
Amino acid metabolism Decarboxylation Deamination ● Transamination ● Urea cycle ● Pyruvate group a Ketoglutarate group Succinyl-CoA group Oxaloacetate group Fumarate oxaloacetate group ● Alanine acetoacetate group Acetyl-CoA acetoacetate group
Amino acid metabolism • Decarboxylation √ • Deamination √ • Transamination • Urea cycle • Pyruvate group • a Ketoglutarate group • Succinyl-CoA group • Oxaloacetate group • Fumarate / oxaloacetate group • Alanine / acetoacetate group • Acetyl-CoA / acetoacetate group
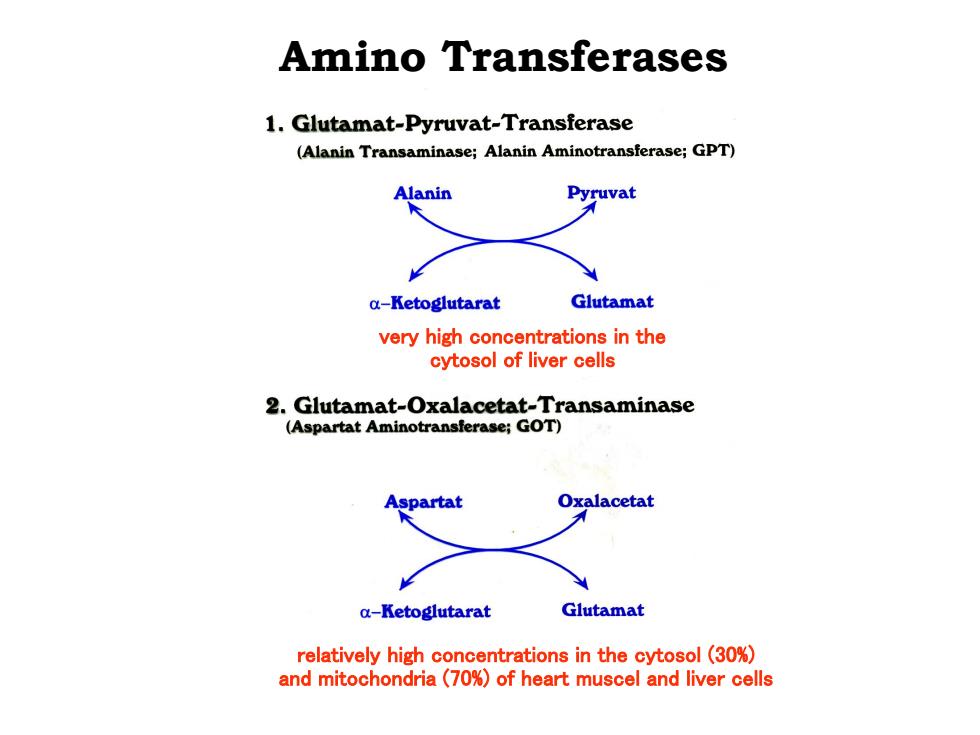
Amino Transferases 1.Glutamat-Pyruvat-Transferase (Alanin Transaminase;Alanin Aminotransferase;GPT) Alanin Pyruvat a-Ketoglutarat Glutamat very high concentrations in the cytosol of liver cells 2.Glutamat-Oxalacetat-Transaminase (Aspartat Aminotransferase;GOT) Aspartat Oxalacetat a-Ketoglutarat Glutamat relatively high concentrations in the cytosol(30%) and mitochondria(70%)of heart muscel and liver cells
