
Chapter 7 The Control of Microbial Growth
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 7 The Control of Microbial Growth

The Control of Microbial Growth Sepsis refers to microbial contamination. Asepsis is the absence of significant contamination. Aseptic surgery techniques prevent microbial contamination of wounds
The Control of Microbial Growth • Sepsis refers to microbial contamination. • Asepsis is the absence of significant contamination. • Aseptic surgery techniques prevent microbial contamination of wounds

Terminology Sterilization:Removal of all microbial life Commercial Sterilization:Killing C.botulinum endospores Disinfection:Removal of pathogens Antisepsis:Removal of pathogens from living tissue Degerming:Removal of microbes from a limited area Sanitization:Lower microbial counts on eating utensils Biocide/Germicide:Kills microbes Bacteriostasis:Inhibiting,not killing,microbes
• Sterilization: Removal of all microbial life • Commercial Sterilization: Killing C. botulinum endospores • Disinfection: Removal of pathogens • Antisepsis: Removal of pathogens from living tissue • Degerming: Removal of microbes from a limited area • Sanitization: Lower microbial counts on eating utensils • Biocide/Germicide: Kills microbes • Bacteriostasis: Inhibiting, not killing, microbes Terminology
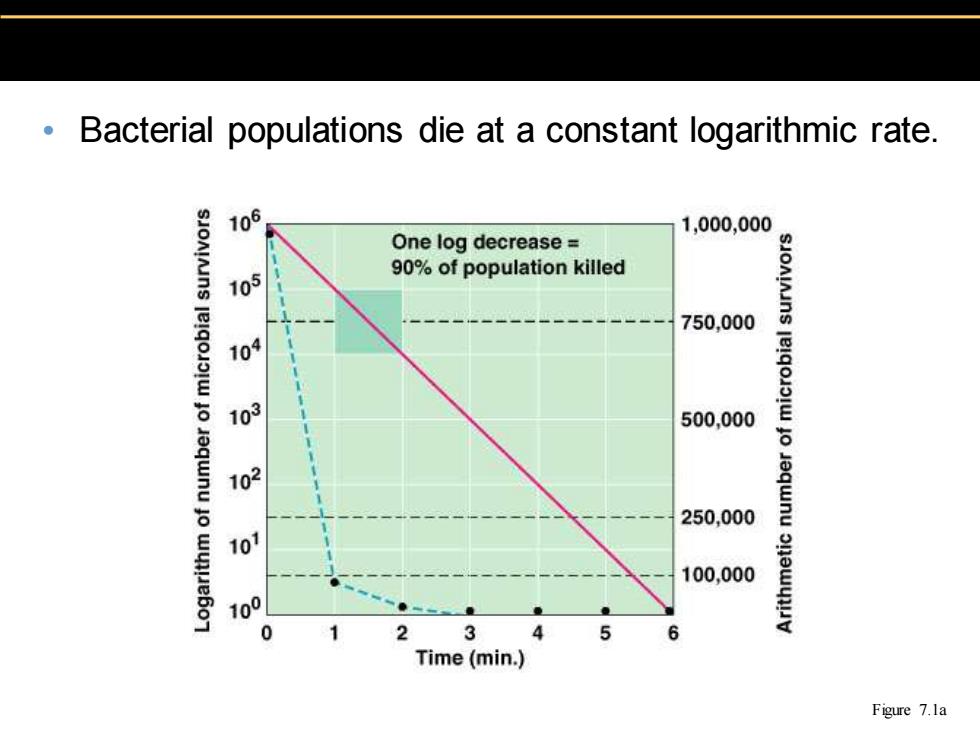
Bacterial populations die at a constant logarithmic rate. 106 1,000,000 One log decrease 90%of population killed 105 750,000 109 103 500,000 6 102 250,000 10 100,000 100 2 3 Time (min.) Figure 7.la
• Bacterial populations die at a constant logarithmic rate. Figure 7.1a
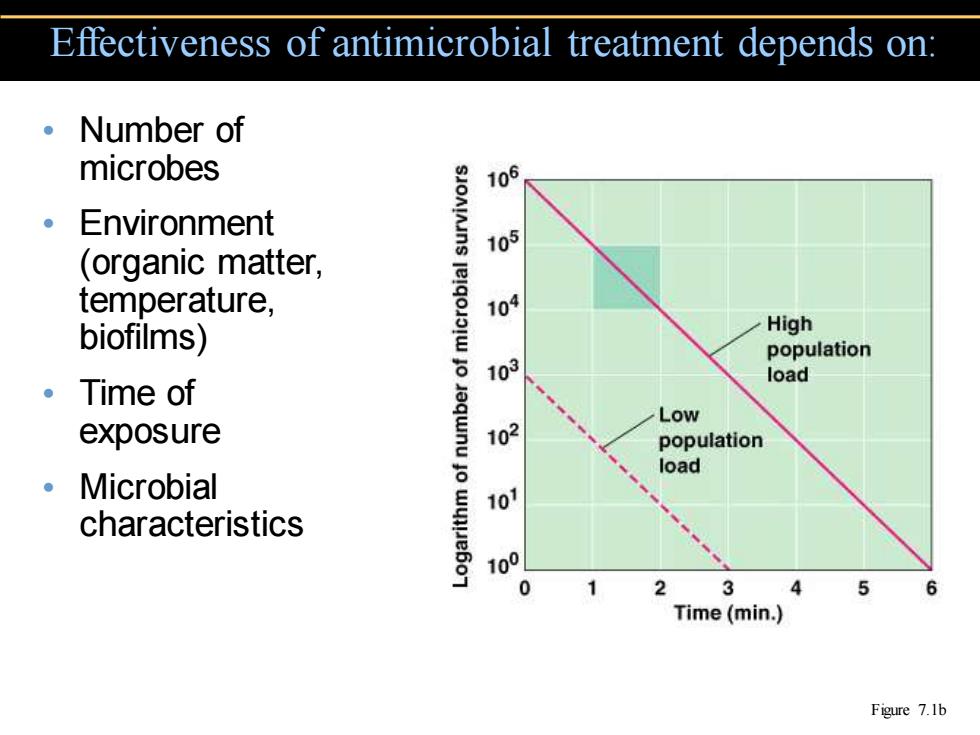
Effectiveness of antimicrobial treatment depends on: Number of microbes SJoNIns 106 Environment 105 (organic matter, temperature, 109 biofilms) High population 103 load Time of Low exposure 102 population load Microbial 10 characteristics 100 0 2 3 4 5 6 Time(min.) Figure 7.1b
• Number of microbes • Environment (organic matter, temperature, biofilms) • Time of exposure • Microbial characteristics Effectiveness of antimicrobial treatment depends on: Figure 7.1b