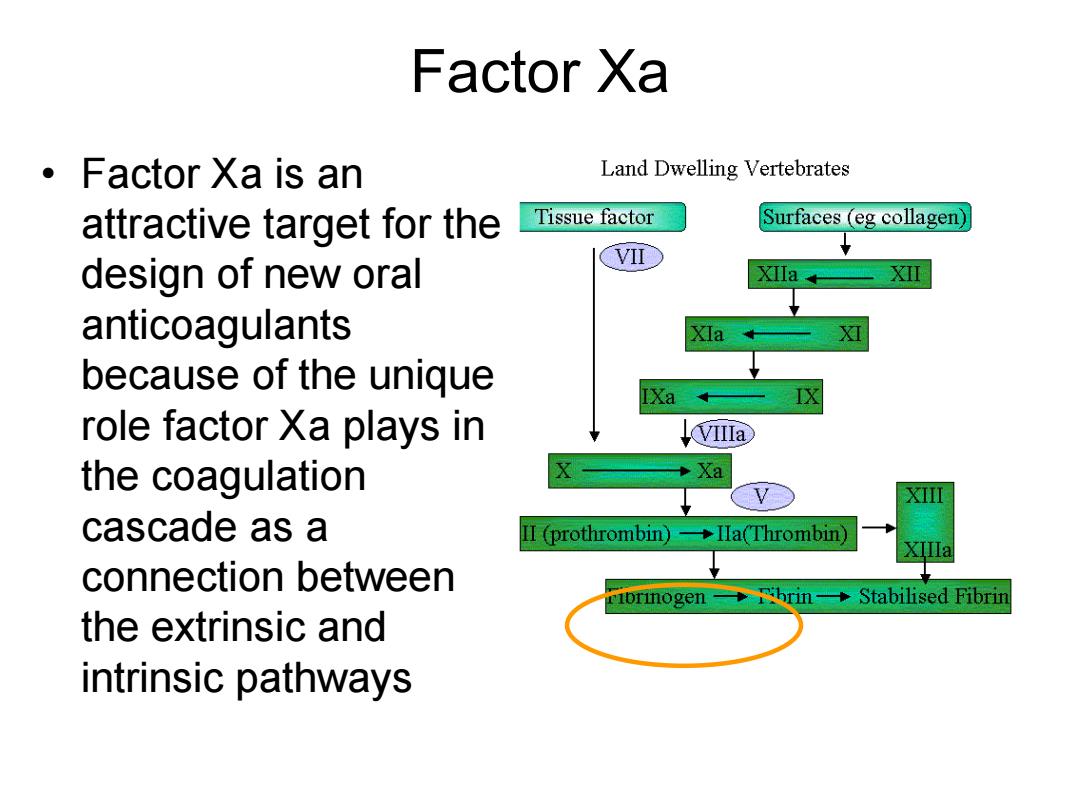
Factor Xa 。Factor Xa is an Land Dwelling Vertebrates attractive target for the Tissue factor Surfaces (eg collagen) design of new oral XII anticoagulants XIa because of the unique IXa role factor Xa plays in the coagulation Xa cascade as a II(prothrombin)一◆Ila(Thrombin) XIIIa connection between riorinogen-:hrin-Stabilised Fibrin the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways
Factor Xa • Factor Xa is an attractive target for the design of new oral anticoagulants because of the unique role factor Xa plays in the coagulation cascade as a connection between the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways
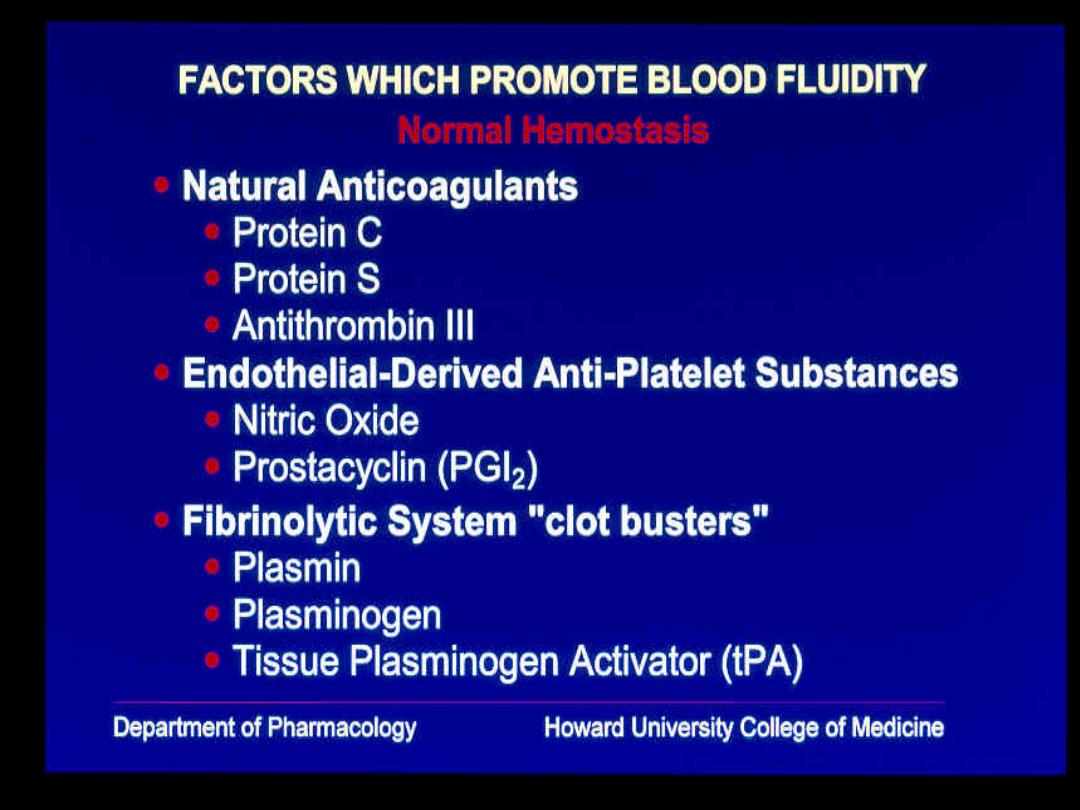
FACTORS WHICH PROMOTE BLOOD FLUIDITY Normal Hemostasis Natural Anticoagulants Protein C ●Protein S ◆Antithrombin Ill Endothelial-Derived Anti-Platelet Substances ◆Nitric Oxide ·Prostacyclin(PGl2) Fibrinolytic System "clot busters" ·Plasmin 。Plasminogen Tissue Plasminogen Activator(tPA) Department of Pharmacology Howard University College of Medicine

