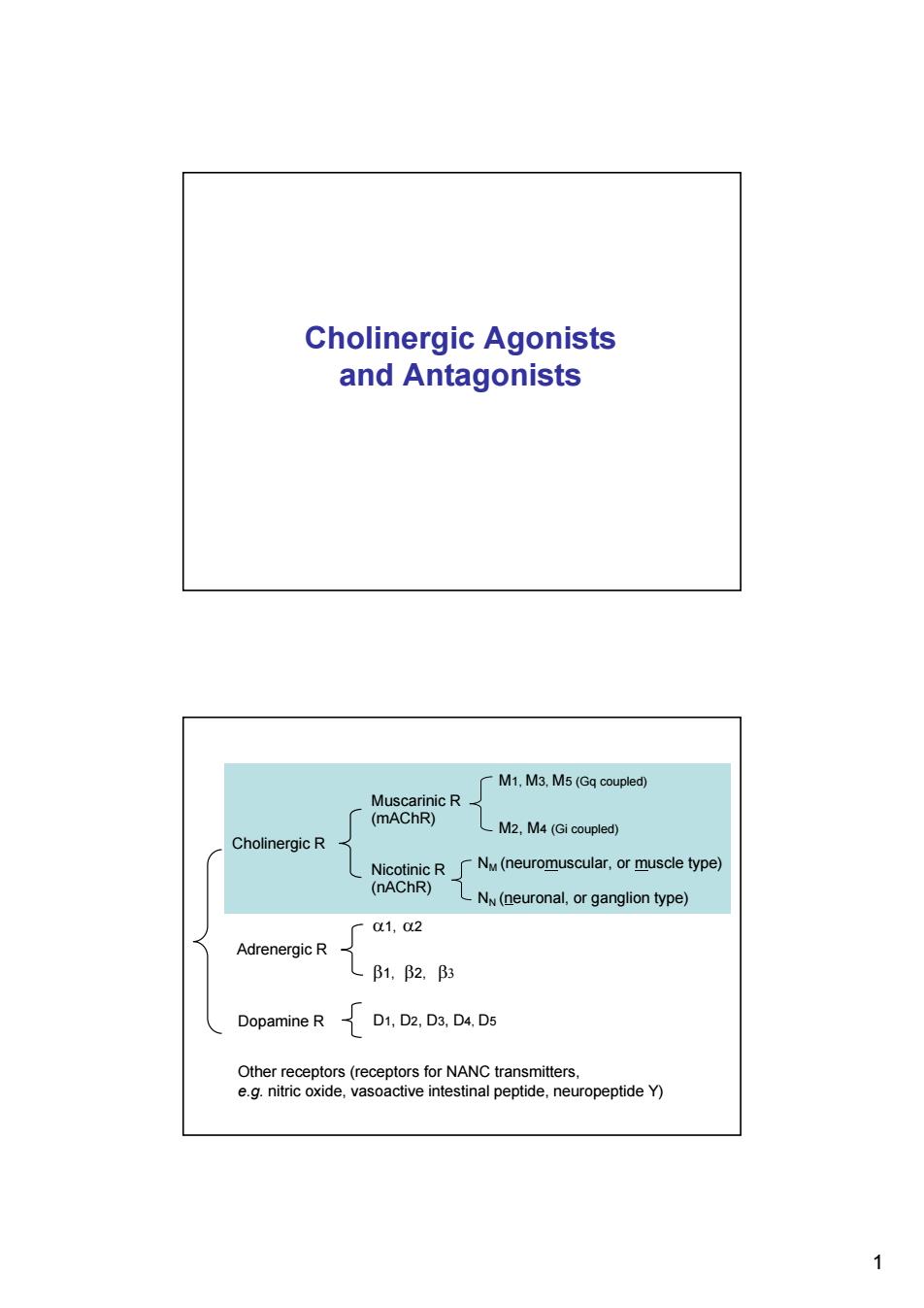
Cholinergic Agonists and Antagonists M1,M3,M5(Gq coupled) Muscarinic R (mAChR) M2,M4(Gi coupled) Cholinergic R Nicotinic R NM(neuromuscular,or muscle type) (nAChR) NN(neuronal,or ganglion type) 1,2 Adrenergic R B1,B2,B3 Dopamine R D1,D2,D3D4,D5 Other receptors(receptors for NANC transmitters, e.g.nitric oxide,vasoactive intestinal peptide,neuropeptide Y) 1
1 Cholinergic Agonists and Antagonists Cholinergic R Adrenergic R Dopamine R Muscarinic R Nicotinic R M1, M3, M5 (Gq coupled) M2, M4 (Gi coupled) NM (neuromuscular, or muscle type) NN (neuronal, or ganglion type) β1, α1, α2 β2, β3 D1, D2, D3, D4, D5 Other receptors (receptors for NANC transmitters, e.g. nitric oxide, vasoactive intestinal peptide, neuropeptide Y) (mAChR) (nAChR)
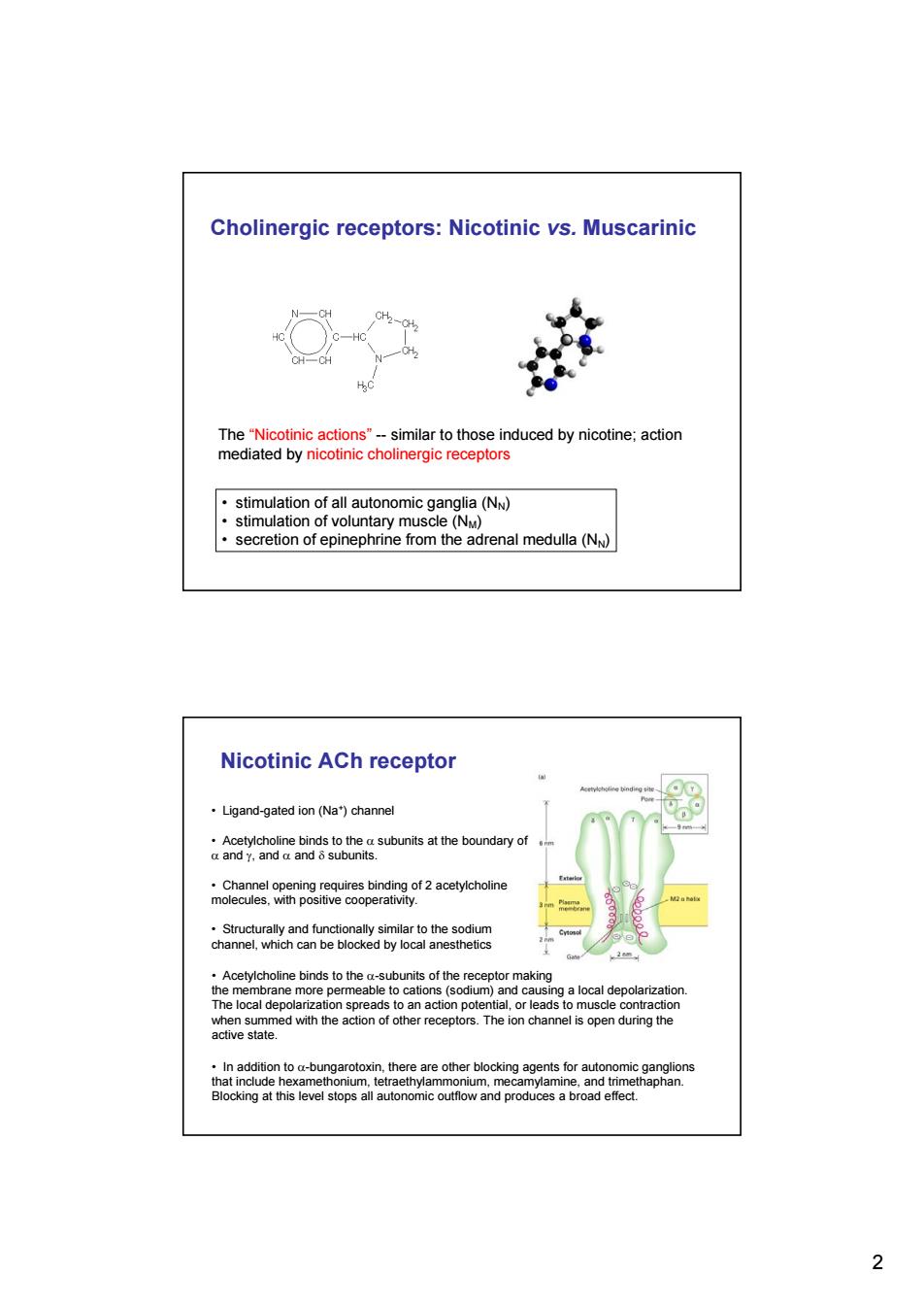
Cholinergic receptors:Nicotinic vs.Muscarinic CH2-CH2 CH-0 The"Nicotinic actions"--similar to those induced by nicotine;action mediated by nicotinic cholinergic receptors stimulation of all autonomic ganglia(NN) stimulation of voluntary muscle (NM) secretion of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla(NN) Nicotinic ACh receptor Ligand-gated ion(Na)channel Acetylcholine binds to the a subunits at the boundary of a and y,and a and subunits. .Channel opening requires binding of 2 acetylcholine Exterior molecules,with positive cooperativity. Structurally and functionally similar to the sodium channel,which can be blocked by local anesthetics 28两 Acetylcholine binds to the