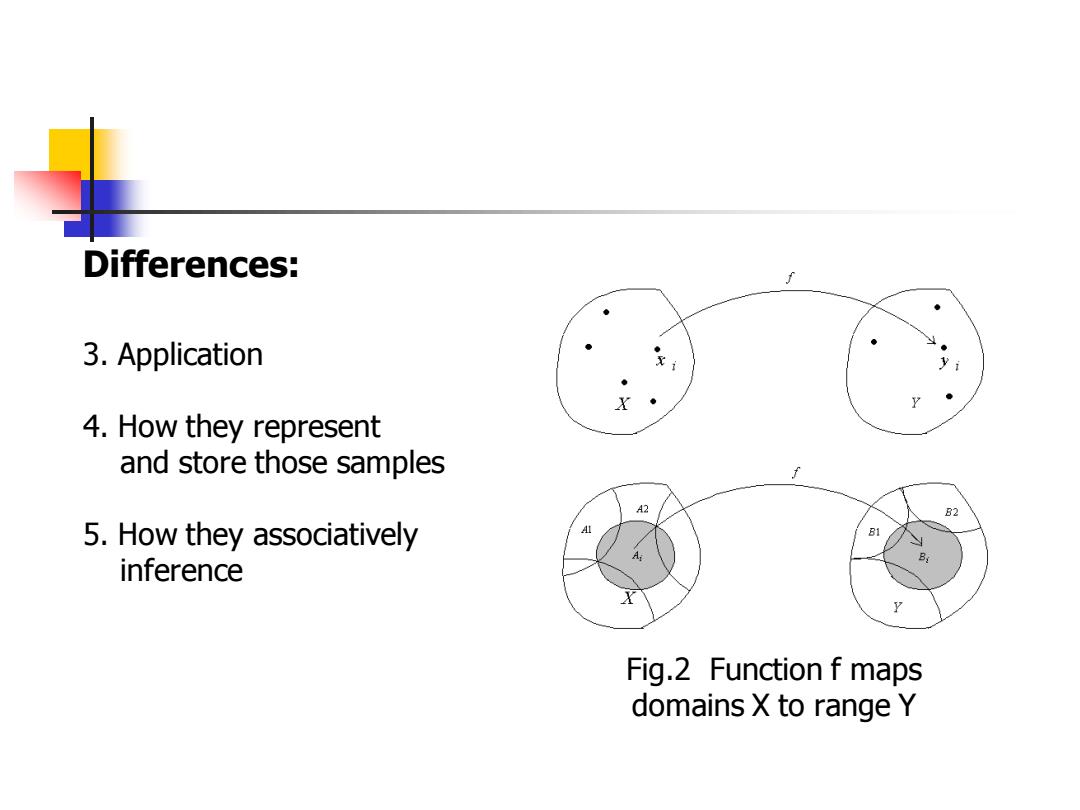
Differences: 3.Application 4.How they represent and store those samples A2 B2 5.How they associatively inference Fig.2 Function f maps domains X to range Y
Fig.2 Function f maps domains X to range Y 3. Application 4. How they represent and store those samples 5. How they associatively inference Differences:
Neural vs.fuzzy representation of structured knowledge ■Neural network problems: 1.computational burden of training 2.system inscrutability There is no natural inferential audit tail,like an computational black box. 3.sample generation
Neural vs. fuzzy representation of structured knowledge ◼ Neural network problems: 1. computational burden of training 2. system inscrutability There is no natural inferential audit tail, like an computational black box. 3. sample generation

Neural vs.fuzzy representation of structured knowledge Fuzzy systems 1.directly encode the linguistic sample (HEAVY,LONGER)in a matrix 2.combine the numerical approaches with the symbolic one Fuzzy approach does not abandon neural-network, it limits them to unstructured parameter and state estimate,pattern recognition and cluster formation
Neural vs. fuzzy representation of structured knowledge ◼ Fuzzy systems 1. directly encode the linguistic sample (HEAVY,LONGER) in a matrix 2. combine the numerical approaches with the symbolic one ◼ Fuzzy approach does not abandon neural-network, it limits them to unstructured parameter and state estimate, pattern recognition and cluster formation