History of Anticoagulants Jay McLean,a second year medical student at Johns Hopkins University,discovered this wonderful drug in 1916 while performing research in the laboratory of W.H.Howell,MD. 上uL: ✉ In 1960,DW Barritt and SC Jordan performed the first randomized trial showing the efficacy of anticoagulant therapy in the treatment of venous thromboembolism.Since then,important therapeutic advances have been made in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. .Barritt,D.W.,and Jordan,S.C.:Anticoagulant drugs in the treatment of pulmonary embolism.A controlled trial.Lancet,1:1309-1312,1960.[Medlinel
History of Anticoagulants In 1960, DW Barritt and SC Jordan performed the first randomized trial showing the efficacy of anticoagulant therapy in the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Since then, important therapeutic advances have been made in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. •Barritt, D. W., and Jordan, S. C.: Anticoagulant drugs in the treatment of pulmonary embolism. A controlled trial. Lancet, 1: 1309-1312, 1960.[Medline] Jay McLean, a second year medical student at Johns Hopkins University, discovered this wonderful drug in 1916 while performing research in the laboratory of W.H. Howell, MD

heparin chemistry and source Sulfated mucopolysaccharides large amount of negative charge strong acidity Characteristics administrated by i.v.or s.c. effective both in vivo and in vitro quick onset and potent effects anticoagulant activity is related to the length of molecular chain
heparin chemistry and source Sulfated mucopolysaccharides large amount of negative charge strong acidity Characteristics • administrated by i.v. or s.c. • effective both in vivo and in vitro • quick onset and potent effects • anticoagulant activity is related to the length of molecular chain

heparin---Mechanism Heparin works by inhibiting the three major clotting factors (thrombin,thromboplastin,and prothrombin). It slows the process of thromboplastin synthesis,decelerates the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin,and inhibits the effects of thrombin on fibrinogen,blocking its conversion to fibrin. heparin heparin AT Ill thrombin* AT II <thrombin* heparin heparin. AT III thrombin AT Ill thrombin* can also be Factor Xa
heparin AT III thrombin* AT III heparin thrombin* thrombin* heparin AT III AT III thrombin* heparin Fig. 50-3 * can also be Factor Xa heparin---Mechanism Heparin works by inhibiting the three major clotting factors (thrombin, thromboplastin, and prothrombin). It slows the process of thromboplastin synthesis, decelerates the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, and inhibits the effects of thrombin on fibrinogen, blocking its conversion to fibrin