a-subunits of the receptor making the membrane more permeable to cations(sodium)and causing a local depolarization. The local depolarization spreads to an action potential,or leads to muscle contraction when summed with the action of other receptors.The ion channel is open during the active state. In addition to a-bungarotoxin,there are other blocking agents for autonomic ganglions that include hexamethonium,tetraethylammonium,mecamylamine,and trimethaphan. Blocking at this level stops all autonomic outflow and produces a broad effect. 2
2 The “Nicotinic actions” -- similar to those induced by nicotine; action mediated by nicotinic cholinergic receptors • stimulation of all autonomic ganglia (NN) • stimulation of voluntary muscle (NM) • secretion of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla (NN) Cholinergic receptors: Nicotinic vs. Muscarinic Nicotinic ACh receptor • Ligand-gated ion (Na+) channel • Acetylcholine binds to the α subunits at the boundary of α and γ, and α and δ subunits. • Channel opening requires binding of 2 acetylcholine molecules, with positive cooperativity. • Structurally and functionally similar to the sodium channel, which can be blocked by local anesthetics • Acetylcholine binds to the α-subunits of the receptor making the membrane more permeable to cations (sodium) and causing a local depolarization. The local depolarization spreads to an action potential, or leads to muscle contraction when summed with the action of other receptors. The ion channel is open