
Chapter 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology

Principles of Disease and Epidemiology 。Pathology Study of disease 。Etiology Study of the cause of a disease 。Pathogenesis Development of disease 。Infection Colonization of the body by pathogens Disease An abnormal state in which the body is not functionally normally
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology • Pathology Study of disease • Etiology Study of the cause of a disease • Pathogenesis Development of disease • Infection Colonization of the body by pathogens • Disease An abnormal state in which the body is not functionally normally

Normal Microbiota and the Host Transient microbiota may be present for days,weeks, or months Normal microbiota permanently colonize the host Symbiosis is the relationship between normal microbiota and the host
• Transient microbiota may be present for days, weeks, or months • Normal microbiota permanently colonize the host • Symbiosis is the relationship between normal microbiota and the host Normal Microbiota and the Host

Normal Microbiota and the Host: In commensalism,one organism is benefited and the other is unaffected. In mutualism,both organisms benefit. In parasitism,one organism is benefited at the expense of the other. Some normal microbiota are opportunistic pathogens
• In commensalism, one organism is benefited and the other is unaffected. • In mutualism, both organisms benefit. • In parasitism, one organism is benefited at the expense of the other. • Some normal microbiota are opportunistic pathogens. Normal Microbiota and the Host:
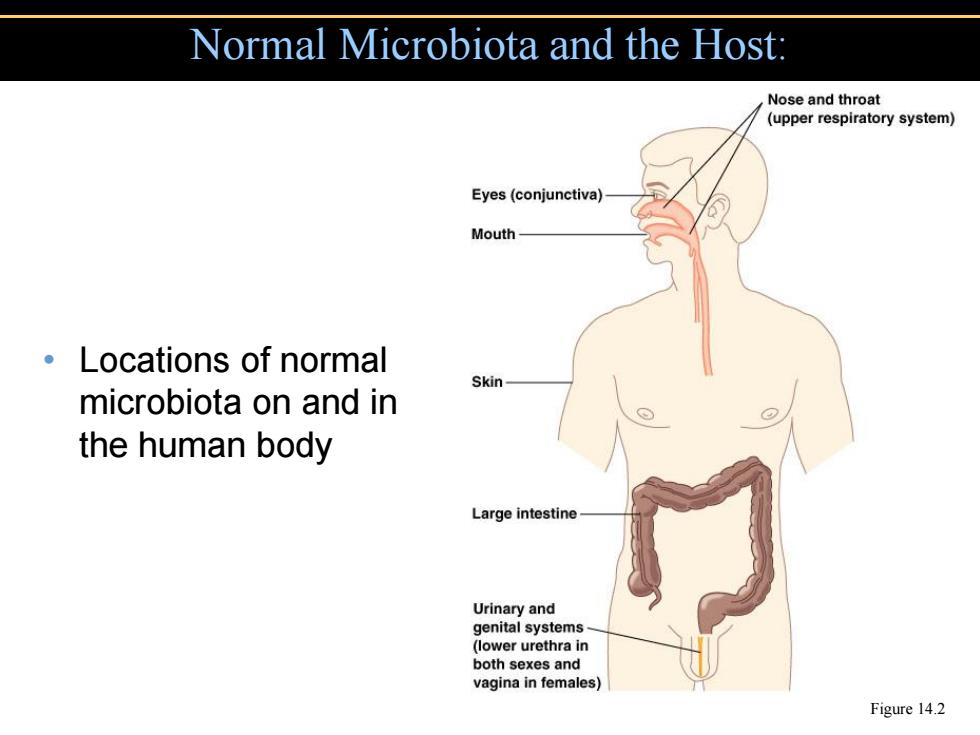
Normal Microbiota and the Host: Nose and throat (upper respiratory system) Eyes(conjunctiva) Mouth- Locations of normal Skin microbiota on and in the human body Large intestine Urinary and genital systems (lower urethra in both sexes and vagina in females) Figure 14.2
Figure 14.2 • Locations of normal microbiota on and in the human body Normal Microbiota and the Host: