
Chapter 3 Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 3 Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope

Units of Measurement 。1μm=10-6m=103mm 。1nm=109m=10-6mm 。1000nm=1μm 。0.001μm=1nm
Units of Measurement • 1 µm = 10-6 m = 10-3 mm • 1 nm = 10-9 m = 10-6 mm • 1000 nm = 1 µm • 0.001 µm = 1 nm
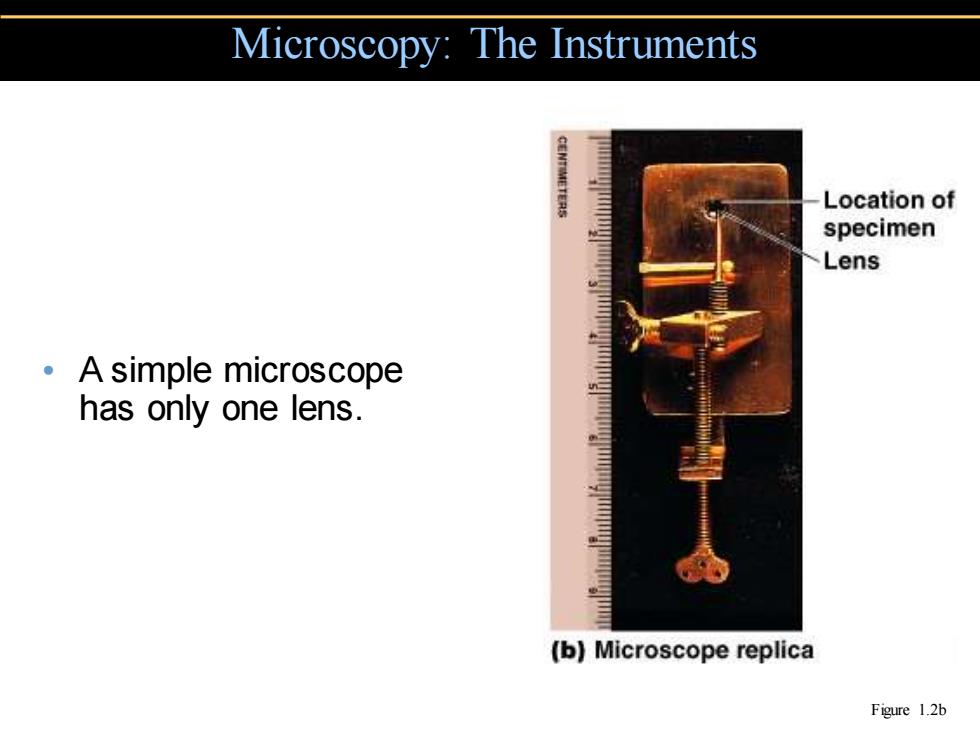
Microscopy:The Instruments CENTIETERS Location of specimen Lens 。A simple microscope has only one lens. (b)Microscope replica Figure 1.2b
• A simple microscope has only one lens. Microscopy: The Instruments Figure 1.2b
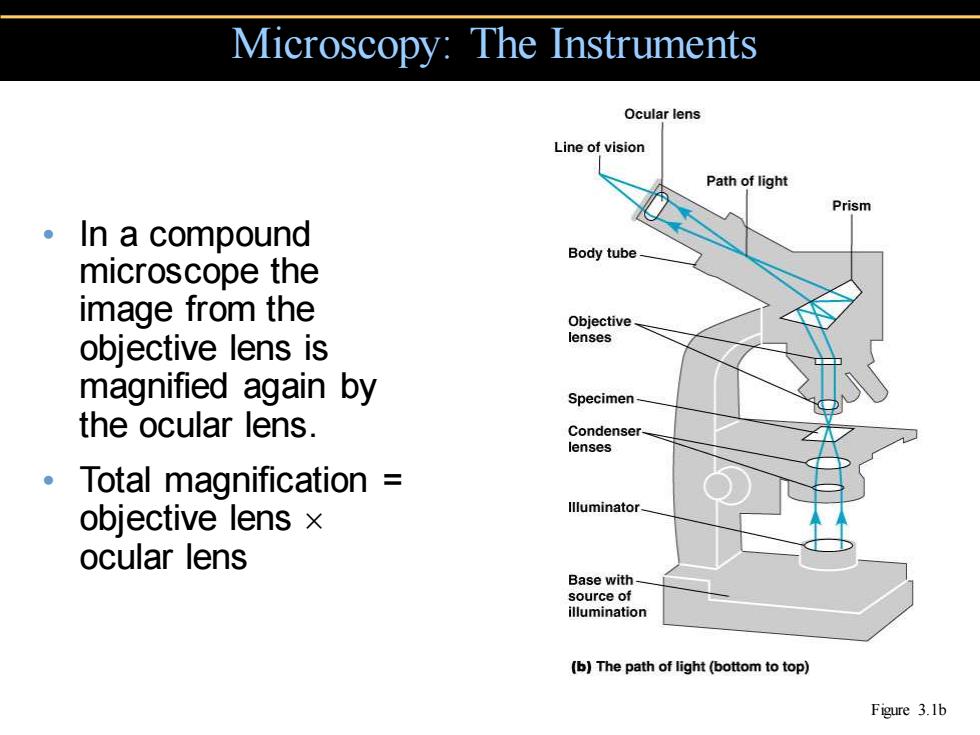
Microscopy:The Instruments Ocular lens Line of vision Path of light Prism 。In a compound Body tube microscope the image from the Objective objective lens is lenses magnified again by Specimen- the ocular lens. Condenser- lenses 。1 Total magnification objective lens x llluminator. ocular lens Base with source of illumination (b)The path of light(bottom to top) Figure 3.1b
• In a compound microscope the image from the objective lens is magnified again by the ocular lens. • Total magnification = objective lens ocular lens Microscopy: The Instruments Figure 3.1b
Microscopy:The Instruments Resolution is the ability of the lenses to distinguish two points. A microscope with a resolving power of 0.4 nm can distinguish between two points 0.4 nm. Shorter wavelengths of light provide greater resolution
• Resolution is the ability of the lenses to distinguish two points. • A microscope with a resolving power of 0.4 nm can distinguish between two points ≥ 0.4 nm. • Shorter wavelengths of light provide greater resolution. Microscopy: The Instruments