during the active state. • In addition to α-bungarotoxin, there are other blocking agents for autonomic ganglions that include hexamethonium, tetraethylammonium, mecamylamine, and trimethaphan. Blocking at this level stops all autonomic outflow and produces a broad effect

Cholinergic receptors:Nicotinic vs.Muscarinic The"Muscarinic actions"--reproduced by injection of muscarine,from Amanita muscaria. Similar to those of parasympathetic stimulation Multiple(5)muscarinic cholinergic receptors distributed in different tissues: Neural(M1):CNS,PNS,gastric parietal cells(excitatory;Gq) Cardiac(M2):atria conducting tissue;presynaptic(inhibitory;Gi) Glandular(M3):exocrine glands;smooth muscle (excitatory;Gq) Muscarinic receptors couple to G proteins Agonist t GEF Downstream D effectors GaGDP GaGTP PLC-B Ion channels Adenylyl cyclase GAP Kinases Pi Others 3
3 The “Muscarinic actions” -- reproduced by injection of muscarine, from Amanita muscaria. Similar to those of parasympathetic stimulation • Neural (M1): CNS, PNS, gastric parietal cells (excitatory; Gq) • Cardiac (M2): atria & conducting tissue; presynaptic (inhibitory; Gi) • Glandular (M3): exocrine glands; smooth muscle (excitatory; Gq) Cholinergic receptors: Nicotinic vs. Muscarinic Multiple (5) muscarinic cholinergic receptors distributed in different tissues: Gα•GDP GAP GEF Gα•GTP Muscarinic receptors couple to G proteins βγ βγ Pi Downstream effectors PLC-β Ion channels Adenylyl cyclase Kinases Others Agonist