very high concentrations in the cytosol of liver cells relatively high concentrations in the cytosol (30%) and mitochondria (70%) of heart muscel and liver cells Amino Transferases

CH,-OH HO-H,C OH Pyridoxin (Vit.B) CH; NH: CH, -0-HC OH -0-HC OH -CH CH H H Pyridoxalphosphat Pyridoxaminphosphat (PALP oder PLP) (PAMP oder PMP)
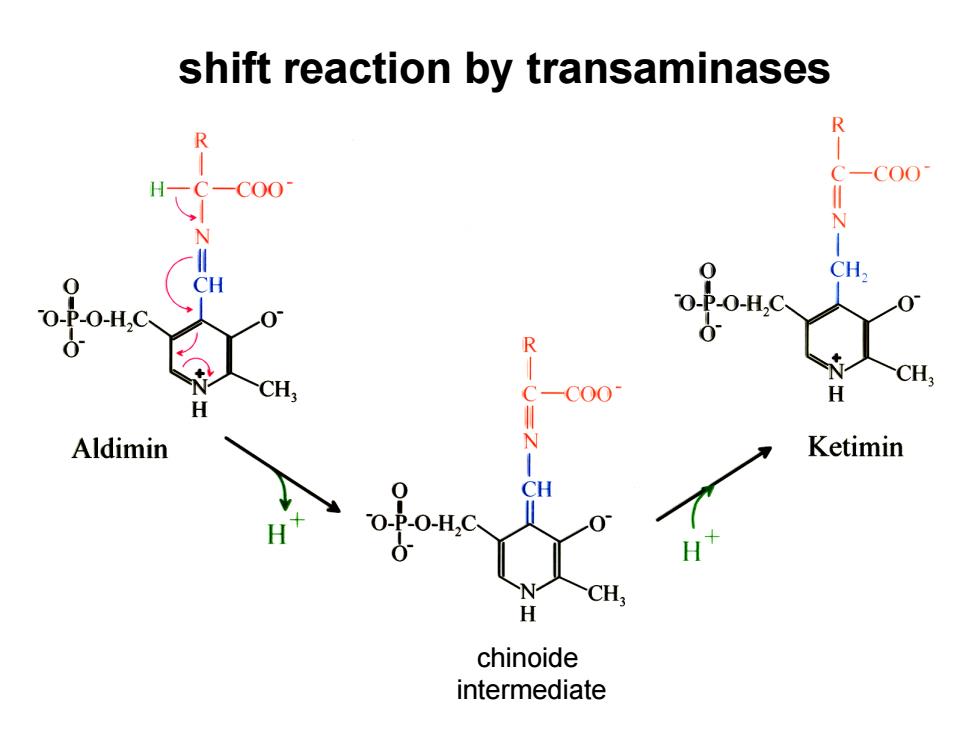
shift reaction by transaminases R C00 CH R C-COO H Aldimin N Ketimin CH -H.C CH H chinoide intermediate
shift reaction by transaminases chinoide intermediate
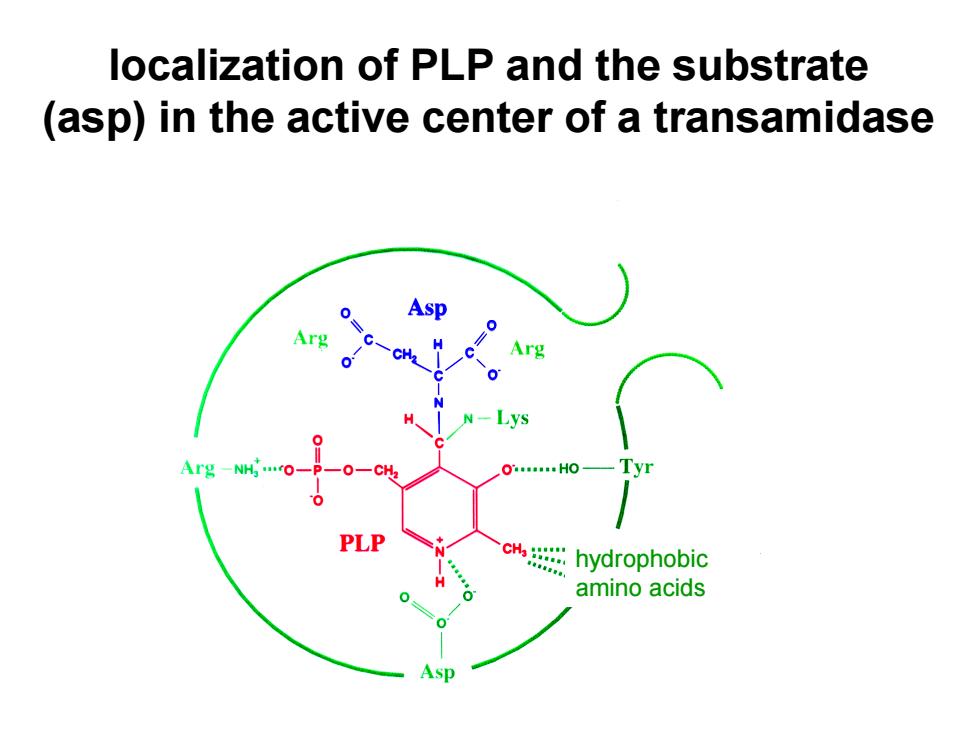
localization of PLP and the substrate (asp)in the active center of a transamidase Asp PLP cH hydrophobic amino acids
localization of PLP and the substrate (asp) in the active center of a transamidase hydrophobic amino acids