
HEAT TRANSFER CHAPTER 8 Internal flow Heat Transfer #1 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 1 HEAT TRANSFER CHAPTER 8 Internal flow
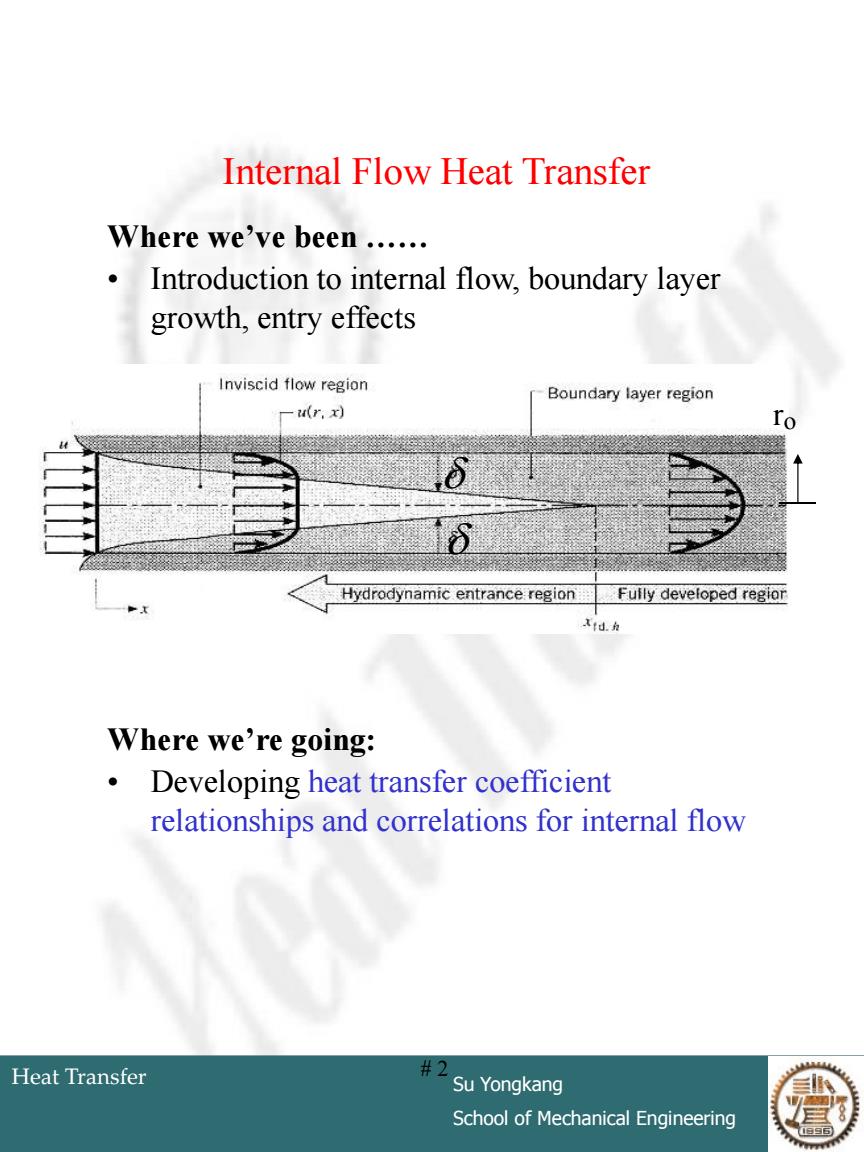
Internal Flow Heat Transfer Where we've been ..... Introduction to internal flow,boundary layer growth,entry effects Inviscid flow region Boundary layer region u(r.x) Hydrodynamic entrance region Fully developed regior xtd. Where we're going: Developing heat transfer coefficient relationships and correlations for internal flow Heat Transfer #2 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 2 Internal Flow Heat Transfer Where we’ve been …… • Introduction to internal flow, boundary layer growth, entry effects Where we’re going: • Developing heat transfer coefficient relationships and correlations for internal flow ro

Internal Flow Heat Transfer KEY POINTS THIS LECTURE 。 Energy balance for internal flow in a tube Temperature and heat transfer relations for two cases: Constant surface heat flux Constant surface temperature Heat Transfer #3 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 3 Internal Flow Heat Transfer KEY POINTS THIS LECTURE • Energy balance for internal flow in a tube • Temperature and heat transfer relations for two cases: – Constant surface heat flux – Constant surface temperature
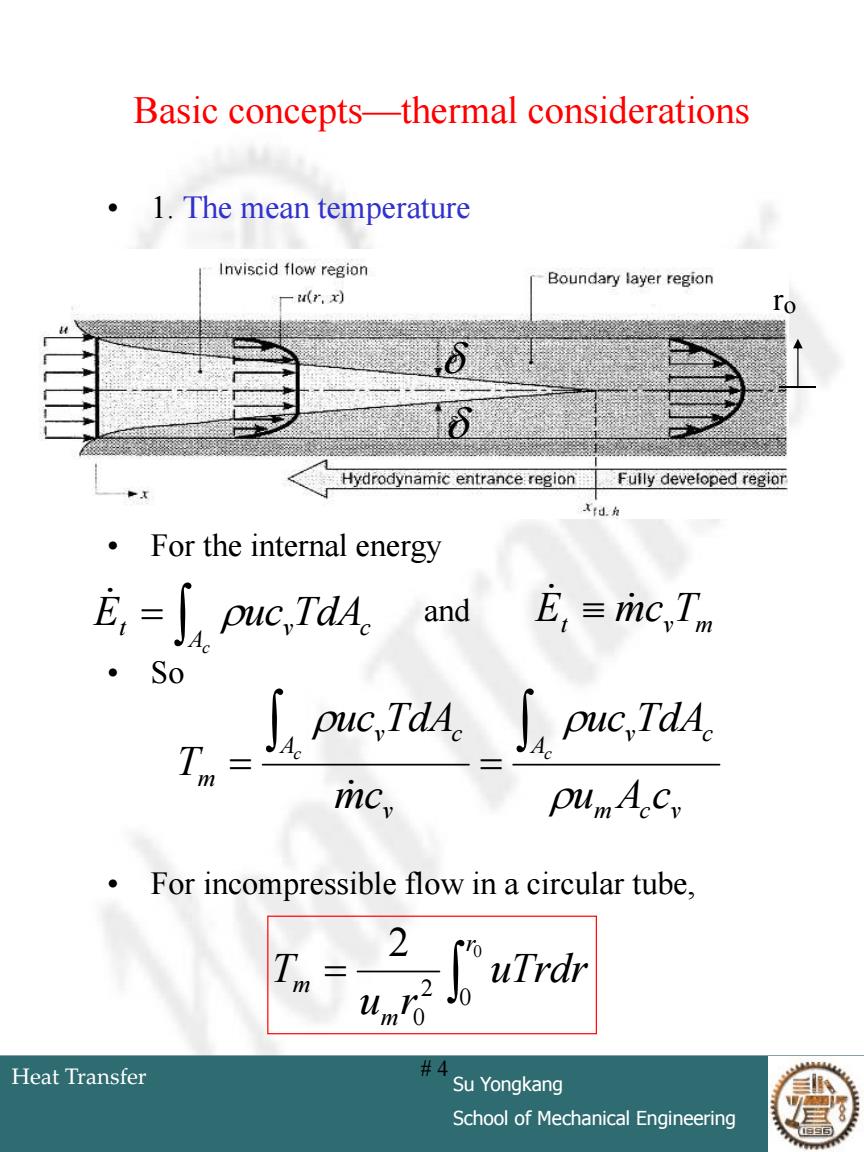
Basic concepts-thermal considerations .1.The mean temperature Inviscid flow region Boundary layer region (r,x) Hydrodynamic entrance region Fully developed regior Xid.h For the internal energy E,=∫puc,TdA and E,三imC,Tm So puc,7TdA.∫puc,TA. T.= mcy pumAcy For incompressible flow in a circular tube, 2 uTrdr Heat Transfer #4 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 4 Basic concepts—thermal considerations • 1. The mean temperature • For the internal energy • So • For incompressible flow in a circular tube, ro Ac t u vTdAc E c t vTm E m c and m c v A v c v A v c m u A c uc TdA mc uc TdA T c c 0 0 2 0 2 r m m uTrdr u r T
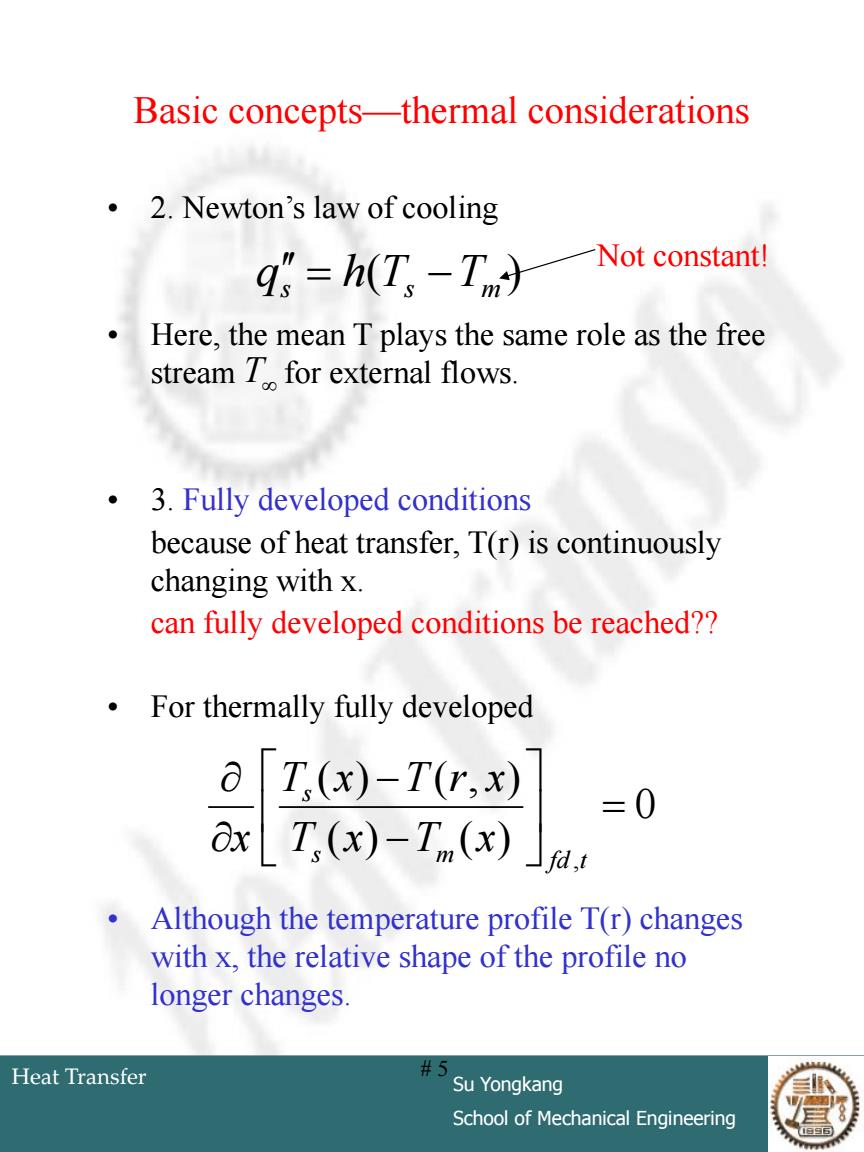
Basic concepts-thermal considerations 2.Newton's law of cooling qs=h(T,-Tm力 Not constant! Here,the mean T plays the same role as the free stream T for external flows. 3.Fully developed conditions because of heat transfer,T(r)is continuously changing with x. can fully developed conditions be reached?? For thermally fully developed a T,(x)-T(r,x) =0 x T(x)-T (x) Although the temperature profile T(r)changes with x,the relative shape of the profile no longer changes. Heat Transfer #5 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 5 Basic concepts—thermal considerations • 2. Newton’s law of cooling • Here, the mean T plays the same role as the free stream for external flows. • 3. Fully developed conditions because of heat transfer, T(r) is continuously changing with x. can fully developed conditions be reached?? • For thermally fully developed • Although the temperature profile T(r) changes with x, the relative shape of the profile no longer changes. ( ) qs h Ts Tm T Not constant! 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( , ) , m fd t s s T x T x T x T r x x