Three Major Muscarinic Receptors(there are five) Agonist Agonist Agonist M1 M2 M3 “neural" “cardiac" "glandular' Gq Gi Gq ↑Inositol phosphates ↓cAMP Inositol phosphates (1P3) (IP3) Diacyl glycerol(DAG) ↓Calcium channels ↑Diacyl glycerol(DAG) ↓K'conductance 个K*conductance Intracellular calcium Depolarization Mostly excitatory Mostly inhibitory Mostly excitatory (decrease of M1 activity in (responsible for the (stimulation of glandular CNS may be a cause of vagal inhibition of the secretion,contraction of dementia) heart) visceral smooth muscle) Classes of cholinergic stimulants Direct-acting Indirect-acting Receptor agonists Cholinesterase inhibitors Carbamates Choline esters PHYSOSTIGMINE Phosphates NEOSTIGMINE ISOFLUROPHATE ACETYLCHOLINE Alkaloids PYRIDOSTIGMINE Antidote BETHANECOL PILOCARPINE EDROPHONIUM PRALIDOXIMINE 4
4 Agonist Three Major Muscarinic Receptors (there are five) Agonist Agonist M1 “neural” M2 “cardiac” M3 “glandular” Gq Gi Gq ↑ Inositol phosphates (IP3) ↑ Diacyl glycerol (DAG) ↑ Inositol phosphates (IP3) ↑ Diacyl glycerol (DAG) ↑ Intracellular calcium ↓ cAMP ↓ Calcium channels ↑ K+ conductance ↓ K+ conductance Mostly excitatory (decrease of M1 activity in CNS may be a cause of dementia) Mostly inhibitory (responsible for the vagal inhibition of the heart) Mostly excitatory (stimulation of glandular secretion, contraction of visceral smooth muscle) Depolarization Classes of cholinergic stimulants Direct-acting Receptor agonists Choline esters ACETYLCHOLINE BETHANECOL Alkaloids PILOCARPINE Cholinesterase inhibitors Carbamates PHYSOSTIGMINE NEOSTIGMINE PYRIDOSTIGMINE EDROPHONIUM Phosphates ISOFLUROPHATE Antidote PRALIDOXIMINE Indirect-acting
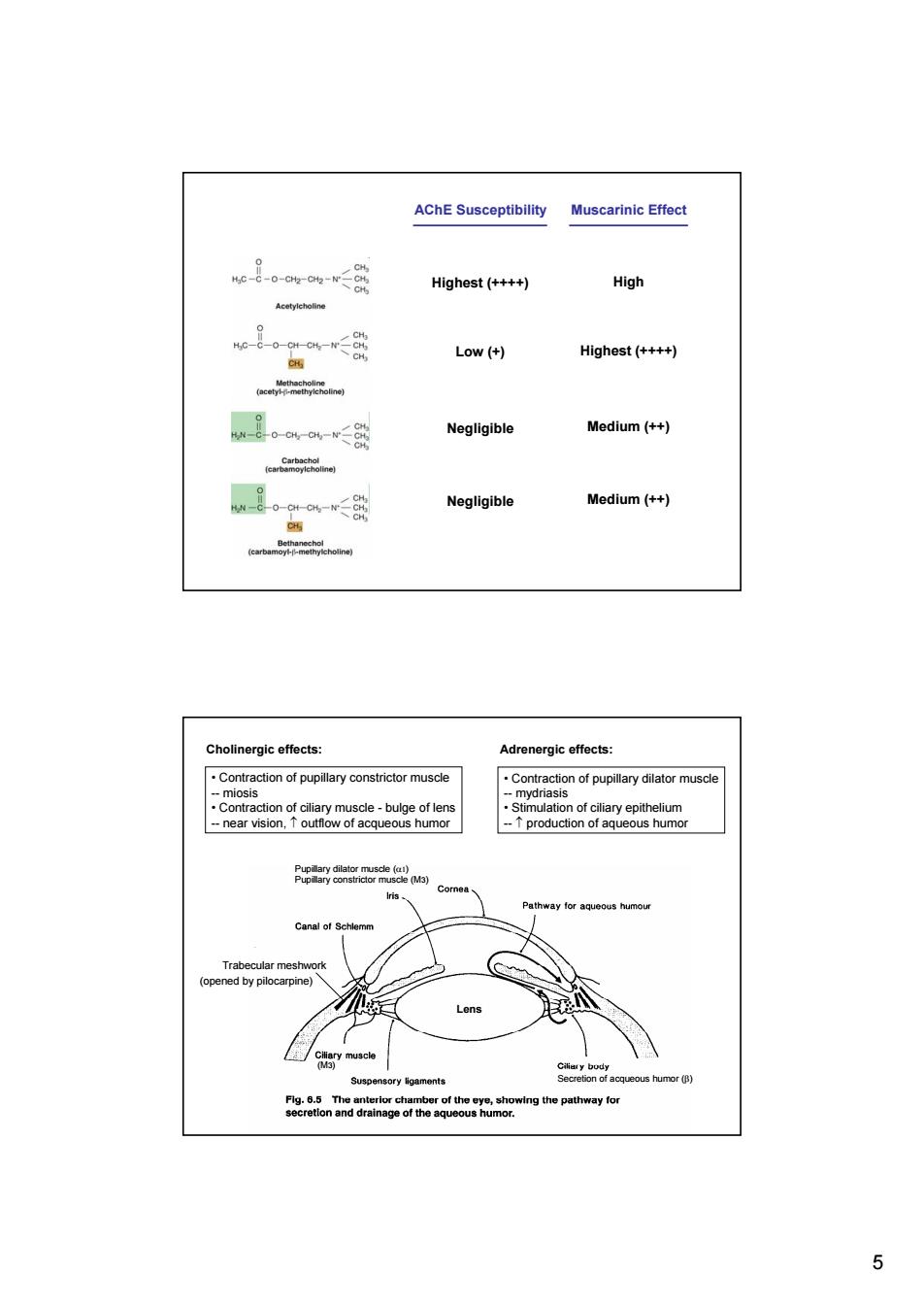
AChE Susceptibility Muscarinic Effect hc是。-0-G-Gh-w二 CH CH Highest (++++ High Acetylcholine CH Low(+) Highest(++++) (cy) w。-otow-r< CH Negligible Medium (++ Negligible Medium(++) Cholinergic effects: Adrenergic effects: Contraction of pupillary constrictor muscle .Contraction of pupillary dilator muscle --miosis --mydriasis Contraction of ciliary muscle-bulge of lens Stimulation of ciliary epithelium --near vision,T outflow of acqueous humor --T production of aqueous humor lris、 Cornea Pathway for aqueous humour Canai of Schlemm Trabecular meshwork (opened by pilocarpine) Lens Suspensory ligaments Secretion of acqueous humor (B) Fig.6.5 The anterior chamber of the eye,showing the pathway for secretlon and drainage of the aqueous humor. 5
5 AChE Susceptibility Muscarinic Effect Highest (++++) High Low (+) Highest (++++) Negligible Medium (++) Negligible Medium (++) Lens Pupillary dilator muscle (α1) Pupillary constrictor muscle (M3) Secretion of acqueous humor (β) (M3) Cholinergic effects: Adrenergic effects: • Contraction of pupillary constrictor muscle -- miosis • Contraction of ciliary muscle - bulge of lens -- near vision, ↑ outflow of acqueous humor • Contraction of pupillary dilator muscle -- mydriasis • Stimulation of ciliary epithelium -- ↑ production of aqueous humor Trabecular meshwork (opened by pilocarpine)